Introduction
The susceptibility of small businesses to fraud is a pressing concern, given the complexity of fraudulent schemes and their potentially devastating impact. Detection often lags, with companies taking an average of 14 months to recognize fraud, and a staggering 54% never recuperating their losses. Frauds can range from cyber-attacks to internal embezzlement, each carrying risks such as financial loss, reputational harm, and erosion of customer trust—outcomes particularly crippling for small enterprises that may already be resource-constrained.
The evolving cyber threat landscape further illustrates the urgency for vigilance; the 2023 Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report highlights a consecutive four-year rise in cyberattacks, with 53% of businesses falling victim in the past year. Notably, small businesses with under ten employees saw attack rates jump from 23% to 35% in just three years. The median cost of these attacks exceeded $16,000, with some incidents threatening the survival of the affected businesses.
In response to these threats, small businesses are turning to technological solutions and advanced risk management strategies to bolster their defenses. Implementing secure payment gateways and staying informed about the signs of fraud are crucial steps in proactively protecting a business's financial integrity. Moreover, this proactive approach is vital when considering the harsh reality that many small business owners erroneously believe their size makes them an unlikely target for cybercriminals, a misconception that often leaves them more vulnerable to scams and fraudulent activities.
Vulnerabilities of Small Businesses to Fraud
The susceptibility of is a pressing concern, given the complexity of fraudulent schemes and their potentially devastating impact. Detection often lags, with companies taking an average of 14 months to recognize fraud, and a staggering 54% never recuperating their losses. Frauds can range from cyber-attacks to internal embezzlement, each carrying risks such as , reputational harm, and erosion of customer trust—outcomes particularly crippling for small enterprises that may already be resource-constrained.
The evolving further illustrates the urgency for vigilance; the 2023 Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report highlights a consecutive four-year rise in cyberattacks, with 53% of businesses falling victim in the past year. Notably, with under ten employees saw attack rates jump from 23% to 35% in just three years. The median cost of these attacks exceeded $16,000, with some incidents threatening the survival of the affected businesses.
In response to these threats, small businesses are turning to technological solutions and advanced risk management strategies to bolster their defenses. Implementing secure payment gateways and staying informed about the signs of fraud are crucial steps in proactively protecting a business's financial integrity. Moreover, this proactive approach is vital when considering the harsh reality that many small business owners erroneously believe their size makes them an unlikely target for cybercriminals, a misconception that often leaves them more vulnerable to scams and fraudulent activities.
