Introduction
In the intricate landscape of project management, understanding and effectively managing stakeholders is paramount to success. Stakeholders, ranging from primary players like employees and customers to secondary influences such as suppliers and regulatory bodies, each hold unique interests that can significantly impact project outcomes.
This article delves into a structured approach for identifying, prioritizing, and engaging stakeholders, equipping CFOs with the tools necessary to navigate complex environments.
With insights drawn from real-world case studies and advanced techniques, the discussion highlights the importance of tailored communication strategies and the role of technology in fostering transparency and collaboration.
By mastering these principles, organizations can enhance their project performance and drive sustainable success.
Understanding Stakeholders: The Foundation of Effective Management
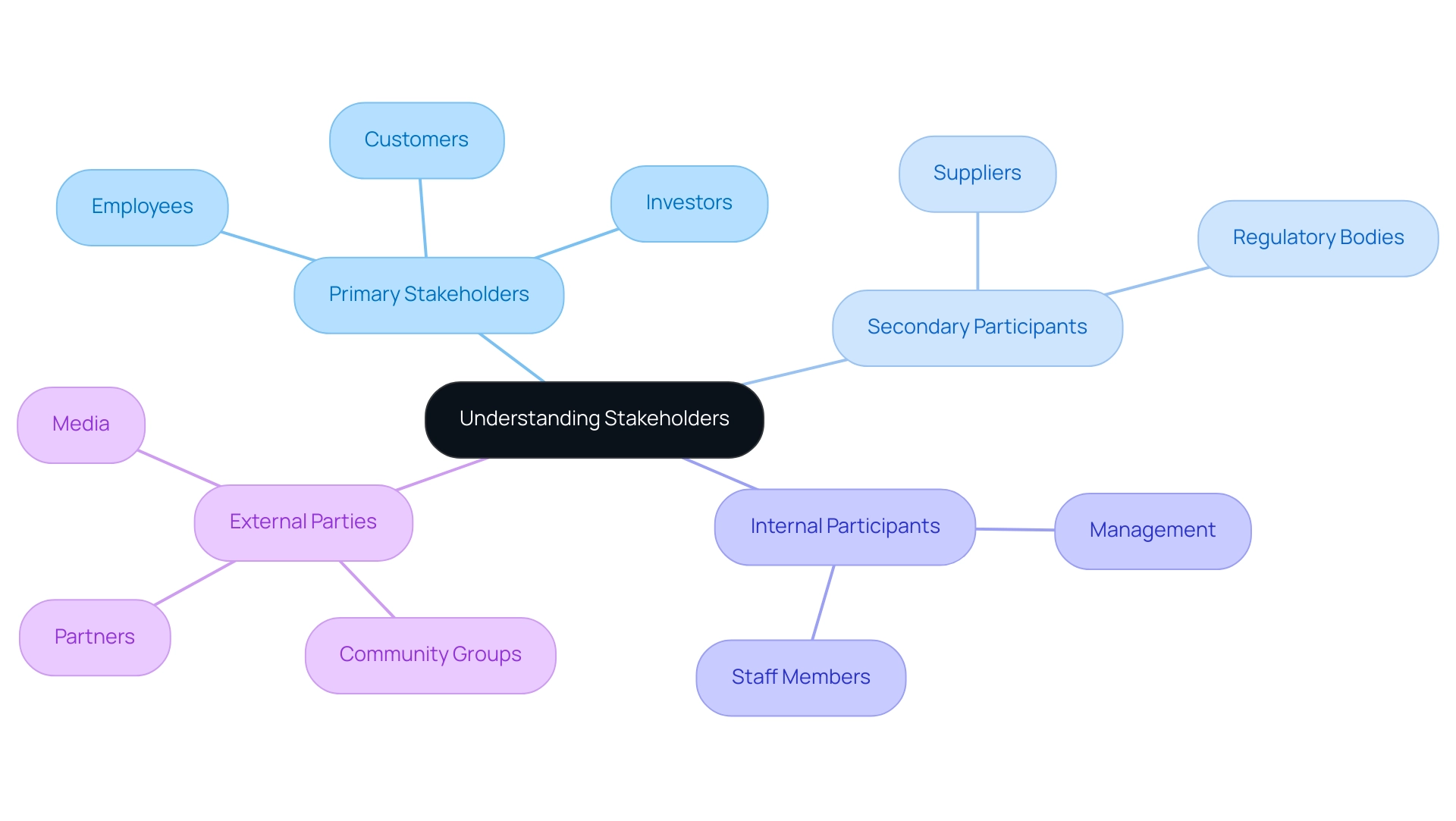
Participants in any initiative can be effectively classified into four key categories: primary, secondary, internal, and external groups.
