Overview
The primary focus of this article is to illustrate the significance of stakeholder analysis in project management and to demonstrate its potential to enhance project success. By outlining various tools and methods, such as the Power-Interest Grid and Stakeholder Impact Table, this article provides a framework for identifying and engaging key participants. This strategic engagement ultimately leads to improved outcomes and more effective risk management in projects.
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of small and medium enterprises (SMEs), understanding the intricate web of stakeholder relationships is crucial for thriving in challenging times. Comprehensive stakeholder analysis services empower businesses to identify and engage with key players, aligning strategies with the diverse interests that influence project outcomes.
By leveraging tools such as the Power-Interest Grid and Stakeholder Engagement Assessment Matrix, organizations can prioritize communication and tailor their approaches to foster collaboration.
Moreover, as case studies reveal, effective stakeholder engagement not only mitigates risks but also enhances resilience and drives sustainable success.
This exploration delves into essential techniques and tools that can transform stakeholder dynamics, paving the way for more informed decision-making and improved project results.
Transform Your Small/ Medium Business: Comprehensive Stakeholder Analysis Services
An example of stakeholder analysis in project management is crucial for aiming to navigate crises effectively. An example of stakeholder analysis in project management involves:
- Identifying key participants
- Gaining a thorough understanding of their interests
This allows businesses to tailor strategies that align with these needs. This targeted approach not only leads to improved project outcomes but also enhances organizational resilience. Research indicates that SMEs in transition countries can significantly boost productivity by leveraging inputs from areas with established institutional connections, underscoring the importance of participant involvement.
Moreover, a case study on regulatory actions in Italy revealed that, despite support measures, micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) continued to face credit limitations. This highlights the necessity for an extensive example of stakeholder analysis in project management to effectively address structural challenges. By ensuring that all voices are heard, businesses can foster collaboration and support, which is crucial during challenging times.
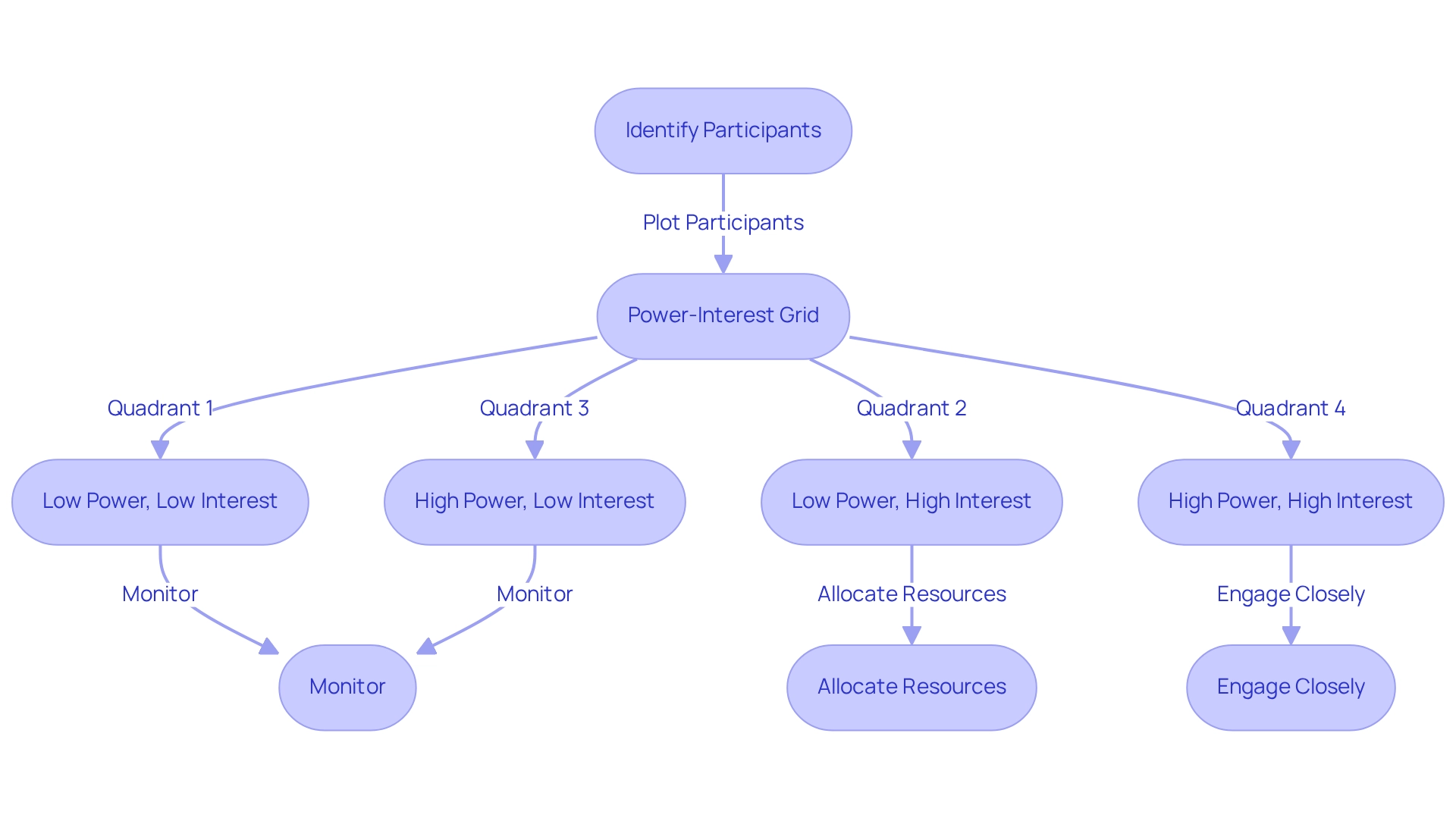
Power-Interest Grid: Prioritize Stakeholders Effectively
The Power-Interest Grid serves as a vital classification tool for participants, categorizing them into four quadrants based on their influence and interest in the initiative. This empowers project managers to identify which participants necessitate close engagement and which should be monitored. By effectively plotting key participants on this grid, businesses can allocate resources judiciously. Consequently, high-power, high-interest individuals are prioritized for communication and active involvement in decision-making processes.
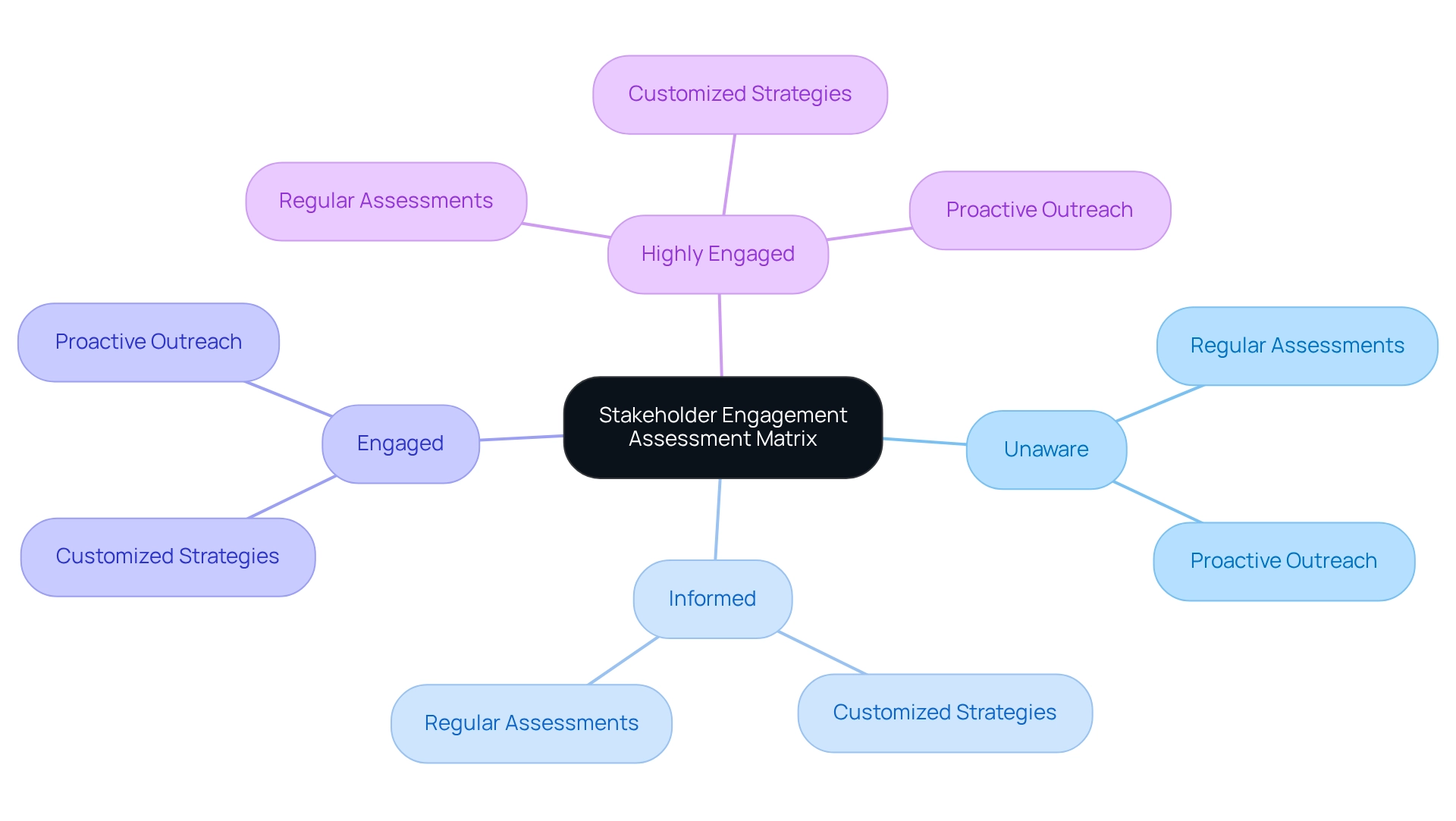
Stakeholder Engagement Assessment Matrix: Enhance Communication Strategies
The Participant Involvement Assessment Matrix serves as a crucial tool for evaluating current participant involvement levels and pinpointing effective strategies for future interactions. By categorizing stakeholders from unaware to highly engaged, managers can devise tailored communication strategies that not only strengthen relationships but also ensure that participants feel valued and informed throughout the initiative's lifecycle.