Common Fraud Schemes in Small Businesses
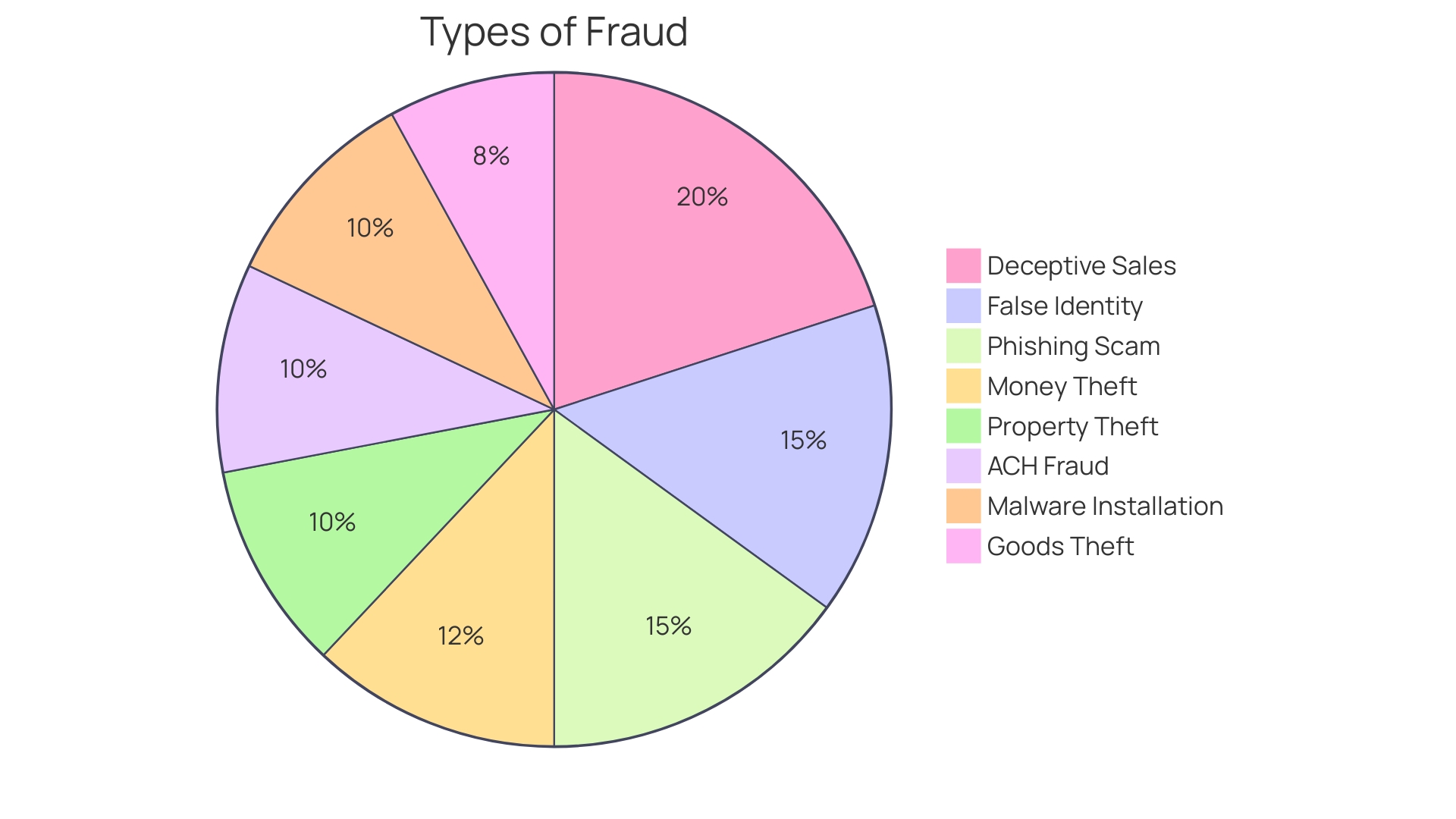
Small businesses are increasingly becoming the targets of sophisticated fraud schemes. Instances where individuals receive mysterious emails or unexpected shipments, like the case where a business owner was contacted by the RCMP, are not isolated. These occurrences often signal deeper fraudulent activities.
In April 2023, such an incident involved confusing emails and shipments from Walmart despite the orders being placed on Amazon, raising suspicion and prompting police involvement. The scams don't stop there. The offers support, but businesses must stay vigilant about where and how they seek assistance, especially post-disaster when fraudulent actors might take advantage of the chaos.
Scammers are becoming more cunning, using tactics that might catch many off guard. A business news editor shares a valuable lesson from falling victim to an online scam, emphasizing the need for businesses to educate themselves and their clients about potential threats. These scams are not rare occurrences; according to the Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report, the number of for four years, with 53% of businesses experiencing at least one in the last year.
The median cost of these attacks is a staggering $16,000, and for 21% of affected businesses, the viability of their operations was put at risk.
To safeguard against these threats, businesses must adopt a . Verification of unusual requests is paramount. A simple phone call can deter a potential fraud attempt.
Awareness of red flags, like mismatched phone numbers, is crucial. Furthermore, implementing a credit freeze and reporting to local law enforcement are key steps in responding to fraud, as well as creating a personal recovery plan.
Understanding the digital banking transaction process, such as chargebacks, is also essential. When disputes arise between customers and businesses, banks often side with the customer, underscoring the importance of . Small businesses must be proactive in protecting themselves, leveraging resources like those provided by SophosLabs, and staying informed about the latest fraud terms and tactics to ensure they are not the next victims of deceit.
Case Study: The Trusted Employee at Acme Tractor
The narrative of Acme Tractor's experience with internal fraud exposes the often-overlooked reality that fraudulent activities can persist undetected within a company for extended periods. The event at Acme Tractor, where a seemingly reliable employee manipulated the system, highlights a significant issue: the necessity for effective . This case study is not isolated, as more than half of are attributed to inadequate internal measures or the deliberate circumvention of the ones in place.
