Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of change management, understanding stakeholder dynamics is not just beneficial—it's essential. Stakeholder analysis emerges as a critical tool, empowering organizations to identify and evaluate the interests and influences of those who can impact or be impacted by change initiatives.
By strategically engaging stakeholders—ranging from employees to customers—businesses can:
- Tailor their approaches
- Mitigate risks
- Enhance the likelihood of successful transformations
With data indicating that poorly managed change can drain substantial revenue and productivity, the importance of a structured stakeholder engagement strategy becomes clear. This article delves into the intricacies of stakeholder analysis, offering a step-by-step guide, highlighting the significance of engagement, and providing practical solutions to common challenges.
By adopting a data-driven mindset and leveraging effective tools, organizations can navigate the complexities of change with confidence, ensuring that every voice is heard and every opportunity for success is seized.
Understanding Stakeholder Analysis in Change Management
Stakeholder analysis in organizational change management serves as an essential framework for identifying and assessing the influence and interests of individuals or groups that may affect or be affected by an entity's transformation initiatives. In the field of transformation management, stakeholder analysis in organizational change management is crucial; it allows entities to tailor their strategies efficiently. Key participants often include:
- Employees
- Management
- Customers
- Suppliers
- The wider community
By utilizing stakeholder analysis in organizational change management to classify interested parties based on their degrees of influence and concern, organizations can prioritize their involvement efforts, ensuring that the most vital viewpoints are recognized and tackled throughout the transformation process. According to recent findings, transformation initiatives that fail can drain 6-10% of annual revenue, while employee resistance may result in a staggering 30% loss in productivity. Conversely, successful transformations can yield an impressive average return on investment of 500%.
Our pragmatic approach involves continuous business performance monitoring and real-time analytics to test every hypothesis, allowing for strategic decision-making that maximizes returns on invested capital. This data-driven approach is essential in creating a collaborative plan to mitigate weaknesses and reinvest in strengths. Additionally, investing in employee training and development can also lower operational expenses by 15%, highlighting the significance of participant involvement and training in management transitions.