Engaging stakeholders effectively is vital; it can significantly enhance outcomes by aligning initiatives with the interests and expectations of those involved. For instance, initiatives characterized by robust stakeholder engagement are more likely to yield relevant and actionable results, as evidenced by case studies in clinical research.
Furthermore, expert insights suggest that meeting the expectations of engaged parties can greatly increase the likelihood of success, fostering active support and minimizing unresolved issues. To bolster participant engagement, organizations should adopt best practices such as:
- Regular assessments of engagement levels
- Customized communication strategies
- Proactive outreach efforts
By implementing these strategies, they can cultivate a collaborative environment that promotes long-term sustainability and success.
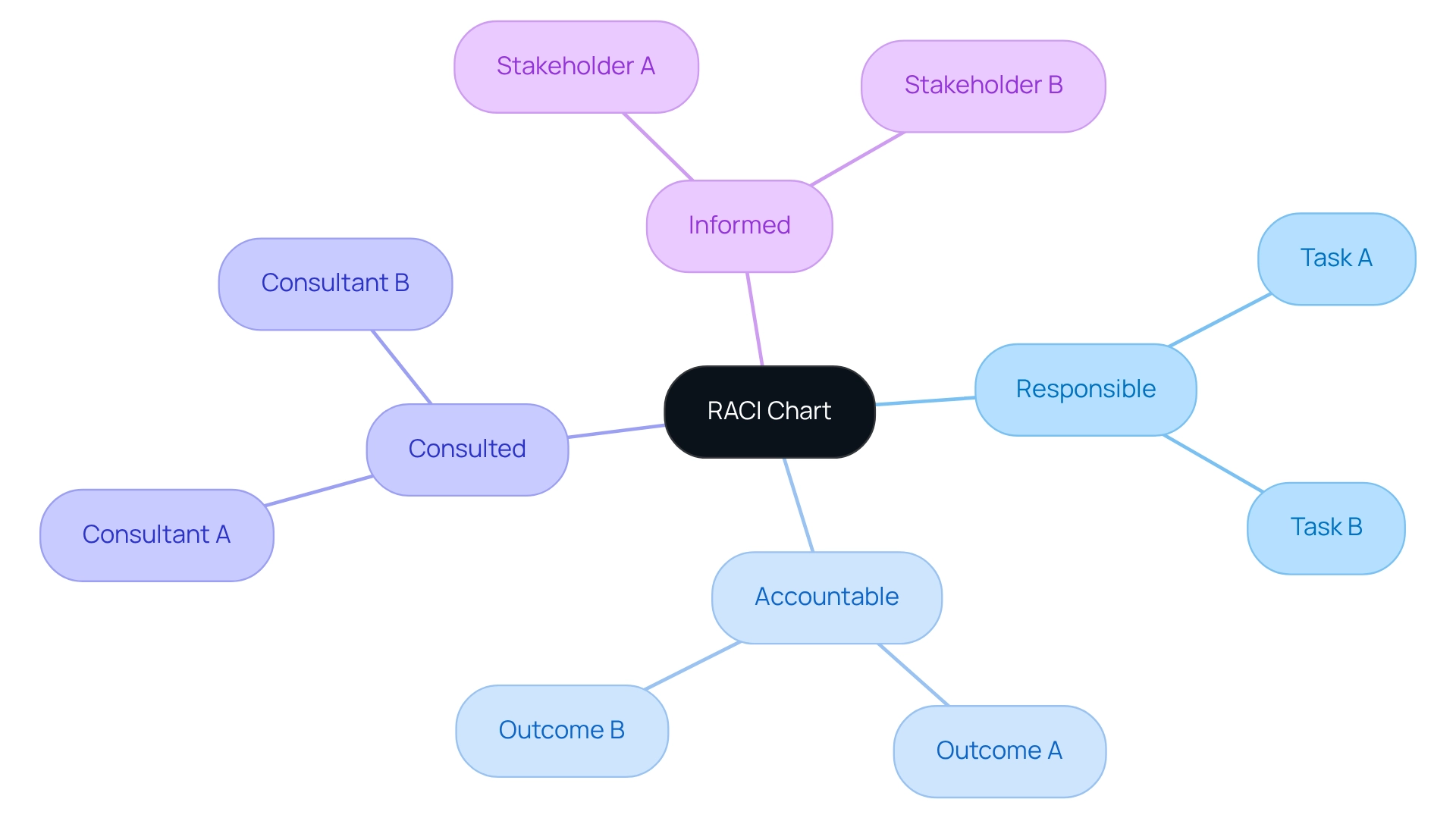
RACI Chart: Clarify Roles and Responsibilities
The RACI chart—representing Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed—serves as a powerful tool for delineating participant roles in any initiative. By clearly identifying:
- Who is responsible for each task
- Who is accountable for outcomes
- Who requires consultation
- Who should be kept informed
managers can significantly enhance collaboration. This clarity is vital for sustaining momentum and achieving objectives.
Furthermore, utilizing within management tools such as monday.com and Smartsheet enables teams to efficiently outline roles and monitor progress. A well-constructed RACI chart not only synchronizes team activities but also evolves with the initiative, ensuring that all participants remain engaged and updated.
As demonstrated in a case study on RACI chart development, incorporating team feedback during the validation process cultivates a sense of ownership and accountability, leading to more informed decision-making and precise task execution.