Through the lens of the 2024 Report to the Nations, we gain insight into the typical profile of a fraudster, which includes their rank, duration of employment, and their preferred methods of concealing fraudulent actions. This report also underscores the growing importance of technology and data analytics in detecting fraud, a stark contrast to the conventional means of discovery.
Recent news stories reflect the pervasive nature of occupational fraud. For instance, a payroll accountant in Ohio embezzled an astonishing $26 million, and a manager at MGM Grand Resorts International is accused of making fraudulent transactions totaling 309 refunds to his own credit card over a year. These incidents demonstrate the far-reaching consequences of fraud and the critical need for businesses to safeguard their operations with robust anti-fraud controls.
The statistics are sobering: pilferage and theft account for around 25% of in India, with being particularly vulnerable due to less stringent controls. The lasting impact of fraud on profitability and trust within an organization cannot be overstated.
It is essential to heed the words of industry leaders who emphasize the dire consequences of cyber attacks and the importance of as a high-level risk. With the evolution of cyber threats, establishing a is not just advisable; it is imperative for the protection and resilience of any organization.
In conclusion, the Acme Tractor case serves as a stark reminder of the consequences of complacency in the face of fraud. It urges businesses to adopt a security-first approach, ensuring that anti-fraud controls are not only present but also ingrained in the corporate culture, thereby fortifying their defenses in an era where the sophistication of fraudulent schemes continues to escalate.
Motivations and Rationalizations for Fraud
Dissecting the psychology behind small business fraud not only sheds light on the issue but also empowers companies to erect stronger safeguards. , perceived opportunities to deceive, and self-justifications are common psychological triggers that lead individuals down the path of deceit. For instance, an entrepreneur might inflate store activity to impress an investor, blurring the lines between shrewd marketing and deception.
Such actions may seem innocuous but can escalate into more serious fraud. are paramount, as the Report to the Nations on Occupational Fraud and Abuse reveals that over half of all fraud cases stem from inadequate or overridden controls. Technology also plays a pivotal role in detection, with data analytics becoming increasingly crucial in uncovering fraudulent schemes.
