Overview
To enhance the performance of distressed companies, four key strategies can be implemented:
- Identifying financial distress indicators
- Conducting comprehensive financial assessments
- Implementing strategic turnaround plans
- Utilizing interim management for crisis stabilization
Each of these strategies is crucial for guiding organizations through challenging times. For instance, monitoring cash flow issues and debt levels is essential to identify potential pitfalls early.
Furthermore, engaging stakeholders in assessments fosters a collaborative approach to recovery. Defining clear recovery objectives ensures that all efforts are aligned towards a common goal.
Lastly, leveraging experienced interim managers can provide the necessary expertise to guide the recovery process effectively, ensuring stability and direction during critical periods.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of corporate finance, recognizing the signs of distress is vital for safeguarding a company's future. As numerous businesses contend with cash flow challenges, escalating debt levels, and dwindling sales, the urgency for proactive measures is more pronounced than ever.
With sectors such as Construction and Food & Drug Retailers confronting alarming rates of financial instability, comprehending the critical indicators of distress becomes essential. This article explores the key signs of financial trouble, underscores the importance of thorough assessments, and outlines strategic turnaround plans that can assist companies in regaining their footing.
By harnessing expert insights and real-time analytics, organizations can not only pinpoint potential pitfalls but also execute effective recovery strategies that pave the way for sustainable growth.
Identify Signs of Financial Distress in Companies
Recognizing indicators of economic distress is essential for prompt intervention and recovery. Key indicators to monitor include:
- Flow Issues: Ongoing negative flow serves as a major warning sign that a company may struggle to meet its monetary obligations. In 2025, a significant number of small enterprises reported financial flow problems, underscoring the necessity for proactive management. Notably, the Food & Drug Retailers sector has 1,343 companies in critical economic distress, highlighting the widespread nature of these challenges. Employing real-time analytics via our client dashboard can assist CFOs in tracking flow trends and making informed decisions swiftly.
- Increased Debt Levels: An escalating debt-to-equity ratio often indicates that a company is increasingly reliant on borrowed funds. For troubled companies, the average debt-to-equity ratio has reached alarming levels, emphasizing the need for financial restructuring. Testing hypotheses around debt management strategies can provide insights into effective restructuring options.
- Declining Sales: A sustained decrease in sales can signal market share erosion or operational inefficiencies. This trend is particularly evident in sectors like Construction, which has the highest number of companies in critical distress, with 7,849 firms facing significant challenges. Additionally, Support Services and Real Estate & Property Services are also experiencing notable distress, indicating a broader issue across multiple sectors. Quick decision-making processes can help address these declines before they escalate.
- Delayed Payments: Frequent late payments to suppliers or creditors indicate liquidity issues. Companies facing cash flow problems often find it challenging to maintain timely payments, further exacerbating their economic situation. Continuous monitoring through our client dashboard can provide real-time insights into payment cycles and liquidity status.
- High Employee Turnover: Increased turnover rates can reflect low morale or instability within the organization, which may be symptomatic of deeper financial troubles. Understanding these dynamics is essential for operationalizing lessons learned and fostering a stable work environment, particularly when addressing distressed company performance. By recognizing these signs early, businesses can implement corrective measures to mitigate further decline and enhance their recovery strategies. Understanding these indicators not only aids in identifying distressed company performance but also helps inform the development of effective turnaround plans. It is crucial for CFOs to be aware of common pitfalls in recognizing economic distress, such as misinterpreting temporary liquidity fluctuations as permanent problems, which can lead to misguided strategies. Integrating expert opinions on these signs can further bolster the credibility of the assessment and guide effective decision-making.