Expert insights underscore that effective management hinges on clearly defining tasks and assigning the right individuals, empowering teams to execute their responsibilities with confidence.
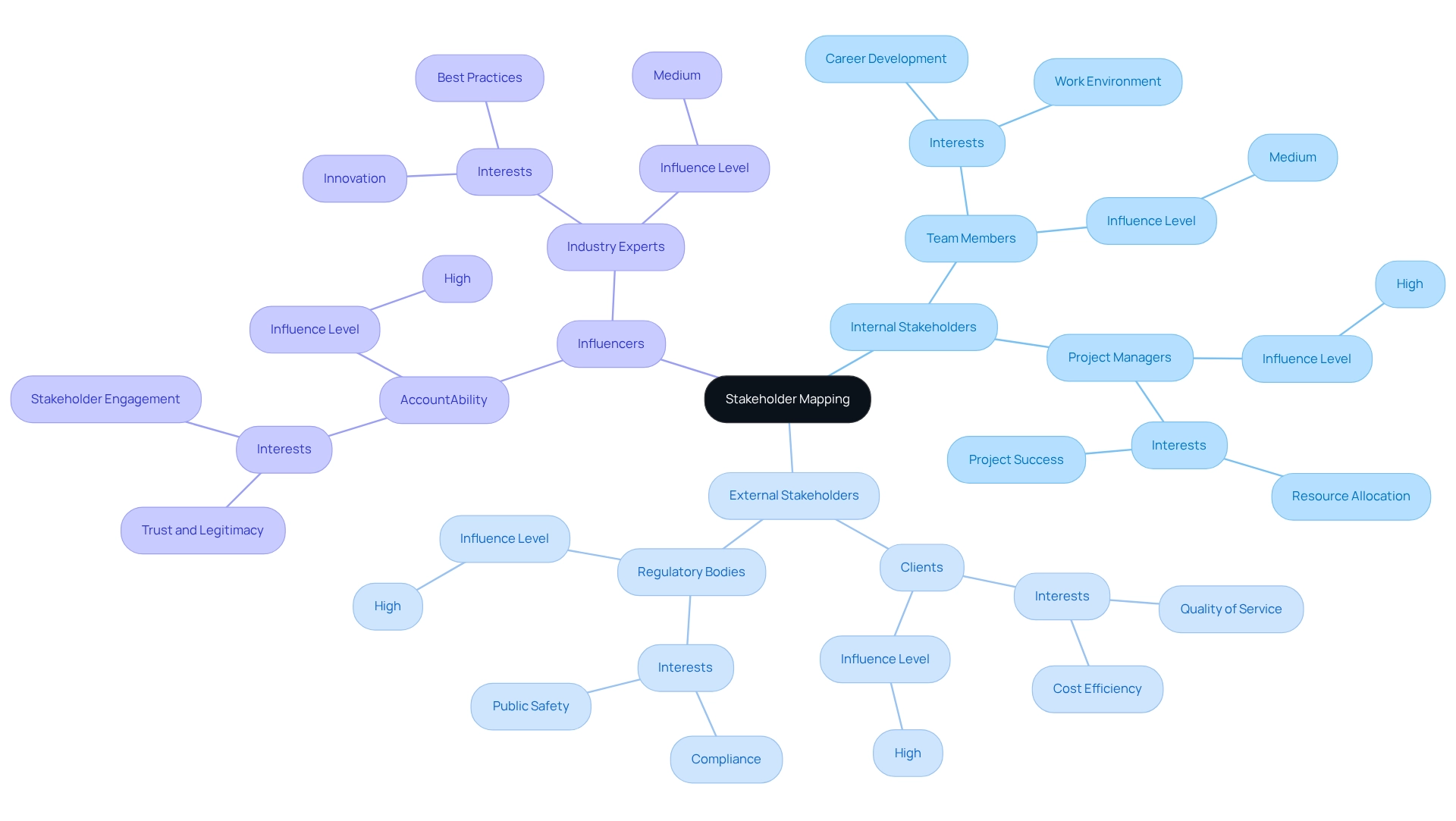
Stakeholder Mapping: Visualize Relationships and Influence
Stakeholder mapping is a pivotal technique and serves as an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, creating visual representations of relationships and influence among stakeholders. This method is an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, empowering managers to identify key individuals, understand their interests, and evaluate their potential impact on initiatives. By visualizing these dynamics, organizations can formulate targeted interaction strategies that illustrate an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, leveraging existing relationships and fostering collaboration.
This strategic alignment is essential; studies indicate that an example of stakeholder analysis in project management shows a correlation with , improved financial outcomes, and enhanced sustainability. For instance, an example of stakeholder analysis in project management demonstrates that organizations prioritizing engagement with interested parties frequently experience a significant rise in trust and legitimacy—elements vital for enduring success. A study conducted by AccountAbility revealed that organizations demonstrating high levels of participant engagement were more likely to be perceived as trustworthy and legitimate.
Furthermore, visualizing relationships among stakeholders serves as an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, allowing managers to navigate conflicting interests and representation challenges, as illustrated in the case study 'Challenges of Engagement with Interested Parties.' This approach serves as an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, ultimately driving transformational change and achieving desired project outcomes. Additionally, participation