- Primary stakeholders—such as employees, customers, and investors—have a direct interest in the initiative and its outcomes.
- Secondary participants, including suppliers and regulatory bodies, have an indirect interest that still warrants attention.
- Internal participants consist of individuals within the organization, while
- External parties encompass outside entities that can both influence and be influenced by the initiative.
Grasping these distinctions is crucial for prioritizing engagement efforts in complex stakeholder management and addressing the unique needs of each group.
With the potential to identify anywhere from 50 to 1000 participants, conducting mapping of these individuals becomes an essential practice that allows organizations to visualize relationships and the potential impact of each participant on the project. This strategic tool not only assists in recognizing key players but also guides your complex stakeholder management approach, ensuring effective interaction and alignment of interests. As Tom Nguyen, Co-founder & CEO, aptly states, "By submitting your information, you acknowledge that you have read and agree to zen8labs’ Privacy Policy," which highlights the significance of transparency in interactions with involved parties.
Recent advancements in participant involvement highlight the significance of customized interaction methods, which can greatly improve success rates. A notable case study, titled "Avoiding Common Stakeholder Analysis Pitfalls," highlights the common challenges in communication with interested parties and offers strategies to overcome them, enhancing the practical application of these concepts. A strong comprehension of participant classification, supported by strategic mapping and insights from real-world situations, enables any CFO to excel in complex stakeholder management and guide their organization towards more successful outcomes.
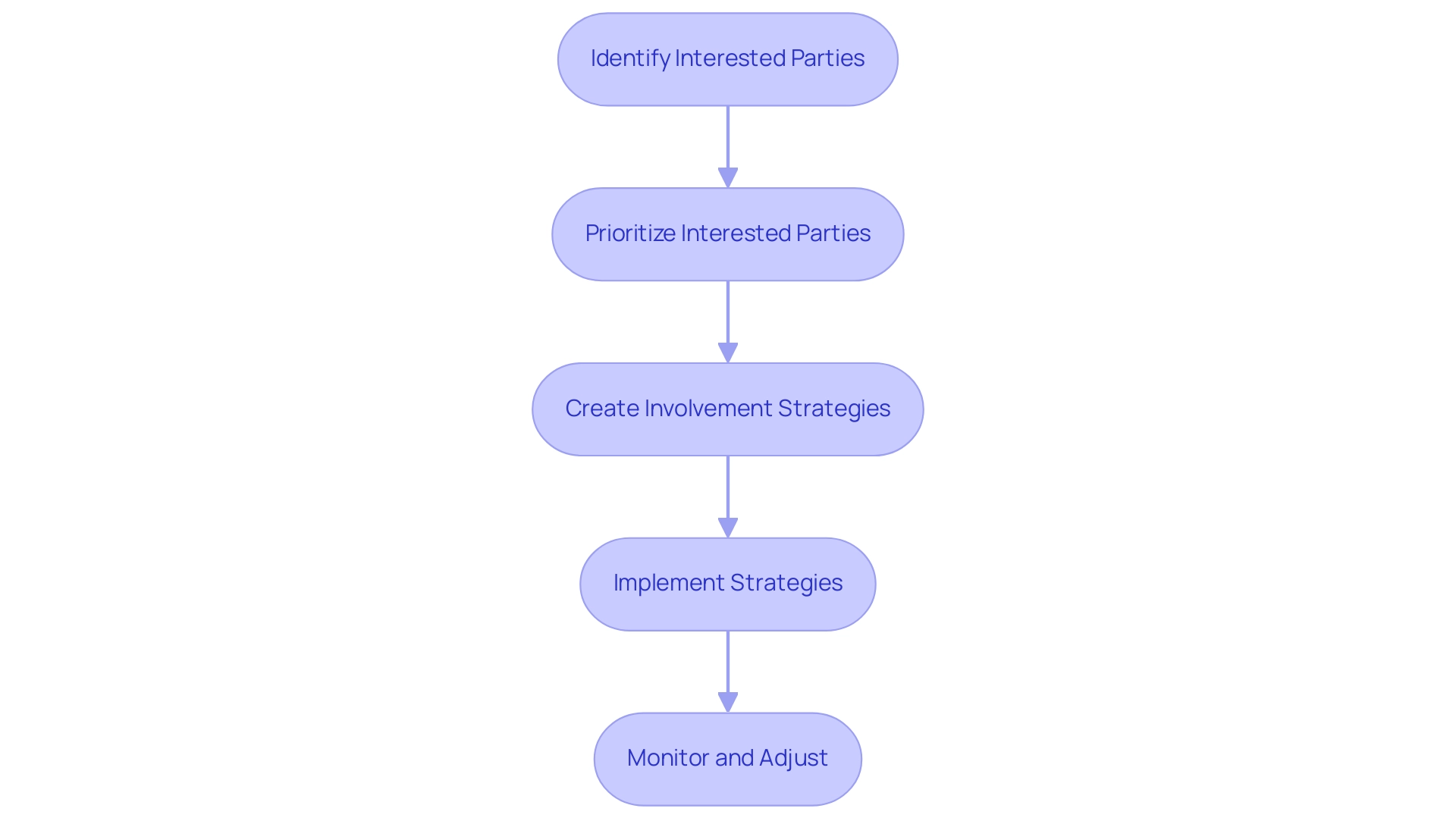
Step-by-Step Process for Managing Stakeholders
-
