Overview
This article delves into the mastery of the stakeholder management power-interest grid, a crucial tool for enhancing project success. By effectively categorizing and engaging stakeholders based on their power and interest levels, project managers can significantly improve outcomes.
The article outlines a systematic approach to:
- Identifying stakeholders
- Assessing their influence
- Developing tailored engagement strategies
It emphasizes that prioritizing interactions with key stakeholders is essential for achieving optimal project results.
To elevate your project management skills, embrace this strategic framework and take decisive action in stakeholder engagement.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of project management, grasping stakeholder dynamics is essential for achieving success. The Power-Interest Grid framework stands out as a strategic instrument that empowers project managers to classify stakeholders according to their levels of influence and interest, thereby facilitating focused engagement strategies.
By adeptly identifying and evaluating stakeholders, organizations can prioritize their interactions, ensuring that resources are allocated with precision. This article explores the complexities of stakeholder management, providing insights into the development of customized engagement strategies and the monitoring of their effectiveness.
By adopting these best practices, project managers can bolster collaboration, mitigate risks, and ultimately propel project success.
Understand the Power-Interest Grid Framework
The stakeholder management power interest grid serves as a vital strategic tool for classifying participants based on two critical dimensions: their degree of power (influence) and their level of interest in the initiative. This framework is segmented into four distinct quadrants:
- High Power, High Interest: Stakeholders in this category are crucial to the project's success and require active management and engagement.
- High Power, Low Interest: These individuals should be kept satisfied, although extensive interaction is not necessary.
- Low Power, High Interest: It is essential to keep these parties informed and engaged, as they can provide valuable insights and support.
- Low Power, Low Interest: Minimal monitoring and communication suffice for participants in this quadrant.
Utilizing the stakeholder management power interest grid allows managers to prioritize engagement strategies effectively, ensuring that resources are allocated where they will have the greatest impact. Insights gained from interest group analysis can lead to critical adjustments and enhancements, ultimately improving overall results.
Recent discussions emphasize that parties categorized as Low Power, Low Interest should be monitored with minimal effort, as indicated by statistics supporting this approach. This focus allows managers to concentrate on individuals who can significantly influence success. As noted by Meredith G. Malinawan, "This tool is not solely focused on marking locations on a grid; it aims to create a strategy that honors and leverages each contributor’s distinct inputs to enhance success."
