Overview
The article underscores the critical role of business ethics through a stakeholder and issues management approach, highlighting the necessity of moral principles such as integrity and fairness in shaping corporate conduct. This approach not only enables businesses to cultivate trust with stakeholders—illustrated by successful examples like Patagonia and Starbucks—but also bolsters long-term sustainability and profitability by mitigating risks and nurturing a robust moral culture within organizations. By prioritizing ethical practices, companies can secure their position in the market while fostering a positive impact on society.
Introduction
Business ethics, which encompasses a stakeholder and issues management approach, plays a pivotal role in shaping the moral framework within which organizations operate. By prioritizing principles such as integrity, fairness, and responsibility, businesses not only enhance their reputations but also cultivate loyalty among customers and employees, ultimately driving long-term success.
However, as ethical challenges become increasingly complex in today’s corporate landscape, how can organizations effectively navigate these dilemmas while ensuring they meet the expectations of all stakeholders?
This article delves into the significance of business ethics, the importance of stakeholder engagement, and the evolving strategies necessary for ethical governance in modern enterprises.
Define Business Ethics: Core Principles and Importance
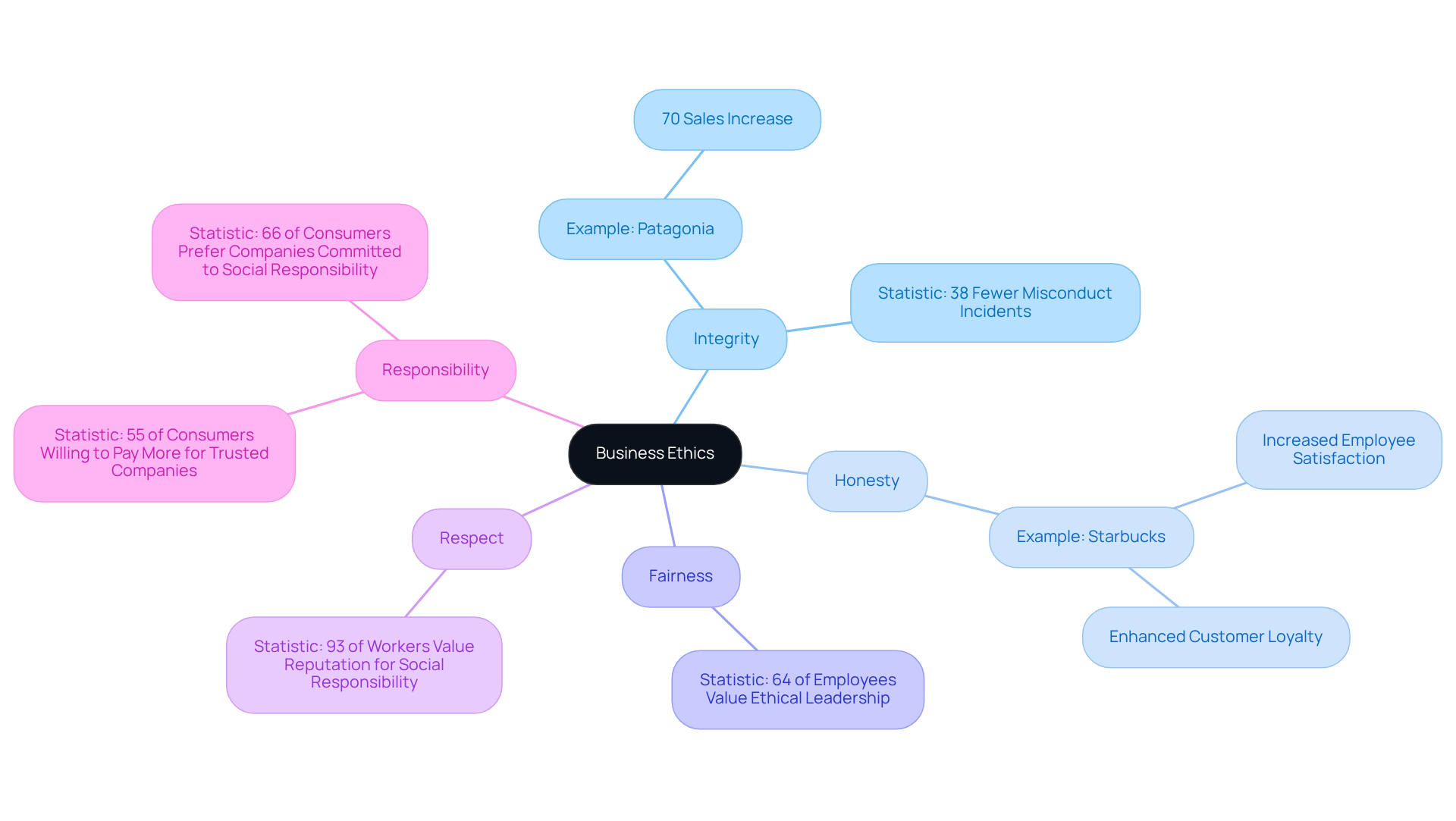
Business ethics a stakeholder and issues management approach encompasses the moral principles and standards that guide corporate behavior, shaping the values that govern both individual and organizational actions. Core principles such as integrity, honesty, fairness, respect, and responsibility are vital for fostering trust among stakeholders and are essential to a business ethics a stakeholder and issues management approach that includes employees, customers, suppliers, and the community. Businesses that prioritize these moral standards not only enhance their reputation but also attract loyal clients and reduce legal risks, contributing to long-term success and sustainability.