Identify Interested Parties: Begin the process by creating a thorough list of potential individuals or groups who may influence or be affected by your initiative. Engage in brainstorming sessions and collaborate with your team to ensure a thorough identification that leaves no one overlooked. Recent studies emphasize that efficient participant identification techniques significantly relate to initiative performance, with a Cronbach's alpha coefficient of 0.82 highlighting the dependability of these techniques. This statistic emphasizes the importance of this initial step.
-
Prioritize Interested Parties: Assess each party's level of influence and interest regarding your project. Utilize a power-interest grid to categorize participants into four distinct groups:
- high power/high interest
- high power/low interest
- low power/high interest
- low power/low interest
This prioritization is crucial, as it informs the customized interaction strategies you will develop.
-
Create Involvement Strategies: Design involvement methods that correspond with the identified participant categories. For individuals with high power and high interest, provide regular updates and actively involve them in decision-making processes. Conversely, for those in the low power/low interest category, keep them informed while reducing involvement efforts to optimize resource allocation.
-
Implement Strategies: Execute your customized interaction plans, ensuring that communication remains consistent and pertinent to each party's specific needs. This approach not only fosters strong relationships but also encourages collective intimacy and entrepreneurial thinking. Regis Dumoulin highlights this by stating, 'Investigating the contributions at a Hackathon hosted by Google, we induce three categories of innovative attitude: collective intimacy, entrepreneurial thinking and technological avant-garde,' which underscores the importance of innovative attitudes in participant interactions.
-
Monitor and Adjust: Continuously assess participant feedback and the overall effectiveness of your involvement strategies. Be prepared to adjust your strategies as necessary to maintain constructive relationships throughout the lifecycle. Utilizing diverse methods for involving interested parties, complex stakeholder management, as demonstrated by project managers at zen8labs who apply expert judgment in customizing interaction strategies, nurtures strong relationships and enhances participant involvement, ultimately resulting in project success.