Consequently, dedicating time to stakeholder analysis in organizational change management not only reduces risks linked to transformation but also boosts the likelihood of successful results, as organizations with strong communication cultures see a 23% rise in profitability. The outcomes of the party analysis should guide and enhance transition planning and execution, followed by a comprehensive assessment of the procedure and results to ensure ongoing enhancement.
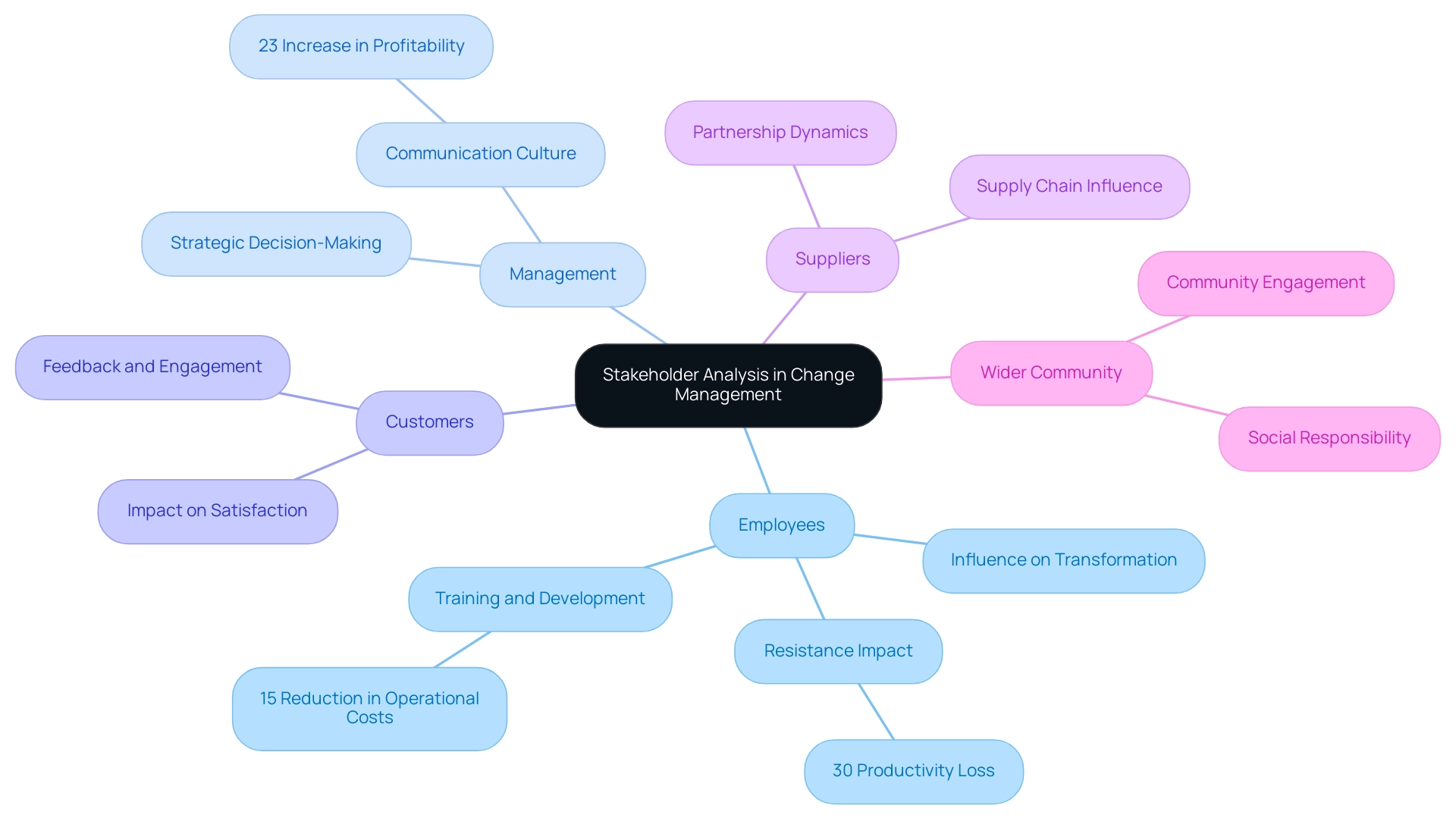
Step-by-Step Process for Conducting Stakeholder Analysis
- Identify Stakeholders: Start by compiling a comprehensive list of all individuals and groups who may be affected by or who could influence the stakeholder analysis in the organizational change management process. This list should encompass both internal parties, such as employees and management, and external entities, including customers and suppliers. Understanding the complete range of participants is essential for effective stakeholder analysis in organizational change management. For instance, successful companies like Canva have demonstrated the impact of engaging with interested parties, as evidenced by their achievement of tripling creative output to produce 60,000 ads in less than a year.
- Categorize Interested Parties: Implement a structured framework to categorize interested parties according to their levels of influence and interest. Utilizing a Power/Interest Grid is a valuable tool for visualizing the positions of involved parties. This approach facilitates a clear comprehension of which parties need more focus based on their potential influence on the transformation process.
- Stakeholder analysis in organizational change management involves conducting a thorough evaluation of how each interested group might be affected by the change and their corresponding influence on the initiative. This assessment guides your interaction strategy, helping to prioritize efforts where they will be most effective. It is crucial to avoid common mistakes in stakeholder analysis in organizational change management, such as only conducting it at the start or using a single mapping method, which can undermine the effectiveness of your strategy.
- Develop Involvement Techniques: Customize particular involvement techniques for each group category. High-power, high-interest parties should receive regular updates and be actively involved in decision-making processes. On the other hand, low-power, low-interest parties may need less frequent communication, but maintaining some degree of involvement is still essential to ensure they stay informed and supportive. As David Hartshorne, Owner of Azahar Media, noted, effective interaction can lead to significant outcomes, as seen in their removal of 657 manual actions.