further uncovers that typically, fraudsters are not new hires but seasoned employees who exploit their deep understanding of company systems. , which constitute a staggering 33.2 million entities in the United States alone, must be especially vigilant, as they might incorrectly assume their size makes them less of a target. However, the Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report indicates that cyberattacks on businesses have risen for four years in a row, with 53% experiencing at least one attack over the past year, and a notable 35% attack rate for companies with fewer than ten employees.
Proactive measures and continuous education are essential in safeguarding the livelihood of small businesses.
Preventive Measures Against Small Business Fraud
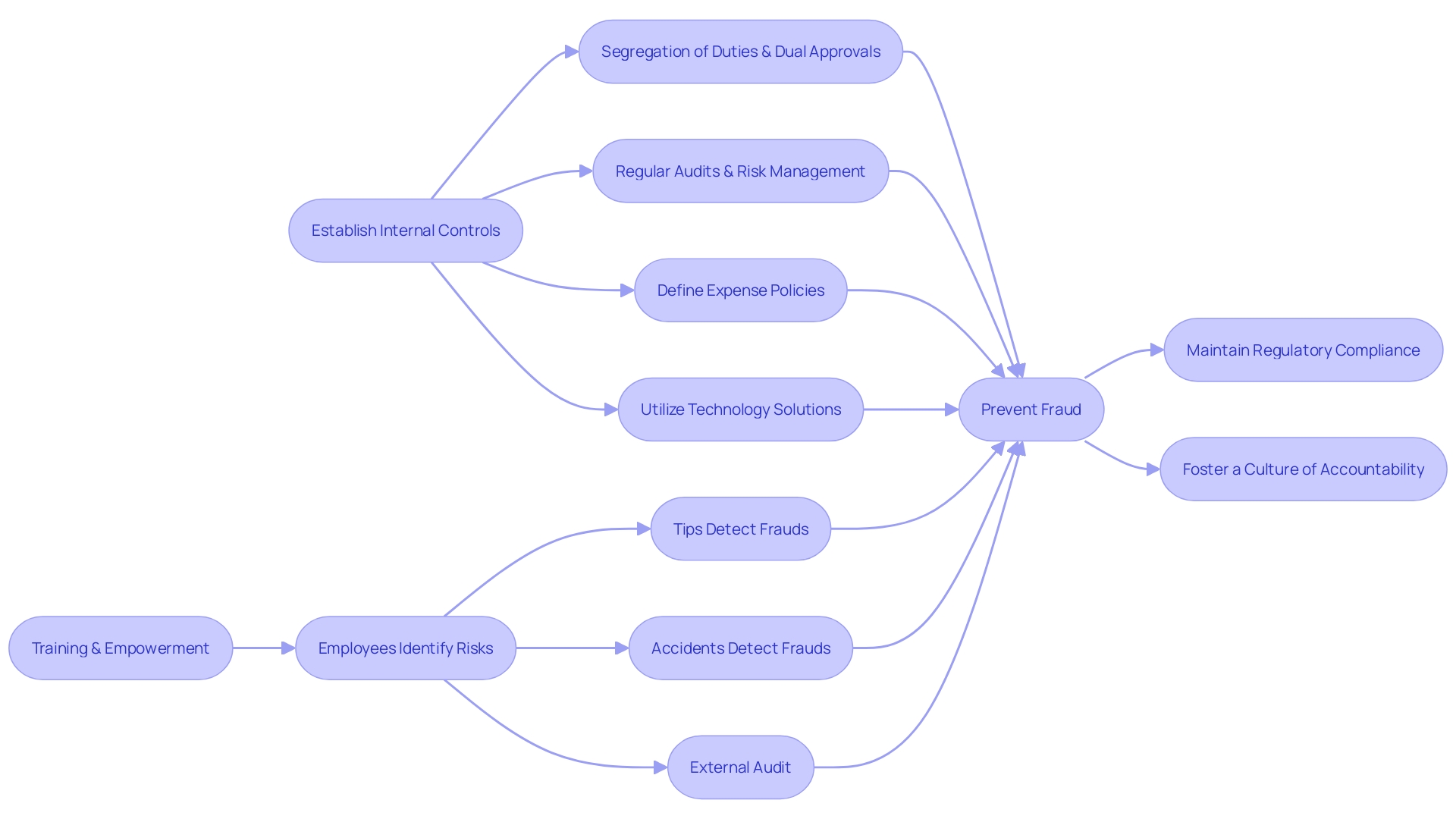
To effectively combat the multifaceted challenge of , it's crucial to before the threat manifests. With an astounding 54% of businesses failing to recover losses post-fraud and an average detection time of 14 months, proactivity is not just beneficial—it's essential. Start by fortifying your with a secure payment gateway to thwart ACH fraud, ensuring that customer data is encrypted and safeguarded from unauthorized access.
A clear expense policy is another cornerstone of fraud prevention. By outlining what constitutes a legitimate business expense and requiring documented proof for reimbursements, you'll not only minimize misunderstandings but also deter deliberate deceit. Advanced technologies and also play a vital role in detecting and preventing fraud, offering small businesses a fighting chance against potential revenue loss, reputational damage, and the erosion of customer trust.
In addition to technology, embrace regular audits and encourage a where employees feel safe to report suspicious activities through mechanisms like whistleblower hotlines. These measures are not just preventive—they're a declaration of your and the long-term viability of your business.
Importance of Internal Controls and Audits
and audits are essential instruments in the fight against fraud, a threat that can linger undetected for months and inflict lasting damage to a business's finances and reputation. Small businesses, with their limited capacity to absorb such shocks, are particularly vulnerable. The complexity of fraud, ranging from pilferage to sophisticated financial manipulations, necessitates a proactive approach to prevention.
Establishing internal controls such as segregation of duties and dual approvals, and ensuring , are cornerstones of an effective defense strategy. Segregation of duties prevents concentration of power and reduces the risk of unauthorized transactions, while dual approvals serve as an additional layer of verification. Regular audits, conducted with a focus on risk management, operational efficiency, and compliance, help to identify and rectify gaps in controls and non-compliance areas.