Navigating Challenges in Complex Stakeholder Environments
The challenges of managing complex interest group environments highlight the necessity of effective complex stakeholder management, addressing conflicting interests, communication barriers, and intricate power dynamics. To successfully navigate these hurdles, consider the following strategies:
-
Identify Conflicts Early: Proactive engagement is crucial. Consistently engage with involved parties to identify possible conflicts and resolve them before they intensify.
Early identification of issues can set the stage for effective resolution.
-
Facilitate Open Communication: Establish forums or platforms where involved parties can voice their concerns and provide feedback. This openness promotes trust and assists in reducing misunderstandings, reinforcing the notion that today's participants must possess not only a strong comprehension of the initiative and its needs but also knowledge of management and how their choices could affect the manner in which an initiative will be handled — H. Kerzner.
-
Leverage Influencers: Recognize key contributors who wield influence over others. Work together with these individuals to promote your initiative, as their backing can influence views and reduce opposition, especially in settings where complexity levels are elevated.
-
Be Flexible: Adaptability is crucial in managing interests. Be ready to adjust your strategies in response to input from interested parties and evolving situations. This flexibility can turn potential challenges into collaborative opportunities.
Implementing these strategies, as emphasized in the case study ‘Guidelines for Managing Complexity,’ can systematically reduce complexity and enhance decision-making processes in projects that involve complex stakeholder management. It's important to note that complexity levels are divided into four levels: Level 1 has effective interaction, while Level 4 has ineffective interaction with no support from executives. As the landscape of participant interaction evolves, future strategies will increasingly depend on dynamic, real-time methods that consider influence, impacts, and the strength of networks.
Understanding the reasons for participant involvement and withdrawal related to the system lifecycle is essential for effective complex stakeholder management.
Effective Communication Strategies for Stakeholder Engagement
-
Tailor Your Message: Customize your communication to align with the unique interests and influence levels of each participant. Employ language and examples that resonate specifically with them, as this personal touch can significantly enhance engagement. The idea of mutual responsiveness among parties is crucial; as stated,
RRI should be understood as a strategy of participants to become mutually responsive to each other and anticipate research and innovation outcomes underpinning the ‘grand challenges’ of our time for which they share responsibility.
-
Utilize Multiple Channels: Engage participants through various means such as emails, meetings, newsletters, and social media platforms. This multifaceted approach ensures that your message reaches interested parties in their preferred formats, thereby increasing the likelihood of effective engagement. Considering the increasing number of participant interactions, centralizing dialogue in one system is recommended to streamline processes. Notably, management software can be produced in as little as 3 minutes, enhancing efficiency in your communication efforts.
Be Transparent: Foster a culture of openness by sharing both successes and challenges with interested parties. This transparency builds trust and encourages ongoing engagement, which is vital for maintaining strong relationships. When involved parties feel informed, they are more likely to remain invested in the outcomes. Addressing potential concerns, it is important to note that depending on the software choice, a CRM can be costly for small teams and may require user training.
-
Solicit Feedback: Actively seek input from interested parties to demonstrate that their opinions matter. Utilize tools such as surveys, feedback forms, or informal discussions to gather valuable insights. Regular feedback loops not only improve relationships with interested parties but also inform future strategies and initiatives. For example, the case study of school leaders emphasizes the importance of being prepared for informal conversations, requiring clear and concise talking points that resonate with individual values. This preparedness significantly enhances the ability to connect with interested parties and reinforces the importance of key initiatives.
Follow Up: After any meetings or discussions, ensure to follow up with interested parties to reinforce key messages and express gratitude for their involvement. This practice keeps lines of communication open and fosters a sense of partnership. The case study of school leaders emphasizes the value of readiness for informal discussions; having clear and concise talking points prepared can significantly enhance the ability to engage with interested parties, thereby reinforcing the significance of key initiatives.