- Observe and Modify: As the transformation initiative progresses, it’s essential to consistently track participant attitudes and perceptions. Consistently evaluate participation strategies to adjust to any changes in supporter backing or new issues. This dynamic approach not only fosters ongoing support but also mitigates potential resistance, ensuring the initiative’s success.
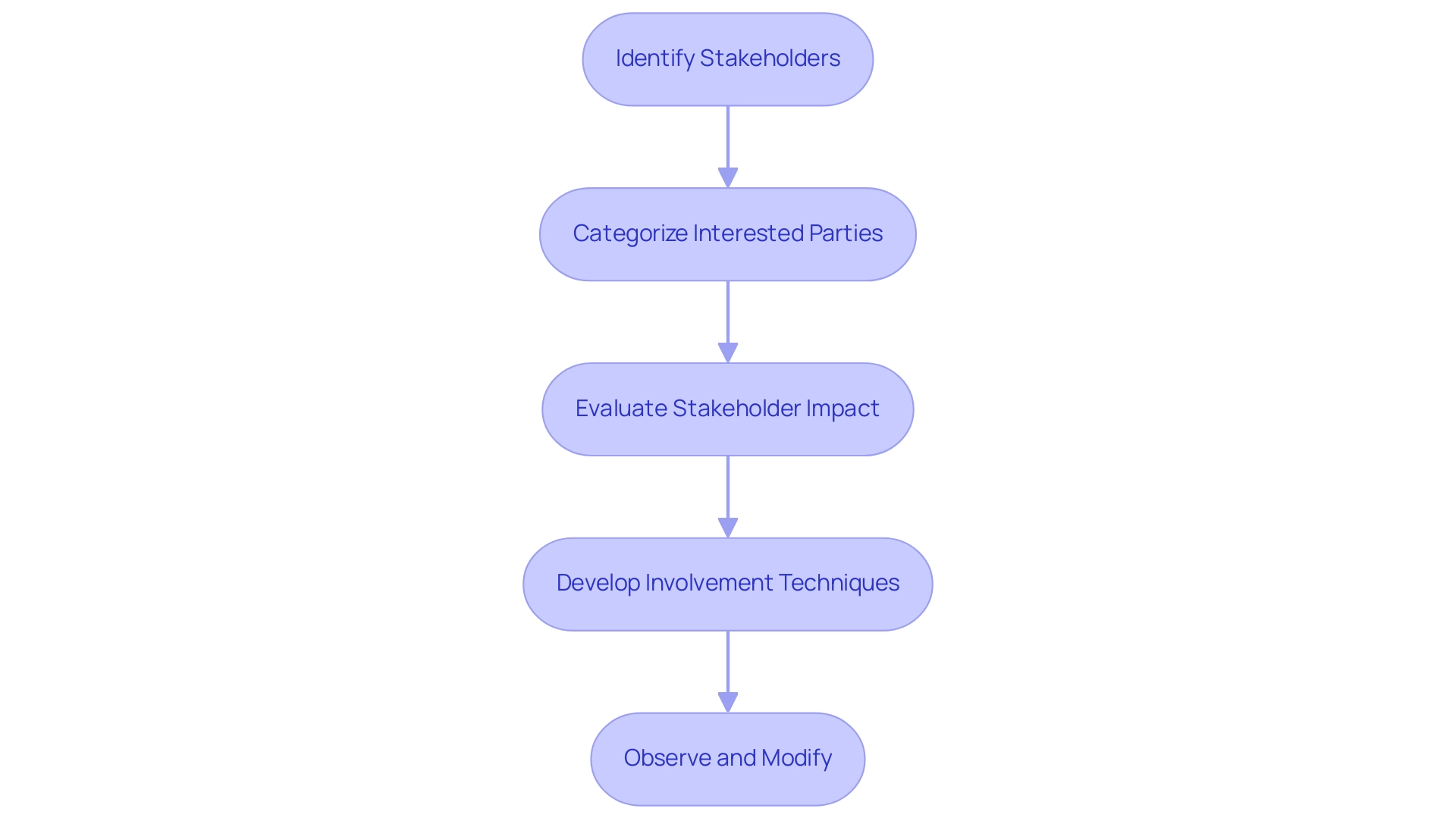
The Importance of Stakeholder Engagement in Change Initiatives
In stakeholder analysis in organizational change management, involving interested parties is pivotal, as it not only builds trust but also cultivates a sense of ownership among those affected by the transition. Studies show that companies that focus on involving their participants can achieve a 10% increase in employee retention, especially in the technology sector. This engagement process allows entities to perform stakeholder analysis in organizational change management, enabling them to gather valuable feedback that informs decision-making and aids in identifying potential resistance early on.