can yield fresh insights, collaborative problem-solving, and sustainable product development, underscoring the broader benefits of mapping involved parties. Notably, Interface has successfully reduced its greenhouse gas emissions by 96% since 1996, exemplifying the tangible positive outcomes of effective collaboration with interested parties.
Stakeholder Impact Table: Assess Potential Effects on Projects
The [Stakeholder Impact Table](https://blog.smbdistress.com/10-essential-cash-flow-management-strategies-for-small-businesses) is an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, as it serves as a vital tool for organizing participants according to their potential influence on an initiative. By conducting an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, project managers can evaluate each party's influence and the nature of their impact—whether beneficial or detrimental—to proactively address challenges and garner support. This systematic assessment is essential for effective risk management, enabling teams to foresee obstacles and devise strategies to mitigate potential disruptions to progress.
A study revealed a significant p-value of 0.012, indicating that projects fostering trust between participants and planners lead to positive attitudinal changes. Moreover, as . noted, grasping the historical context of participant relationships can greatly improve policy design and effectiveness.
Additionally, a case study entitled 'Sharing Value for Stakeholder Commitment' demonstrated how Wei Ling's approach of sharing value through resource access and training not only strengthened relationships with stakeholders but also enhanced the quality of soft assets, ultimately reinforcing the company's value propositions.
Such instances underscore the effectiveness of the Impact Table, which serves as an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, in assessing influence and its critical role in achieving successful outcomes.