For instance, Patagonia's dedication to responsible practices has resulted in an impressive 70% rise in sales, showcasing the tangible advantages of principled leadership. Similarly, Starbucks has observed enhanced employee satisfaction and customer loyalty linked to its principled leadership practices. Research indicates that organizations with robust moral cultures encounter 38% fewer misconduct incidents and generate 2.5 times more revenue than their less principled counterparts. Furthermore, firms in the S&P 500 index that emphasized sustainability surpassed those that did not by 25%, underscoring the financial benefits of responsible practices.
Moreover, 93% of workers regard a firm's reputation for social responsibility as essential when selecting a workplace, and 64% stated that principled leadership significantly affects their chances of remaining with their organization. By adopting business ethics a stakeholder and issues management approach in their operations, companies can establish a foundation of trust that enhances their reputation and fosters loyalty, ultimately positioning them for sustainable growth.
Explore the Stakeholder Approach: Engaging with Key Players
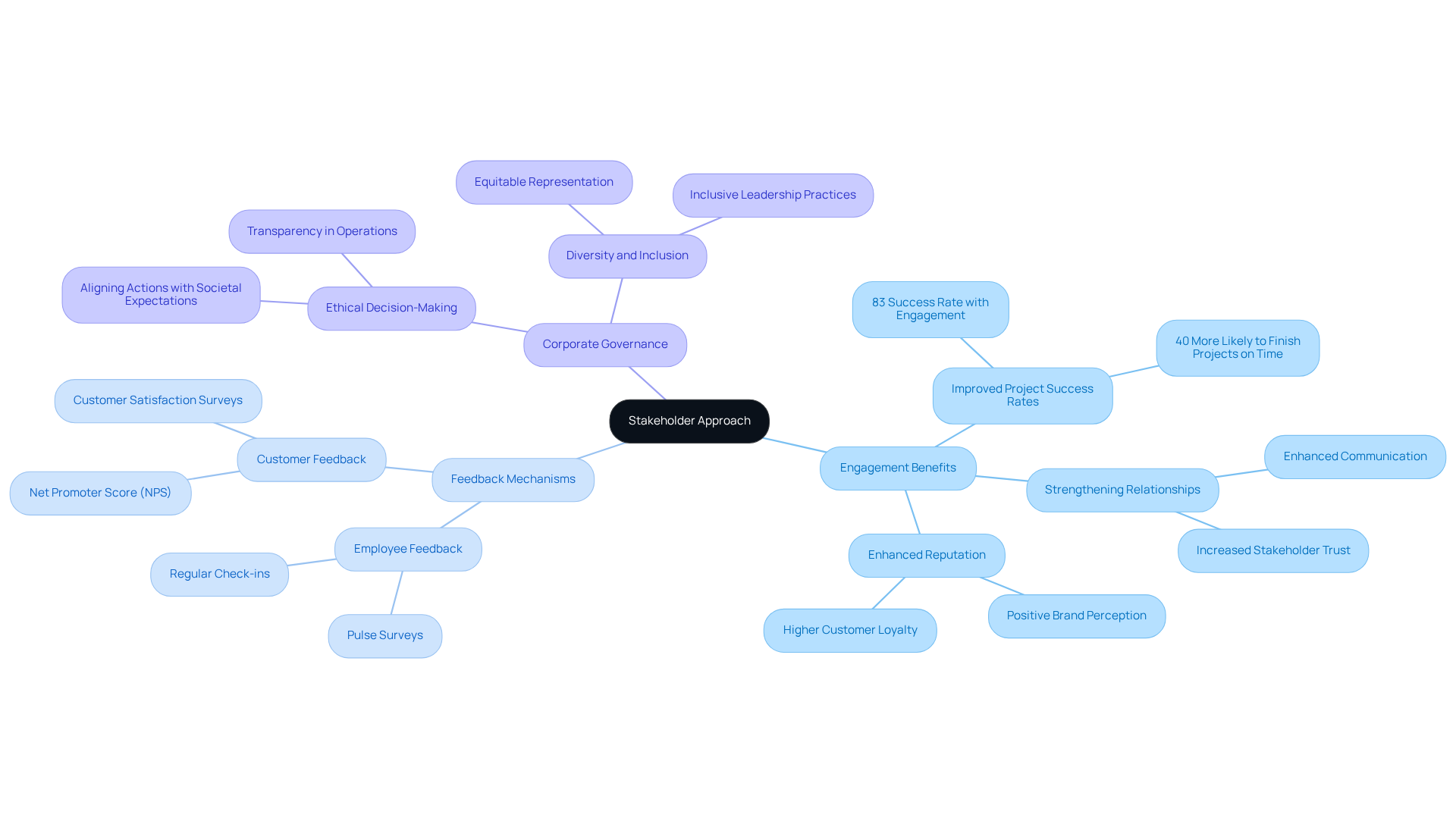
The participant approach, rooted in business ethics, a stakeholder and issues management approach, underscores the necessity of considering the interests of all groups impacted by a business's actions, extending beyond shareholders to include workers, customers, suppliers, and the broader community. Engaging with interested parties requires a profound understanding of their needs, expectations, and concerns, which can lead to more informed decision-making.
For instance, companies that actively seek feedback from employees and customers are better equipped to identify potential ethical dilemmas early, enabling them to address issues proactively. This proactive engagement not only fosters open communication but also strengthens relationships with stakeholders, ultimately enhancing corporate reputation and ensuring long-term success.
Current trends indicate that organizations prioritizing feedback mechanisms from interested parties are more likely to achieve their strategic goals, with studies revealing that effective engagement with these groups can improve project success rates by up to 83%. Furthermore, companies that interact with interested parties are 50% more likely to meet their significant objectives.
Industry leaders assert that integrating the perspectives of interested parties into decision-making processes is vital for ethical governance, as it aligns corporate actions with societal expectations and bolsters overall organizational integrity through a business ethics, a stakeholder and issues management approach.
By leveraging efficient decision-making and real-time analytics through our client dashboard, Transform Your Small/Medium Business can consistently monitor performance and apply insights gained from turnaround processes, thereby cultivating strong, lasting connections with partners.
As Dame Vivian Hunt observes, diverse leadership groups correlate with greater financial gains, highlighting the importance of inclusive participant engagement.