By conducting a stakeholder analysis in organizational change management and engaging interested parties in the transition process, companies can cultivate supporters who promote the initiative, thereby greatly improving its chances of success. As noted, by developing strategies for each group, entities can gain the most from their participants. Consistent communication, openness, and requesting feedback are vital practices in stakeholder analysis in organizational change management that strengthen involvement and enable smoother transitions during times of transformation.
Moreover, comprehending the eight essential elements that aid in sustaining support from involved parties during the transition process is vital for effective stakeholder analysis in organizational change management to tackle challenges efficiently. Employing sentiment analysis enables organizations to assess the emotional tone of participant reactions, offering insights that can inform interaction strategies. Establishing mechanisms for continuous feedback not only shows that contributions are valued but also reinforces their role in shaping the change process.
This practice, as emphasized in the case study on continuous feedback and adaptation, demonstrates that regularly conveying how feedback influences decisions promotes ongoing participant engagement, ultimately resulting in sustained support and successful outcomes.
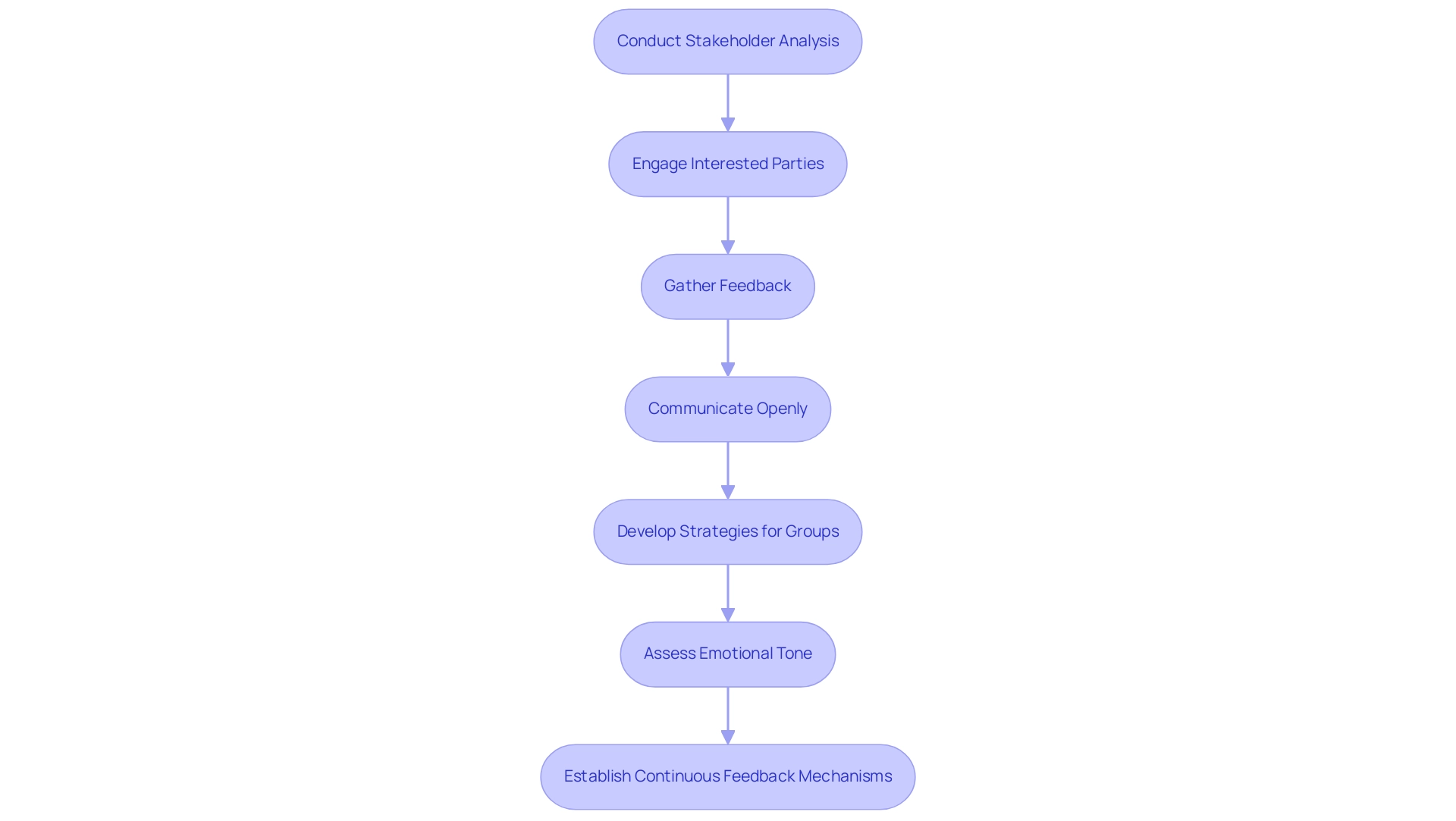
Challenges and Solutions in Stakeholder Analysis
Navigating the complexities of stakeholder analysis in organizational change management presents several challenges, including the identification of relevant individuals, management of conflicting interests, and the need for effective communication. To address these challenges effectively:
- Comprehensive Identification: Conduct brainstorming sessions and participant mapping workshops to ensure no voice is overlooked. Engaging diverse perspectives early on is crucial for effective stakeholder analysis in organizational change management, which will help you build a robust participant database.
- Conflict Resolution: Establish clear communication channels to facilitate discussions aimed at resolving conflicting interests as soon as they arise. This proactive approach incorporates stakeholder analysis in organizational change management, reducing risks and promoting a collaborative environment.
- Effective Communication: Tailor your communication strategies to the unique interests of various groups. Ensure that your messages are clear and relevant. Regular updates and feedback loops are essential for effective stakeholder analysis in organizational change management to maintain engagement and address concerns proactively. As Tony Cole, founder of the Anthony Cole Training Group, emphasizes, assertive, client-focused communication not only clarifies expectations but also builds trust, ultimately enhancing engagement with interested parties. Furthermore, it is critical to establish and follow clear and consistent policies and procedures for data collection and usage as part of the stakeholder analysis in organizational change management. This transparency is vital for effective management of those involved. Furthermore, entities can gain insights from case studies, such as the one titled 'Be Ready When Conditions Change.' This case study examines various potential scenarios to adjust resource allocations efficiently, illustrating how modeling and evaluating these options can assist businesses in managing participant dynamics with agility. By preparing for different future scenarios, companies can better handle conflicting interests and improve their overall strategy for involving interested parties.