Moreover, clear expense policies and the use of technology can streamline processes and reduce opportunities for fraud. Policies should define legitimate expenses and require documentation such as receipts, which aids in the verification process during audits. Technological solutions like corporate card programs provide real-time data that is harder to manipulate, offering another line of defense.
To underscore the importance of internal controls, consider the requirement under the and as a component of best practices compliance programs. Effective internal controls not only help in maintaining regulatory compliance but also instill a culture of accountability throughout the organization.
Monitoring Employee Behavior and Lifestyle
Strengthening internal protocols to identify fraud starts with recognizing that behind every deceptive act is an individual or group with ill intentions. It's not just about the transactions themselves but about understanding the behaviors and patterns of those who perpetrate fraud. For instance, Chime's Risk Analysis team is dedicated to scrutinizing data trends to pinpoint patterns indicative of fraudulent transactions.
Similarly, in the case of Journey Bank, the focus is on , with an emphasis on education to preempt scams.
Education is indeed a powerful tool in . As per the 2022 A Report to the Nations by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, are detected through tips, predominantly reported by employees. This underscores the value of that are not just generic but tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of staff members.
Such training equips employees to spot risks and irregularities, such as unexplained wealth or atypical , and take appropriate action.
Moreover, it's crucial to acknowledge the psychological impact of electronic monitoring on employees. Intense scrutiny can induce stress, reduce autonomy, and foster job insecurity, with 56% of monitored workers reporting tension compared to 40% of their non-monitored counterparts. While monitoring can be an essential component of , it must be balanced with the mental well-being of employees.
In the realm of e-commerce, anomaly detection is key. This involves identifying patterns or data points that stray from the norm, like unusual transaction amounts or irregular purchasing behaviors. Anomalies could signal fraudulent activities such as identity theft or credit card fraud, necessitating businesses to invest in security measures, fraud detection systems, and, importantly, to safeguard against these risks.
Consequences of Fraud and Importance of Zero Tolerance
Fraudulent activities can have significant consequences for , impacting them both financially and legally. When considering the gravity of these outcomes, businesses must recognize that can lead to detrimental consequences, including substantial and potential legal actions. A proactive stance against fraud is essential, which is why implementing a can serve as a powerful deterrent to would-be fraudsters.
For instance, in the realm of digital banking, the simplicity of issuing chargebacks highlights the ease with which customers can contest transactions they believe to be fraudulent. If a cardholder dispute escalates to a bank chargeback, it often results in the bank siding with the customer, underscoring the importance of maintaining vigilant transaction oversight.
Education plays a crucial role in fraud prevention, with tailored enabling employees to recognize and report potential risks. According to the 2022 A Report to the Nations by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, 42% of frauds were detected by tips, with over half being reported by employees. This demonstrates the value of well-informed staff as a frontline defense against fraud.
The rise in fraudulent attempts is also a concern, with over two-thirds of businesses noting an increase in consumer account fraud, and just over half reporting the same for business accounts. The direct cost of fraud is not negligible, with nearly 60% of banks, fintechs, and credit unions reporting over $500K in direct fraud losses in 2023 alone.
Prominent cases, such as the high-profile trials of Elizabeth Holmes and Sam Bankman-Fried, emphasize the perils of the 'fake it till you make it' approach, as highlighted by US Attorney Damian Williams. His warning to startup founders and corporate executives is clear: fraud will result in severe penalties.
Ensuring are vital, as Mike Walters, President of Business Banking at KeyBank, points out. Small businesses, often the backbone of local communities, need to be proactive in safeguarding against fraudulent activity to protect their contributions to society and the economy.
In light of this, companies are urged to establish and training programs, as these measures are not just about protecting the business itself, but also about preserving trust and integrity within the communities they serve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, small businesses are highly vulnerable to fraud, with potentially devastating consequences. Detection often lags, and many businesses never recover their losses. The evolving cyber threat landscape further underscores the urgency for vigilance, as cyberattacks continue to rise, particularly targeting small businesses.