Understand Issues Management: Navigating Ethical Challenges
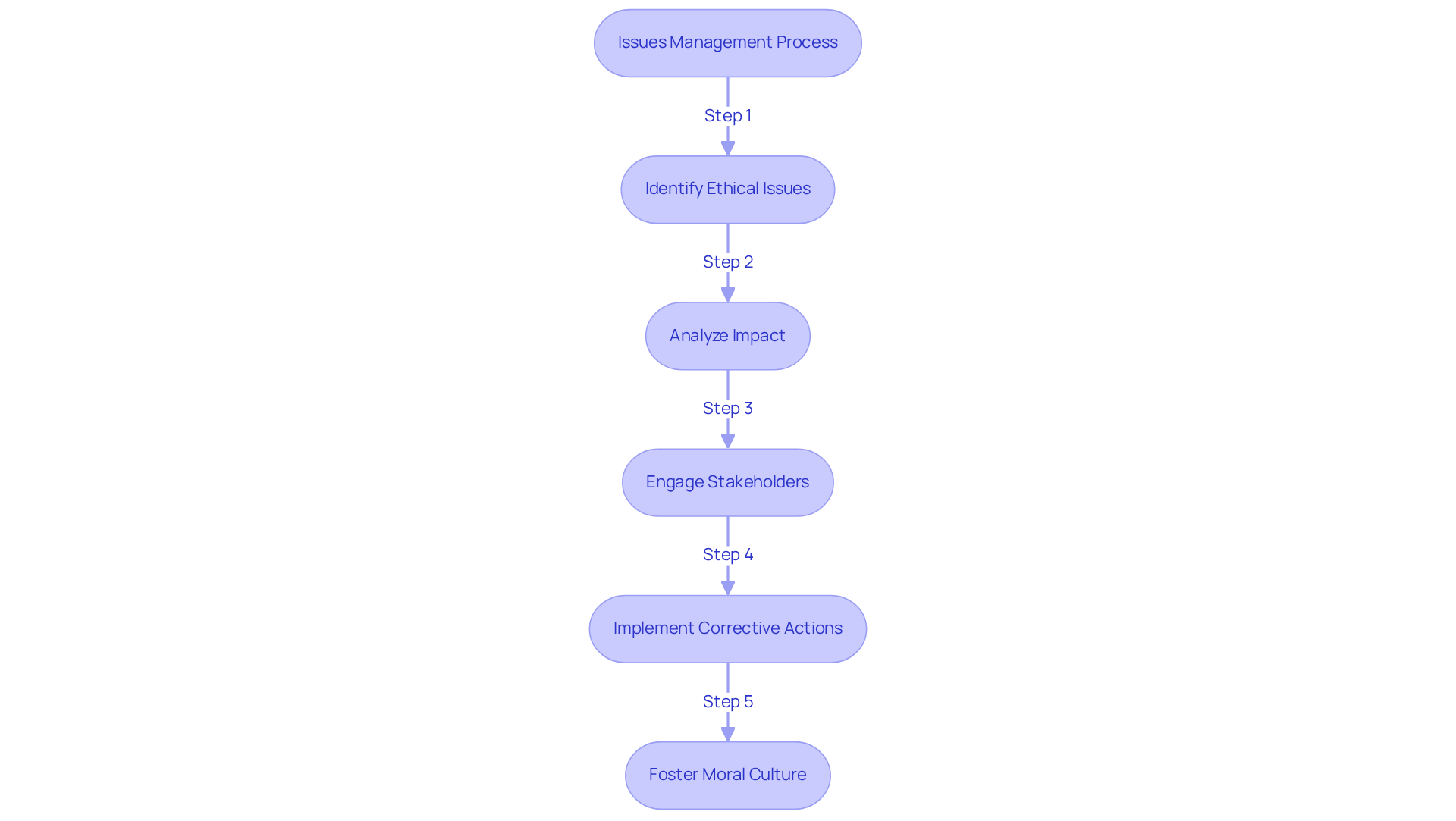
The process of issues management, which includes business ethics, a stakeholder and issues management approach, is critical for the identification, analysis, and resolution of moral challenges within business operations. This proactive strategy enables organizations to mitigate risks and respond effectively to potential crises. For instance, when a company faces claims of discrimination, it is vital to conduct a thorough investigation, communicate transparently with stakeholders, and implement corrective actions. Establishing a robust issues management framework within the context of business ethics, a stakeholder and issues management approach not only addresses moral dilemmas but also enhances the overall moral culture of the organization.
Educating employees on moral decision-making is essential, as 95% of workers believe that companies should benefit all stakeholders, not just shareholders. Furthermore, 87% of employees reported that their workplace lacks a strong moral culture, underscoring the urgency to address these challenges. Creating accessible channels for reporting unethical behavior fosters a culture of accountability, with 72% of staff sharing their observations of misconduct—a significant increase from previous years. Additionally, 48% of investors have opted not to invest in a company due to its public stance on an issue, highlighting the financial repercussions of responsible management, particularly relevant for CFOs.
Moreover, fostering an environment that adopts business ethics, a stakeholder and issues management approach, where moral considerations are prioritized in all business activities, can greatly enhance employee engagement and retention. Organizations that implement a business ethics, a stakeholder and issues management approach are better positioned to effectively navigate moral challenges, ensuring long-term success and sustainability. As Sarah Lane, Head of Ethics and Assurance at ACCA, articulates, "These insights emphasize the necessity for strong moral leadership and culture in organizations.