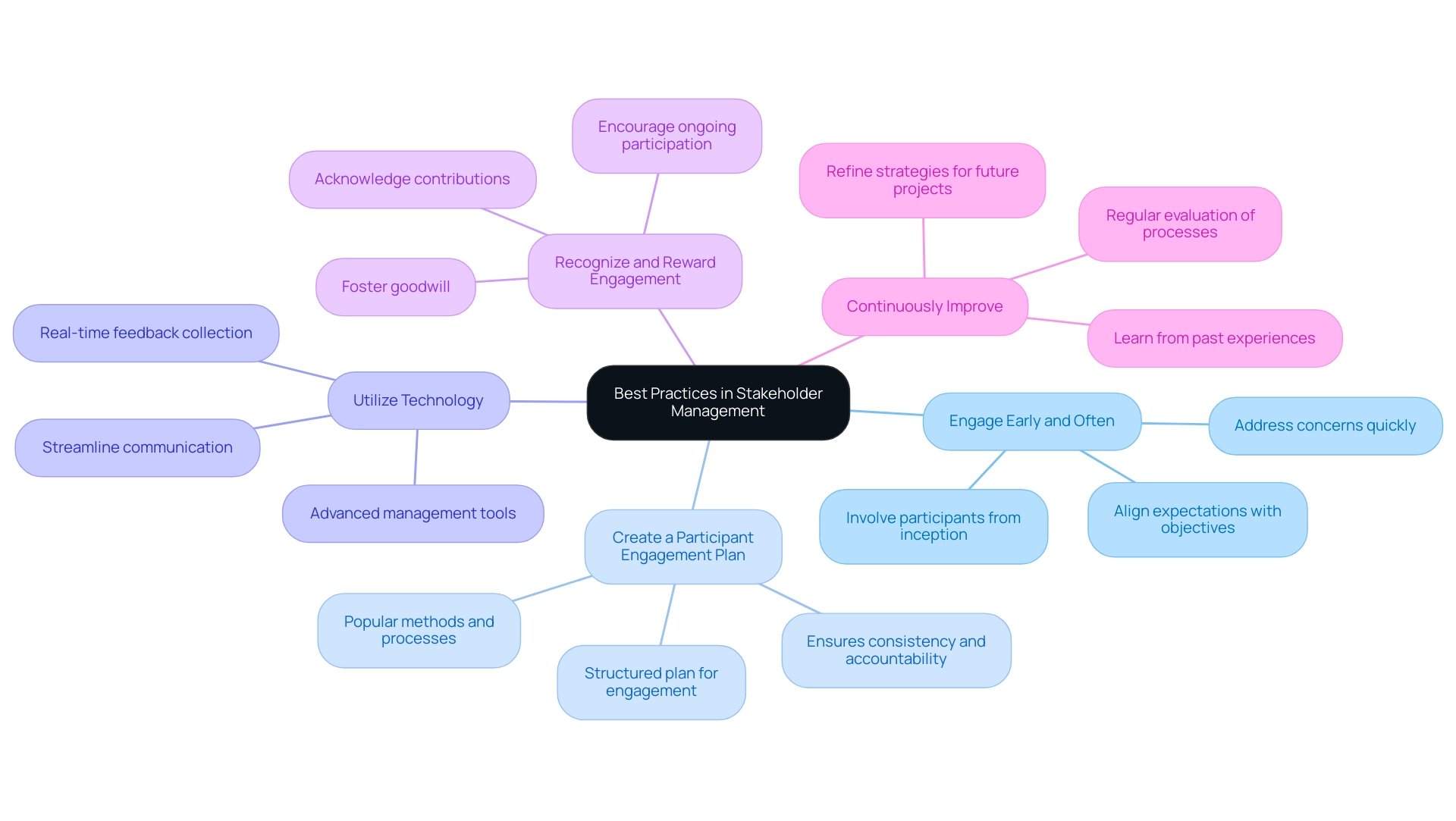
Best Practices and Advanced Techniques in Stakeholder Management
- Engage Early and Often: Start involving participants from the initiative's inception. Their insights are invaluable in shaping the initiative's direction, ultimately leading to enhanced outcomes. Early involvement aids in recognizing potential issues and aligns participant expectations with project objectives. Addressing concerns quickly is vital for maintaining good working relationships with stakeholders.