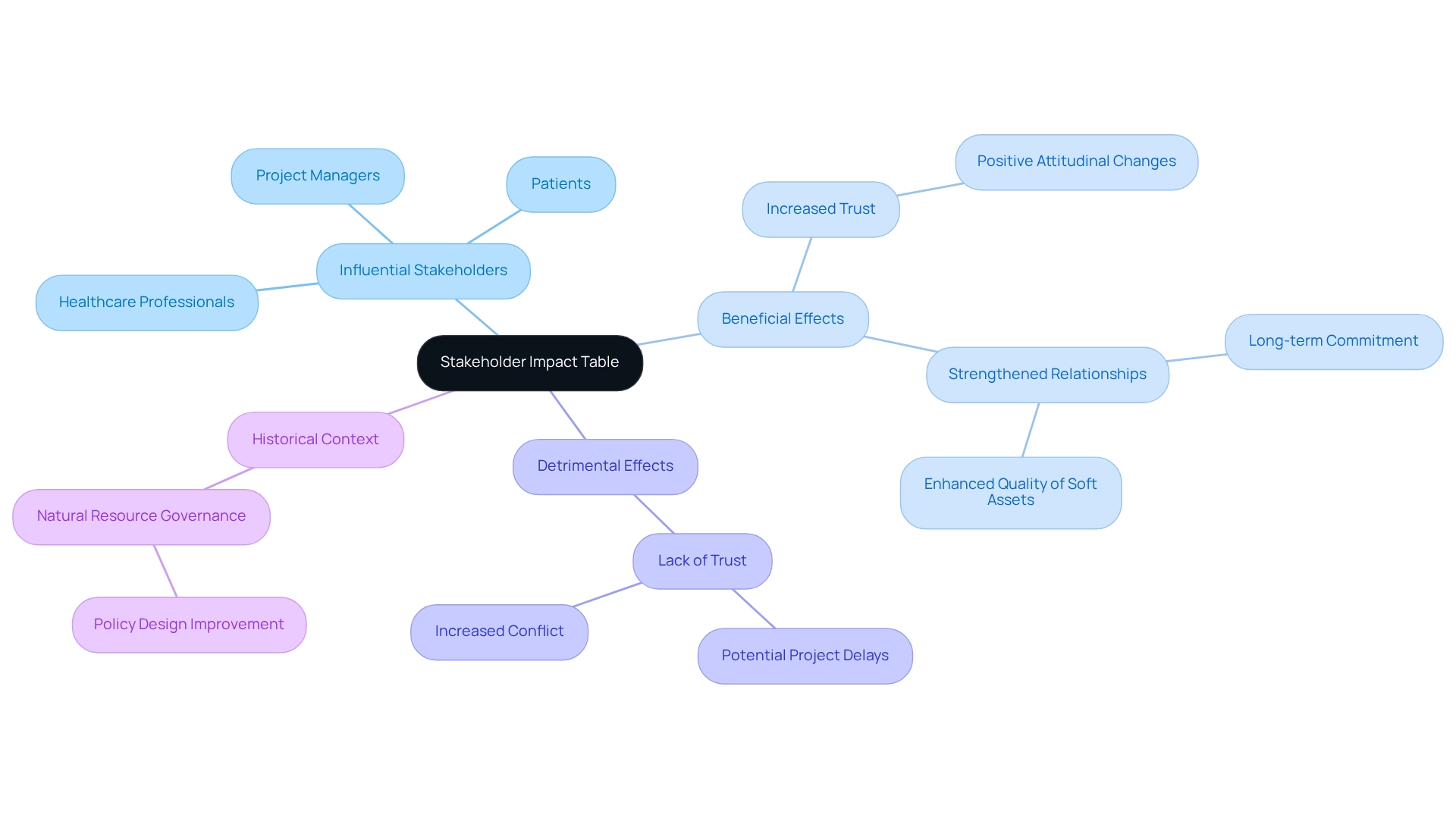
Stakeholder Analysis Template: Document and Structure Insights
A Participant Analysis Template serves as an invaluable resource for documenting insights gained during the participant analysis process. This template typically includes sections for identifying participants, evaluating their interests, influence, and potential effects on the initiative. By employing a standardized format, project teams can ensure that all relevant information is captured and readily accessible, thereby fostering collaboration and informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Thorough documentation of participant insights is essential, as it lays the groundwork for and facilitating productive conversations, ultimately leading to more fruitful interactions. As one specialist remarked, "the readiness of investigators to invest the time and effort into making that participation significant is regrettably insufficient," underscoring the necessity for comprehensive involvement strategies. Moreover, establishing the right tone and environment for discussions significantly contributes to fostering openness and comfort.
For instance, a case study on training participants for effective involvement demonstrated that providing education and resources significantly improved engagement, thereby enhancing the overall quality of project reviews. This outcome highlights the practical value of utilizing a Participant Analysis Template.
Optimal methods for employing a Participant Analysis Template involve:
- Regularly updating the information to reflect changes in participant dynamics
- Ensuring that all team members are trained in its application
This proactive approach not only enhances communication but also aligns goals with participant expectations, driving successful results.