To protect against fraud, small businesses must take proactive measures. Implementing secure payment gateways and staying informed about the signs of fraud are crucial steps in safeguarding financial integrity. It is essential to dispel the misconception that small businesses are unlikely targets for cybercriminals, as they are increasingly becoming victims.
A comprehensive prevention strategy is vital. This includes fortifying financial transactions with secure payment gateways, establishing clear expense policies, and adopting advanced technologies and risk management strategies. Regular audits, transparency, and employee education are also key components of an effective anti-fraud approach.
Internal controls and audits play a crucial role in detecting and preventing fraud. Segregation of duties, dual approvals, and regular audits help identify gaps in controls and reduce the risk of unauthorized transactions. By establishing effective internal controls, businesses foster a culture of accountability.
Understanding the behaviors and patterns of fraud perpetrators is essential. Tailored training programs equip employees to recognize and report potential risks. Monitoring employee behavior must be balanced with their well-being.
The consequences of fraud for small businesses are significant, impacting finances and legal standing. Implementing a zero-tolerance policy deters fraudsters, and education plays a crucial role in prevention. Businesses must be proactive in safeguarding against fraudulent activity.
In conclusion, by implementing comprehensive prevention strategies, strengthening internal controls, and fostering a culture of vigilance, small businesses can protect their financial integrity and preserve trust within their communities.
Take action now to protect your business from fraud!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are small businesses particularly vulnerable to fraud?
Small businesses are especially susceptible to fraud due to their limited resources, the complexity of fraudulent schemes, and a common misconception that their size makes them unlikely targets. This vulnerability can result in significant financial loss, reputational harm, and erosion of customer trust.
How long does it typically take for businesses to detect fraud?
On average, it takes companies about 14 months to recognize fraudulent activities.
What is the Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report, and what does it indicate about cyberattacks on small businesses?
The Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report is an annual analysis that has shown a four-year consecutive rise in cyberattacks, with 53% of businesses experiencing an attack in the past year. Notably, small businesses with fewer than ten employees have seen an increase in attack rates from 23% to 35% in three years.
What are some common fraud schemes targeting small businesses?
Common fraud schemes include cyber-attacks, internal embezzlement, confusing emails, unexpected shipments, post-disaster scams, and more sophisticated online scams.
What was the median cost of these attacks on small businesses, and how did they affect operations?
The median cost of cyberattacks on small businesses exceeded $16,000, with some incidents threatening the survival of the businesses affected.
How can small businesses protect themselves against fraud?
Small businesses can protect themselves by implementing secure payment gateways, staying informed about signs of fraud, verifying unusual requests, and having a clear understanding of digital banking transactions. It's also important to implement a credit freeze when necessary and create a personal recovery plan.
What are internal controls, and how do they help prevent fraud?
Internal controls are processes and procedures put in place to help manage risk and prevent fraud, such as segregation of duties, dual approvals, and regular audits. They are essential in detecting and rectifying any gaps in controls and ensuring regulatory compliance.
How important are audits for small businesses?
Audits are crucial as they provide an in-depth examination of a company's records and can identify gaps in internal controls, areas of non-compliance, and potential fraudulent activities.
What role does employee monitoring play in fraud prevention?
Employee monitoring can help identify suspicious behaviors and transaction patterns indicative of fraud. However, the psychological impact of intense scrutiny on employees must be balanced with the mental well-being of staff.
What are the consequences of fraud for small businesses, and why is a zero-tolerance policy important?
Fraud can lead to substantial financial losses, legal consequences, and damage to a business's reputation. A zero-tolerance policy towards fraud acts as a powerful deterrent and demonstrates a commitment to ethical business practices.
What can businesses do to improve fraud detection and prevention?
Businesses can adopt a multi-layered approach to security, educate employees and clients about potential threats, and invest in advanced technologies and risk management strategies. Regular training programs and encouraging a culture of transparency and reporting are also key steps in fraud prevention.
Why is cybersecurity particularly important for small businesses?
Cybersecurity is essential for small businesses because the evolving cyber threat landscape poses significant risks that can disrupt operations, lead to financial losses, and damage customer trust. Establishing a strong cybersecurity program helps protect against these threats and ensures business resilience.