Trace the Evolution of Business Ethics: Historical Context and Development
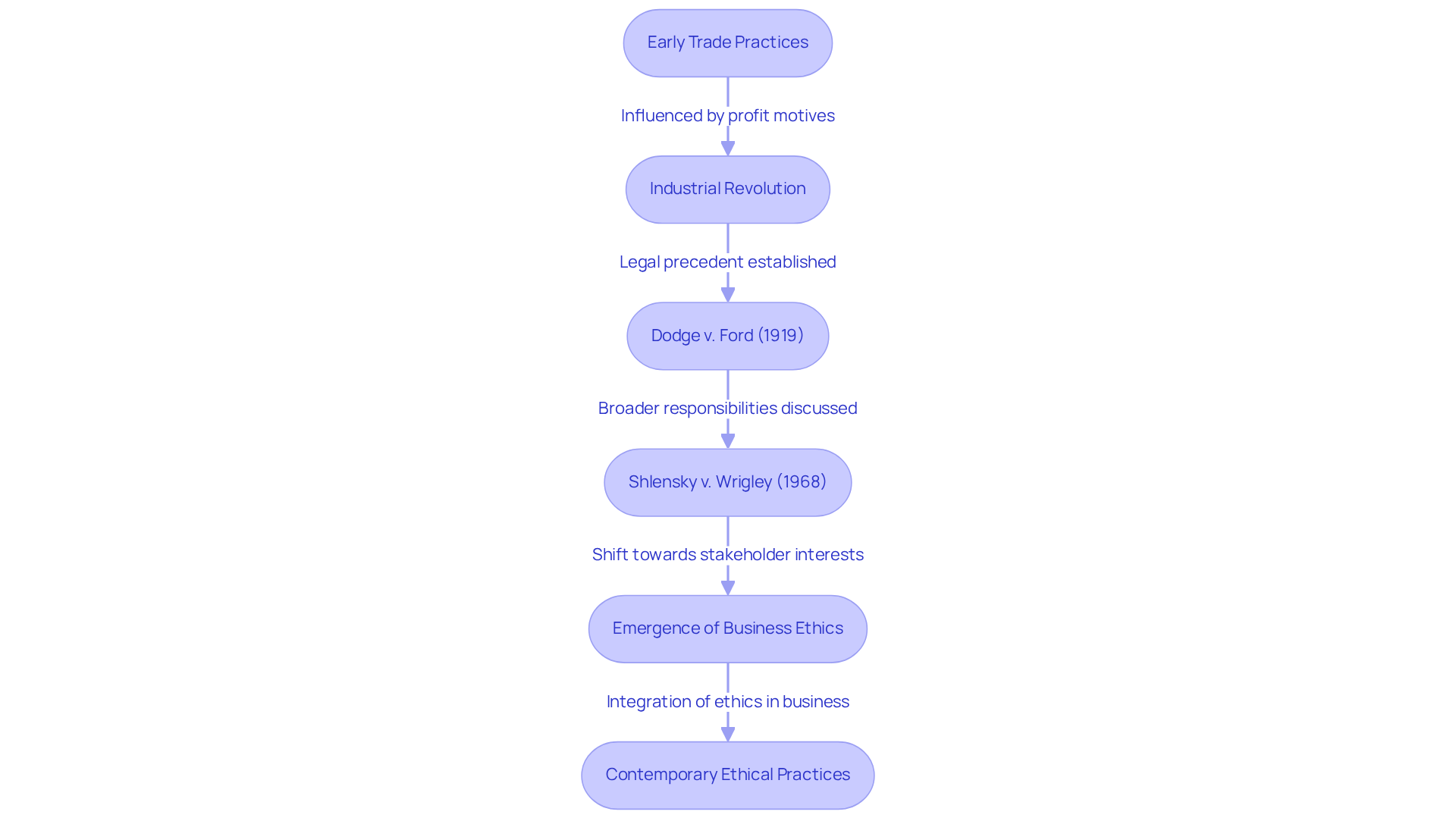
The evolution of commerce principles can be traced back to the early days of trade, where moral considerations were often overshadowed by profit motives. However, significant events—such as the Industrial Revolution and the rise of corporate social responsibility in the late 20th century—have profoundly transformed the landscape of business ethics, particularly through a stakeholder and issues management approach. The Industrial Revolution, which commenced in the late 18th century, introduced mass production and corporate frameworks that prioritized efficiency and profit, frequently at the expense of ethical practices. This era witnessed a surge in labor exploitation and environmental degradation, prompting early calls for ethical reform.