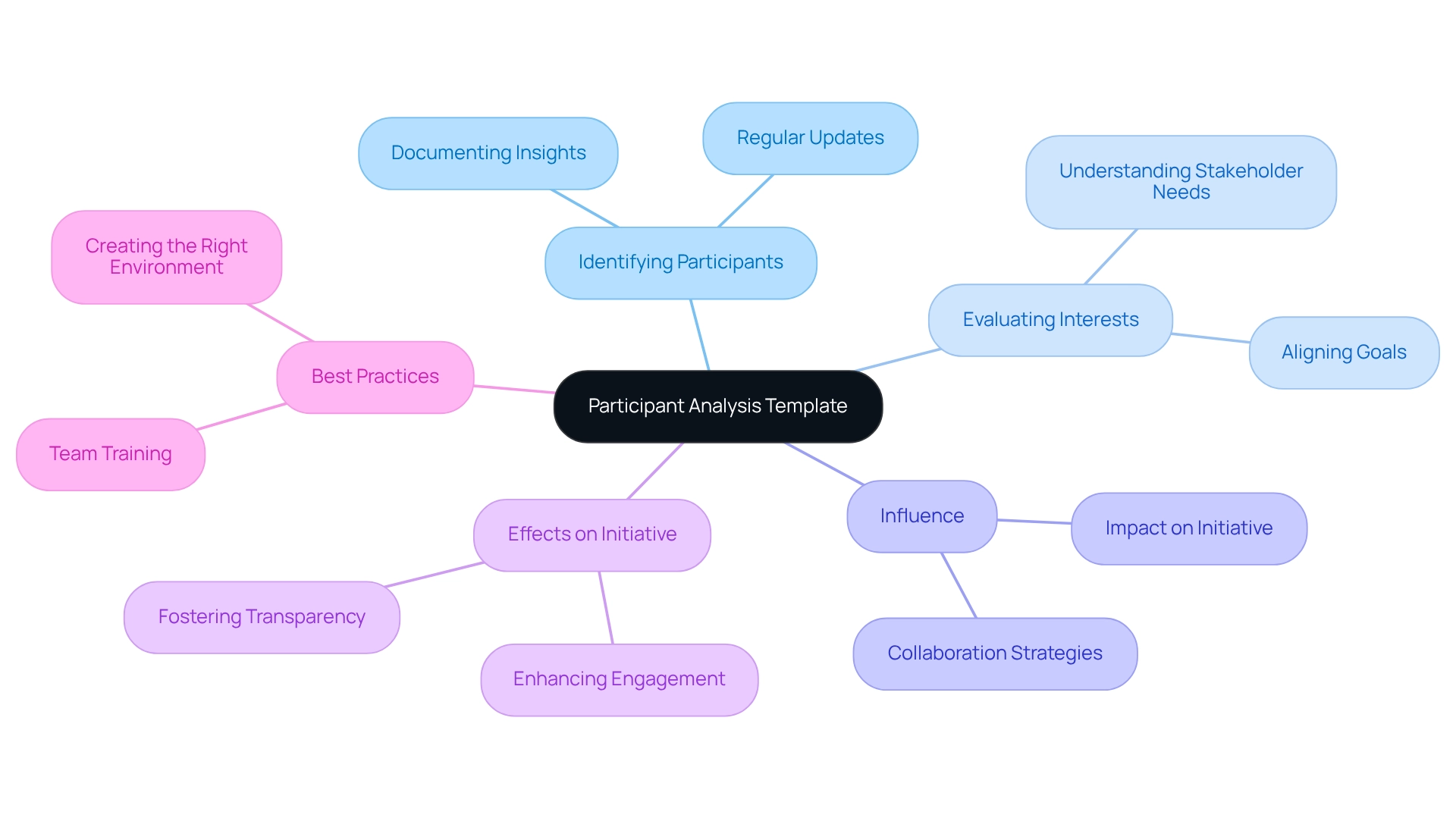
Case Studies: Learn from Real-World Stakeholder Analysis Applications
Examining case studies serves as an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, revealing crucial lessons and best practices. An example of stakeholder analysis in project management is a building initiative that effectively utilized interest group mapping to recognize key influencers, resulting in a more efficient approval process. This aligns with broader transportation policies focused on enhancing urban mobility, underscoring the significance of participant involvement in such initiatives.
In the healthcare sector, a program that utilized a Power-Interest Grid to prioritize participants skillfully navigated regulatory challenges, providing an example of stakeholder analysis in project management to achieve success. Notably, PlainJoe Studios enhanced billing rates by 15% after transitioning to Mavenlink, showcasing the tangible advantages of effective participant analysis in management.
As Ricardo Gomes observes, "This article seeks to add to the theory by comparing the environment in which public managers make decisions," emphasizing the theoretical framework that supports these practical examples. These instances serve as an example of stakeholder analysis in project management, highlighting how can significantly improve outcomes and stressing the importance of customized methods across various sectors.