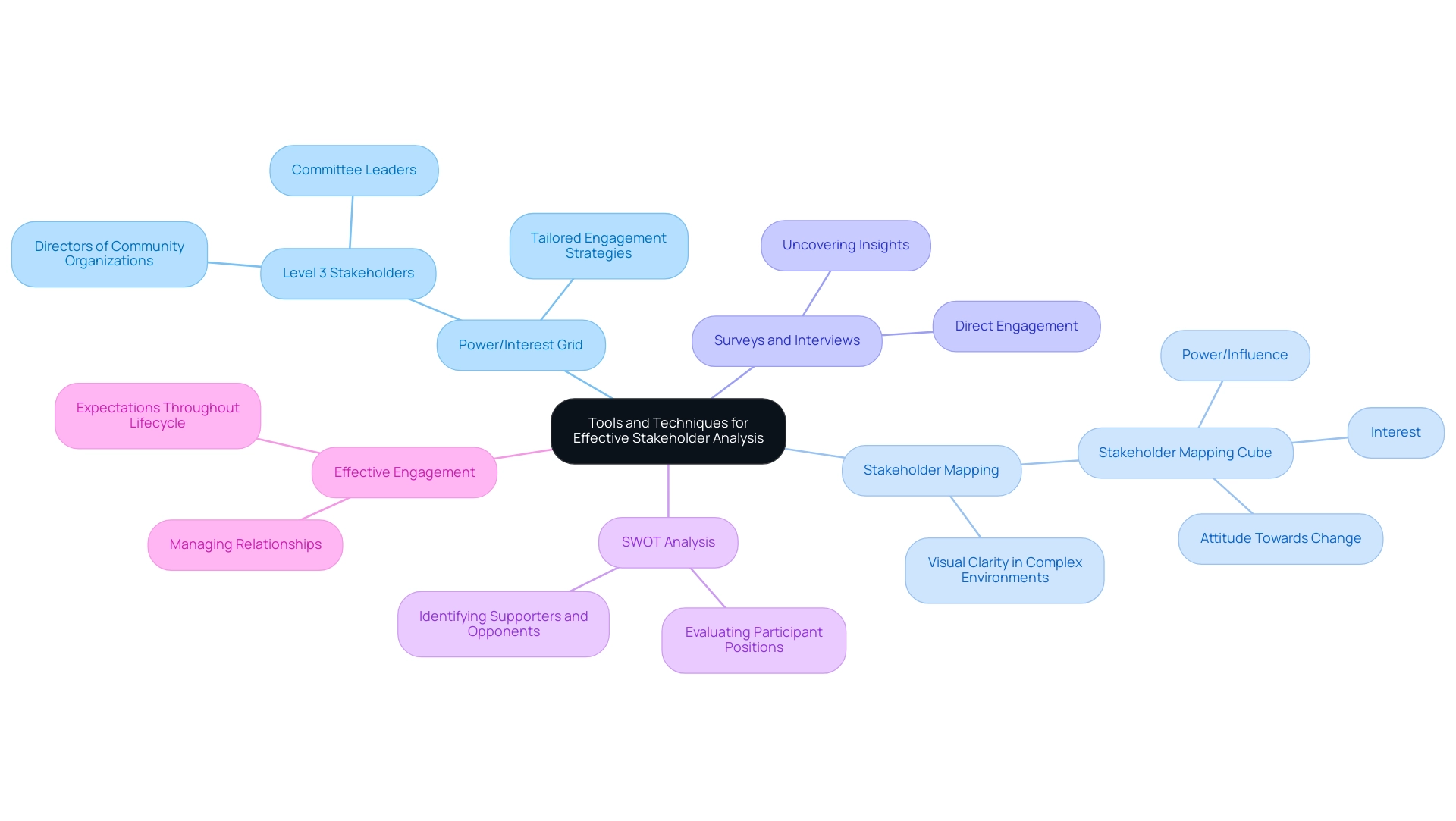
Tools and Techniques for Effective Stakeholder Analysis
To effectively engage stakeholders in change management, several proven tools and techniques can be employed:
- Power/Interest Grid: This essential tool categorizes stakeholders based on their power and interest levels, enabling CFOs to tailor engagement strategies that resonate with each group's unique dynamics. For instance, understanding that Level 3 Stakeholders include directors of community organizations and committee leaders, who are updated annually, can inform targeted communication efforts.
- Stakeholder Mapping: Utilizing visual mapping techniques offers clarity in complex environments by illustrating the relationships and influence among participants, simplifying the decision-making process. The Stakeholder Mapping Cube, a three-dimensional model that considers power/influence, interest, and the individual's attitude towards the transformation initiative, allows for a nuanced analysis of participant relationships, capturing their complexities effectively.