- Create a Participant Engagement Plan: Develop a structured plan that outlines how and when you will engage with each group of participants. This formalized approach ensures consistency and accountability, allowing for effective tracking of interactions and outcomes. As Angela Rodgers emphasizes, in this guide, we define what prioritization of interested parties is, why it’s worth doing, popular methods and processes, challenges, and best practices. This organized involvement is crucial, particularly given that more than 100,000 readers worldwide have gained from efficient participant management practices.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage advanced management tools and software to streamline communication and monitor participant interactions effectively. Recent advancements in technology have transformed how participants can be engaged, making it easier to share updates and gather feedback in real time.
- Recognize and Reward Engagement: Acknowledge the contributions of participants who actively engage in the project. This recognition fosters goodwill and encourages ongoing participation, creating a positive cycle of engagement that benefits all parties involved.
- Continuously Improve: Regularly evaluate your partner management processes and seek opportunities for enhancement. Learning from past experiences can lead to more effective strategies in future projects. For instance, a large global furniture brand adopted Simply Stakeholders to enhance complex stakeholder management of internal relationships, which improved collaboration through better management of involved parties. This serves as a reminder that refining your approach can yield significant benefits in stakeholder relationships.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing stakeholders is essential for any CFO aiming to drive project success. By categorizing stakeholders into:
- Primary
- Secondary
- Internal
- External
groups, organizations can prioritize their engagement efforts effectively. This structured approach not only enhances communication but also ensures that the unique interests of each stakeholder are addressed, leading to more favorable project outcomes.
Implementing a step-by-step process—ranging from identifying and prioritizing stakeholders to developing tailored engagement strategies—enables organizations to foster strong relationships and navigate complex environments. Continuous monitoring and adaptation of these strategies are vital, as they allow for responsive adjustments that align with stakeholder feedback and changing dynamics.
Moreover, leveraging technology and employing effective communication strategies can significantly enhance stakeholder engagement. By utilizing diverse channels, fostering transparency, and actively soliciting feedback, organizations can build trust and encourage ongoing collaboration. Recognizing and rewarding stakeholder contributions further solidifies these relationships, creating a positive cycle of engagement.
Ultimately, mastering stakeholder management equips CFOs with the tools necessary to navigate complexities and drive sustainable success. By prioritizing stakeholder engagement and employing best practices, organizations can enhance project performance and achieve their strategic objectives. Now is the time to take decisive action in refining stakeholder management practices, ensuring that every project thrives amidst the intricacies of diverse interests and influences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the four key categories of participants in an initiative?
The four key categories are primary stakeholders, secondary participants, internal participants, and external parties.
Who are considered primary stakeholders?
Primary stakeholders include employees, customers, and investors who have a direct interest in the initiative and its outcomes.
What defines secondary participants in an initiative?
Secondary participants, such as suppliers and regulatory bodies, have an indirect interest in the initiative that still warrants attention.
What is the difference between internal participants and external parties?
Internal participants are individuals within the organization, while external parties are outside entities that can influence and be influenced by the initiative.
Why is it important to understand participant classifications?
Understanding participant classifications is crucial for prioritizing engagement efforts in complex stakeholder management and addressing the unique needs of each group.
How many participants can be identified in an initiative?
Organizations can identify anywhere from 50 to 1000 participants.
What is the purpose of mapping participants in an initiative?
Mapping participants helps visualize relationships and the potential impact of each participant on the project, guiding stakeholder management efforts.
What recent advancements have been made in participant involvement?
Recent advancements emphasize customized interaction methods, which can greatly improve success rates in stakeholder engagement.
What is the significance of prioritizing interested parties?
Prioritizing interested parties allows for the assessment of each party's level of influence and interest, informing the development of customized interaction strategies.
What steps should be taken to create involvement strategies for participants?
Involvement strategies should correspond with participant categories, providing regular updates and involvement for high power/high interest individuals, while keeping low power/low interest individuals informed with reduced involvement efforts.
How should organizations monitor and adjust their involvement strategies?
Organizations should continuously assess participant feedback and the overall effectiveness of their strategies, making necessary adjustments to maintain constructive relationships throughout the project lifecycle.