Furthermore, understanding the evolving interactions among participants, as discussed in the case study 'Dynamic Relationships Among PPP Participants,' is vital for effective management and success. CFOs can leverage these insights to implement more efficient analysis strategies for involved parties in their initiatives.
Understanding Stakeholder Needs: Align Project Goals with Interests
Understanding the needs of involved parties necessitates active engagement to gather insights regarding their expectations and concerns. By initiating with a comprehensive business assessment, managers can align key participants and gain a profound understanding of the business context that transcends mere figures. This alignment not only enhances stakeholder satisfaction but also significantly increases the likelihood of success, as stakeholders are more inclined to support initiatives that resonate with their priorities.
Furthermore, by identifying fundamental business challenges and collaboratively developing a strategic plan, managers can fortify advantages and mitigate vulnerabilities, thereby fostering teamwork and reducing opposition.
Importance of Stakeholder Analysis: Mitigate Risks and Ensure Success
An example of stakeholder analysis in project management is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring the success of any initiative. By recognizing and comprehending the involved parties, managers can anticipate potential obstacles and formulate proactive plans to address them. This analysis not only aids in managing expectations but also cultivates a collaborative atmosphere where participants feel valued and engaged.
Studies indicate that projects with comprehensive participant involvement boast significantly higher success rates. Specifically, entities that conducted stakeholder analyses prior to embarking on complex initiatives reported increased support and reduced opposition, leading to smoother execution.
As one expert aptly noted, "This is why it is prudent to conduct a stakeholder assessment before launching any intricate corporate initiative, identifying all potential individuals and strategizing on how to secure their support."
Ultimately, the example of stakeholder analysis in project management serves as a cornerstone of , empowering teams to navigate complexities and achieve their objectives while promoting sustainable growth.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively engaging stakeholders is not merely a beneficial practice; it is a necessity for small and medium enterprises striving for success in today’s complex business environment. Insights gathered from comprehensive stakeholder analysis services underscore the importance of identifying key players and aligning strategies with their interests. Tools such as the Power-Interest Grid and Stakeholder Engagement Assessment Matrix empower organizations to prioritize communication and tailor their approaches, ensuring that all voices are heard and valued.
The various methods discussed, including stakeholder mapping, RACI charts, and stakeholder impact assessments, illustrate how structured engagement can significantly enhance project outcomes. By fostering collaboration and proactively addressing stakeholder concerns, businesses can mitigate risks and drive sustainable success, as evidenced by real-world case studies that showcase the transformative power of effective stakeholder engagement.
In conclusion, prioritizing stakeholder analysis is essential for navigating challenges and fostering resilience. Organizations that invest in understanding stakeholder needs and aligning project goals with their interests are better positioned to achieve successful outcomes and build lasting relationships. The path to improved project results and organizational growth is paved with informed decision-making and strategic stakeholder engagement. Thus, it is imperative for SMEs to embrace these practices as a core component of their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of stakeholder analysis in small and medium businesses?
The purpose of stakeholder analysis in small and medium businesses is to identify key participants, understand their interests, and tailor strategies that align with these needs, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes and enhanced organizational resilience.
How can stakeholder analysis improve productivity in SMEs?
Research indicates that SMEs in transition countries can significantly boost productivity by leveraging inputs from areas with established institutional connections, highlighting the importance of participant involvement in stakeholder analysis.
What challenges do micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) face according to the case study in Italy?
The case study revealed that MSMEs continued to face credit limitations despite support measures, underscoring the necessity for comprehensive stakeholder analysis to effectively address structural challenges.
What is the Power-Interest Grid and how is it used in stakeholder management?
The Power-Interest Grid is a classification tool that categorizes participants into four quadrants based on their influence and interest in an initiative. It helps project managers identify which participants require close engagement and which should be monitored, allowing for judicious resource allocation.
How does the Participant Involvement Assessment Matrix enhance communication strategies?
The Participant Involvement Assessment Matrix evaluates current participant involvement levels and helps managers devise tailored communication strategies to strengthen relationships and ensure participants feel valued and informed throughout the initiative's lifecycle.
Why is effective stakeholder engagement important?
Effective stakeholder engagement is vital as it can significantly enhance outcomes by aligning initiatives with the interests and expectations of involved parties, increasing the likelihood of success and fostering active support.
What best practices can organizations adopt to bolster participant engagement?
Organizations can adopt best practices such as regular assessments of engagement levels, customized communication strategies, and proactive outreach efforts to cultivate a collaborative environment that promotes long-term sustainability and success.