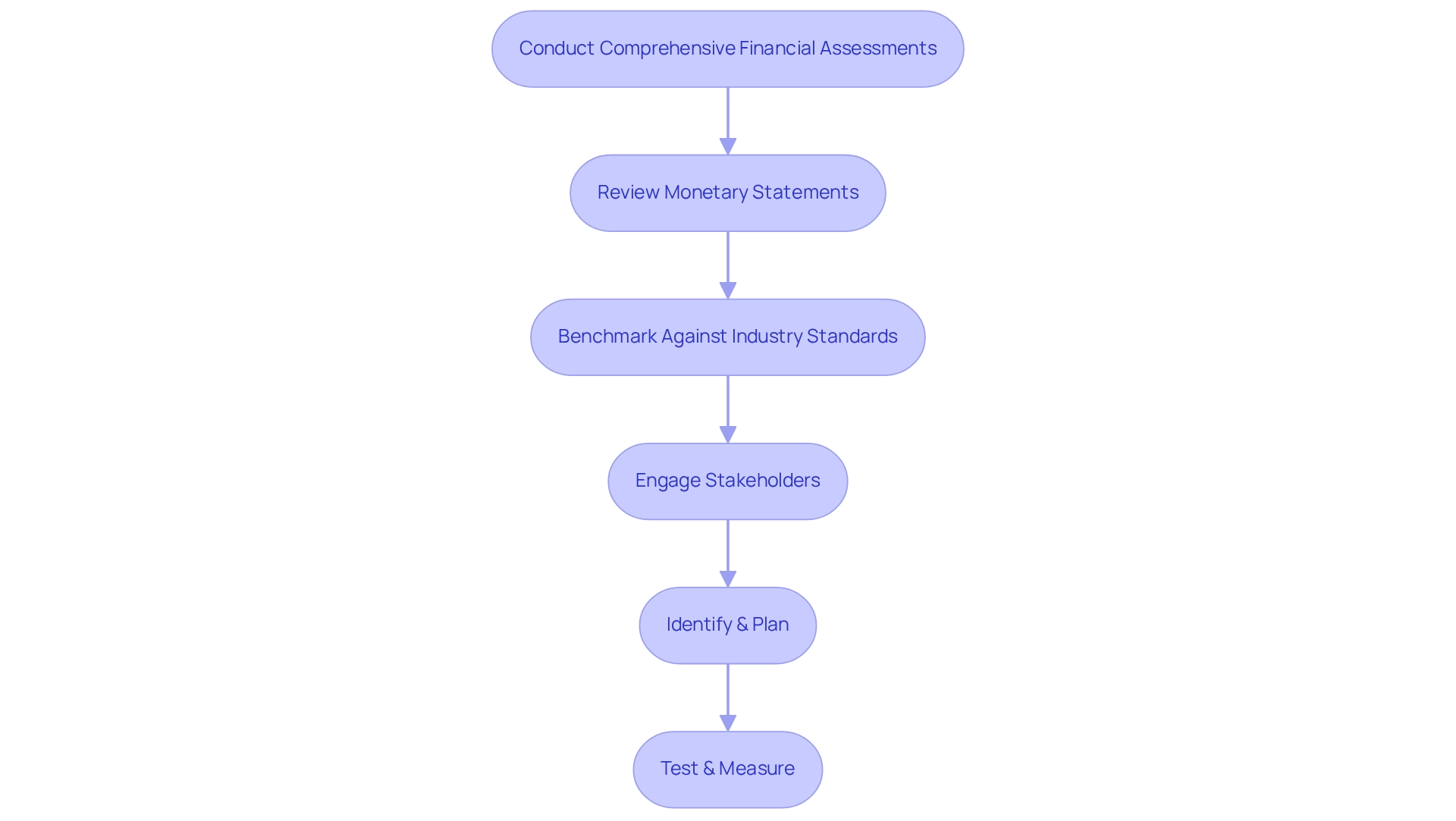
Conduct Comprehensive Financial Assessments
Performing a thorough monetary evaluation involves several essential steps:
- Review Monetary Statements: Analyze income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements to understand the economic position. Evaluate Key Ratios: Utilize economic ratios such as liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, and leverage ratios to gauge performance. Identify Cost Drivers: Assess operational costs to pinpoint areas where expenses can be reduced without sacrificing quality.
- Benchmark against industry standards by comparing financial metrics with industry peers to identify gaps in distressed company performance. Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the assessment process to gain insights and foster buy-in for necessary changes.
- Identify & Plan: Collaborate with your team to pinpoint underlying organizational issues and develop a strategic plan that reduces weaknesses while facilitating reinvestment in key strengths. Test & Measure: Adopt a pragmatic approach to data by testing every hypothesis to ensure maximum return on invested capital, both in the short and long term.
These assessments should be ongoing to adapt to changing market conditions and internal dynamics, ensuring continuous business performance monitoring and relationship-building through real-time analytics.
Implement Strategic Turnaround Plans
Implementing a strategic recovery plan involves several critical steps:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish specific, measurable goals that the recovery plan aims to achieve, focusing on financial health and operational efficiency.
- Develop a Detailed Action Plan: Outline the necessary steps to reach these objectives, including timelines and responsible parties, leveraging our comprehensive recovery and restructuring consulting services, including bankruptcy case management.