- Surveys and Interviews: Engaging directly with participants through surveys and interviews can uncover valuable insights regarding their concerns and expectations, fostering a collaborative environment.
- SWOT Analysis: Conducting a SWOT analysis allows leaders to evaluate participant positions while recognizing potential supporters or opponents in the transformation process. This strategic approach can significantly enhance the effectiveness of involvement efforts.
As Patrick, who has led significant infrastructure projects globally for the past twenty years, observes, "Effective involvement of interested parties is essential for the success of any transformation initiative." By leveraging these tools, CFOs can streamline stakeholder analysis, ensuring informed decision-making and effective communication throughout the change initiative.
Conclusion
Engaging stakeholders is not merely a checkbox in the change management process; it is a strategic imperative that can determine the success or failure of transformation initiatives. Through a structured stakeholder analysis, organizations can identify and prioritize the interests and influences of those involved, ensuring that every voice is acknowledged. By categorizing stakeholders and tailoring engagement strategies, companies can effectively mitigate risks and enhance the potential for successful change.
The article outlines a comprehensive step-by-step approach to conducting stakeholder analysis, emphasizing the importance of continuous monitoring and adaptation. By fostering a culture of open communication and collaboration, organizations can build trust and cultivate advocates for their change initiatives. This proactive engagement not only reduces resistance but also amplifies support, ultimately leading to improved outcomes.
In an environment where change is constant, investing in stakeholder analysis is essential for navigating complexities and achieving strategic objectives. By employing effective tools and techniques, organizations can enhance their stakeholder engagement efforts, ensuring that they are well-equipped to meet challenges head-on. The takeaway is clear: successful change management hinges on understanding and valuing stakeholder dynamics, paving the way for transformative growth and sustained profitability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of stakeholder analysis in organizational change management?
Stakeholder analysis serves as a framework for identifying and assessing the influence and interests of individuals or groups that may affect or be affected by an entity's transformation initiatives, allowing organizations to tailor their strategies effectively.
Who are the key participants in stakeholder analysis for organizational change management?
Key participants typically include employees, management, customers, suppliers, and the wider community.
How does stakeholder analysis help organizations during transformation initiatives?
By classifying interested parties based on their degrees of influence and concern, organizations can prioritize involvement efforts, ensuring that crucial viewpoints are recognized and addressed throughout the transformation process.
What are the potential consequences of failing to conduct effective stakeholder analysis?
Transformation initiatives that fail can drain 6-10% of annual revenue, and employee resistance may lead to a 30% loss in productivity.
What benefits can successful transformations yield?
Successful transformations can result in an impressive average return on investment of 500%.
What approach is recommended for monitoring and decision-making during transformation?
A pragmatic approach involving continuous business performance monitoring and real-time analytics is essential for testing hypotheses and maximizing returns on invested capital.
How can investing in employee training and development impact operational expenses?
Investing in employee training and development can lower operational expenses by 15%, highlighting the importance of participant involvement in management transitions.
What is the significance of strong communication cultures in organizations undergoing change?
Organizations with strong communication cultures can experience a 23% rise in profitability during transformation initiatives.
What are the steps to conduct stakeholder analysis effectively?
The steps include identifying stakeholders, categorizing interested parties, evaluating their influence and impact, developing involvement techniques, and observing and modifying strategies as needed.
What tools can be used to categorize interested parties in stakeholder analysis?
A Power/Interest Grid is a valuable tool for visualizing the positions of involved parties based on their levels of influence and interest.
How should organizations interact with high-power, high-interest parties during transformation?
High-power, high-interest parties should receive regular updates and be actively involved in decision-making processes.
Why is it important to continuously track participant attitudes during a transformation initiative?
Consistently tracking participant attitudes helps organizations adjust their strategies to maintain support and mitigate potential resistance, ensuring the initiative's success.