By the 1960s, a pivotal shift emerged as societal values began to emphasize accountability and transparency. Landmark cases, such as Dodge v. Ford Motor Company (1919), established the legal precedent that corporations must operate in the interests of their shareholders. Yet, this also ignited discussions regarding broader responsibilities to diverse stakeholders from the perspective of business ethics a stakeholder and issues management approach. The 1968 case of Shlensky v. Wrigley further expanded the understanding of corporate governance, allowing boards to consider stakeholder interests alongside profit.
As the late 20th century approached, the emergence of business ethics a stakeholder and issues management approach became a defining characteristic of ethical practices. Businesses began to recognize the importance of principled practices, not only for compliance but also for building trust with consumers. This shift was underscored by the fact that U.S. companies now invest over $70 billion annually in ethics training, reflecting a commitment to fostering a culture of integrity.
Today, companies are increasingly required to meet elevated moral benchmarks, influenced by consumer demand for responsible practices and regulatory pressures. The fallout from scandals, such as the LIBOR scandal and the Volkswagen emissions scandal, has underscored the severe consequences of unethical behavior, costing billions in fines and damaging reputations. Understanding this historical context is essential for organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of contemporary practices through a business ethics a stakeholder and issues management approach and align their actions with evolving societal expectations. Moving forward, the integration of ethical considerations into business strategies will be crucial for sustainable success.
Conclusion
Business ethics, particularly through a stakeholder and issues management approach, is essential for fostering a culture of integrity and trust within organizations. By prioritizing moral principles such as honesty, fairness, and responsibility, businesses not only enhance their reputations but also pave the way for sustainable growth and success. The commitment to ethical practices serves as a foundation for building lasting relationships with stakeholders, ultimately benefiting both the organization and the communities it serves.
The article highlights several key arguments that reinforce the importance of business ethics. Notable examples, such as Patagonia and Starbucks, demonstrate how principled leadership can lead to tangible business benefits, including increased sales and employee satisfaction. Furthermore, the proactive engagement with stakeholders allows organizations to navigate ethical challenges more effectively, reducing risks and improving overall decision-making. The historical evolution of business ethics underscores the growing expectation for companies to act responsibly in today's marketplace, illustrating the necessity of adapting to societal demands.
Reflecting on these insights, it becomes clear that integrating business ethics into corporate strategies is not merely a compliance measure but a vital component of long-term success. Organizations are encouraged to embrace ethical leadership and stakeholder engagement as essential practices that can drive innovation, enhance employee morale, and ultimately lead to greater financial performance. As the landscape of business continues to evolve, prioritizing ethical considerations will be crucial for those looking to thrive in an increasingly conscientious marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are business ethics?
Business ethics refers to the moral principles and standards that guide corporate behavior, influencing the values that govern both individual and organizational actions.
What are the core principles of business ethics?
The core principles of business ethics include integrity, honesty, fairness, respect, and responsibility.
Why are business ethics important?
Business ethics are important because they foster trust among stakeholders, enhance a company's reputation, attract loyal clients, reduce legal risks, and contribute to long-term success and sustainability.
Can you provide examples of companies that practice strong business ethics?
Yes, Patagonia's commitment to responsible practices led to a 70% increase in sales, while Starbucks experienced improved employee satisfaction and customer loyalty due to its principled leadership.
What are the benefits of having a strong moral culture in an organization?
Organizations with a robust moral culture experience 38% fewer misconduct incidents and generate 2.5 times more revenue than those with weaker ethical standards.
How does sustainability impact financial performance?
Firms in the S&P 500 index that focus on sustainability have outperformed those that do not by 25%, highlighting the financial advantages of responsible practices.
How do employees view a company's reputation for social responsibility?
Research shows that 93% of workers consider a firm's reputation for social responsibility essential when choosing a workplace, and 64% believe principled leadership affects their likelihood of staying with the organization.
What is the relationship between business ethics and sustainable growth?
By adopting a stakeholder and issues management approach to business ethics, companies can build trust, enhance their reputation, foster loyalty, and position themselves for sustainable growth.