- Communicate the Plan: Ensure that all stakeholders understand the plan and their roles in its execution, fostering a culture of transparency and collaboration.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly review performance against the established goals using real-time analytics from our client dashboard, allowing for timely adjustments to the plan as necessary.
- Foster a Culture of Accountability: Encourage ownership of tasks among team members to enhance commitment to the recovery efforts, supported by our interim management services that provide hands-on executive leadership.
Real-world examples of successful recoveries often highlight the importance of adaptability and responsiveness to market changes. This demonstrates the effectiveness of our Rapid-30 process in identifying organizational issues and implementing transformational change.
Utilize Interim Management for Crisis Stabilization
Effectively utilizing interim management involves several critical steps:
- Assessing Leadership Gaps: Identify areas where leadership is lacking or where expertise is urgently needed, particularly in recovery situations.
- Hiring Experienced Interim Managers: Engage professionals such as Peter Griscom, M.S., a leading expert in business integration and recovery with extensive experience in manufacturing and technology, recognized as the Business Recovery of the Year in 2018 and 2022, or Jason Collyer, a Top 100 COO with expertise in defense, aviation entrepreneurship, and supply chain transformation. Their proven track records in leadership during recovery can significantly enhance efforts.
- Establishing Clear Mandates: Define the scope of the interim manager's role, including specific objectives and expected outcomes, to ensure alignment with the overall recovery strategy.
- Facilitating Knowledge Transfer: Ensure that interim managers share their insights and strategies with permanent staff to build internal capabilities and operationalize lessons learned from the turnaround process.
- Evaluating Performance: Regularly assess the interim manager's impact on the organization and adjust their role as necessary, utilizing real-time analytics to monitor business performance and make informed decisions. This includes continuous performance monitoring and relationship-building to ensure sustained improvement.
In conclusion, interim managers provide the necessary focus and expertise to navigate through crises, ensuring that the company remains on track toward recovery.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of financial distress is imperative for any organization aiming to secure its future. The key indicators—cash flow problems, rising debt levels, declining sales, delayed payments, and high employee turnover—serve as critical markers that warrant immediate attention. By monitoring these signs closely, companies can implement timely corrective measures that not only prevent further decline but also lay the groundwork for recovery.
Conducting thorough financial assessments is equally essential. By reviewing financial statements, evaluating key ratios, identifying cost drivers, and benchmarking against industry standards, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their financial health. Engaging stakeholders in this process fosters collaboration and buy-in, ensuring that strategic plans are well-informed and robust.
Moreover, implementing strategic turnaround plans, supported by interim management when necessary, can further enhance recovery efforts. Clear objectives, detailed action plans, and a culture of accountability are vital for steering the organization back to stability and growth. The adaptability and responsiveness to market changes showcased through successful turnaround examples underline the importance of proactive management.
In conclusion, the path to financial recovery is paved with vigilance and strategic action. By staying attuned to the indicators of distress and leveraging expert insights, organizations can navigate challenges effectively and emerge stronger, ready to embrace sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key indicators of economic distress that companies should monitor?
Key indicators include flow issues, increased debt levels, declining sales, delayed payments, and high employee turnover.
What does ongoing negative flow indicate for a company?
Ongoing negative flow serves as a major warning sign that a company may struggle to meet its monetary obligations, necessitating proactive management.
How does an increased debt-to-equity ratio affect a company?
An escalating debt-to-equity ratio indicates that a company is increasingly reliant on borrowed funds, which may necessitate financial restructuring.
What does a sustained decrease in sales suggest?
A sustained decrease in sales can signal market share erosion or operational inefficiencies, particularly evident in sectors like Construction, which faces significant distress.
What are the implications of frequent late payments to suppliers or creditors?
Frequent late payments indicate liquidity issues, as companies facing cash flow problems often struggle to maintain timely payments.
How can high employee turnover rates be interpreted?
Increased turnover rates may reflect low morale or instability within the organization, which can be symptomatic of deeper financial troubles.
Why is it important for CFOs to recognize these indicators early?
Recognizing these signs early allows businesses to implement corrective measures to mitigate further decline and enhance their recovery strategies.
What common pitfalls should CFOs be aware of when assessing economic distress?
CFOs should avoid misinterpreting temporary liquidity fluctuations as permanent problems, as this can lead to misguided strategies.
How can integrating expert opinions assist in recognizing economic distress?
Integrating expert opinions can bolster the credibility of the assessment and guide effective decision-making regarding distressed company performance.