Practical applications of the stakeholder management power interest grid, as demonstrated in the case study titled 'Importance of the Power Interest Grid in Project Management,' have illustrated its effectiveness in prioritizing interactions with involved parties. By mapping participants on this grid, managers can identify essential contributors and manage their involvement efficiently, ensuring project success.
Identify Your Stakeholders
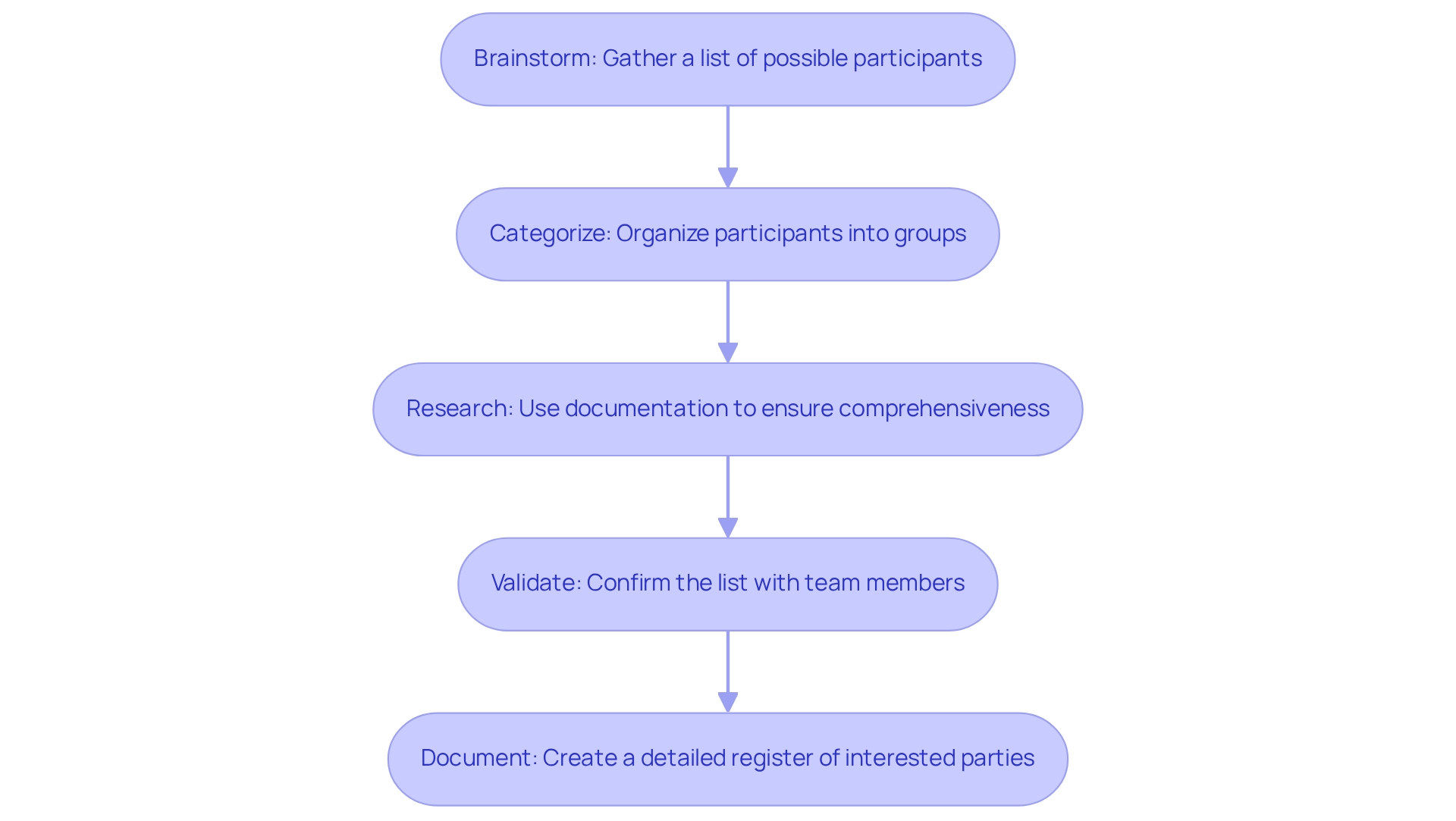
Recognizing participants is a crucial phase in the stakeholder management power interest grid for managing initiatives that significantly impact success. To effectively recognize your interested parties, follow these steps:
- Brainstorm: Gather your team to create an extensive list of possible participants. Consider anyone who may be affected by the project or who holds influence over its outcomes using the stakeholder management power interest grid.
- Categorize: Organize participants into distinct groups, such as internal (employees, management) and external (customers, suppliers, regulatory bodies). This categorization aids in understanding their varying interests and influences within the stakeholder management power interest grid.
- Research: Utilize existing documentation, organizational charts, and participant registers to ensure your list is comprehensive. This step is vital, as 73% of organizations using a stakeholder management power interest grid frequently achieve their objectives, emphasizing the significance of a systematic approach.
- Validate: Engage with team members and other involved parties to confirm your list. This joint validation procedure utilizes the stakeholder management power interest grid to ensure that no important participants are neglected, as unknown contributors are a frequent reason for project failure. Notably, only 34% of underperformers provide comparable training, underscoring the necessity for organized participant management training.
- Document: Create a detailed register of interested parties that includes names, roles, interests, and contact information for each individual. This documentation serves as an essential reference throughout the lifecycle of the initiative, and by applying these best practices, organizations can enhance their processes using the stakeholder management power interest grid, ultimately resulting in improved outcomes and sustainable growth. As highlighted in the case study on Management Training and Support, sufficient organizational backing can greatly improve the acceptance and efficient utilization of management tools, further reinforcing the importance of training in identifying and managing participants.
Assess Stakeholder Power and Interest
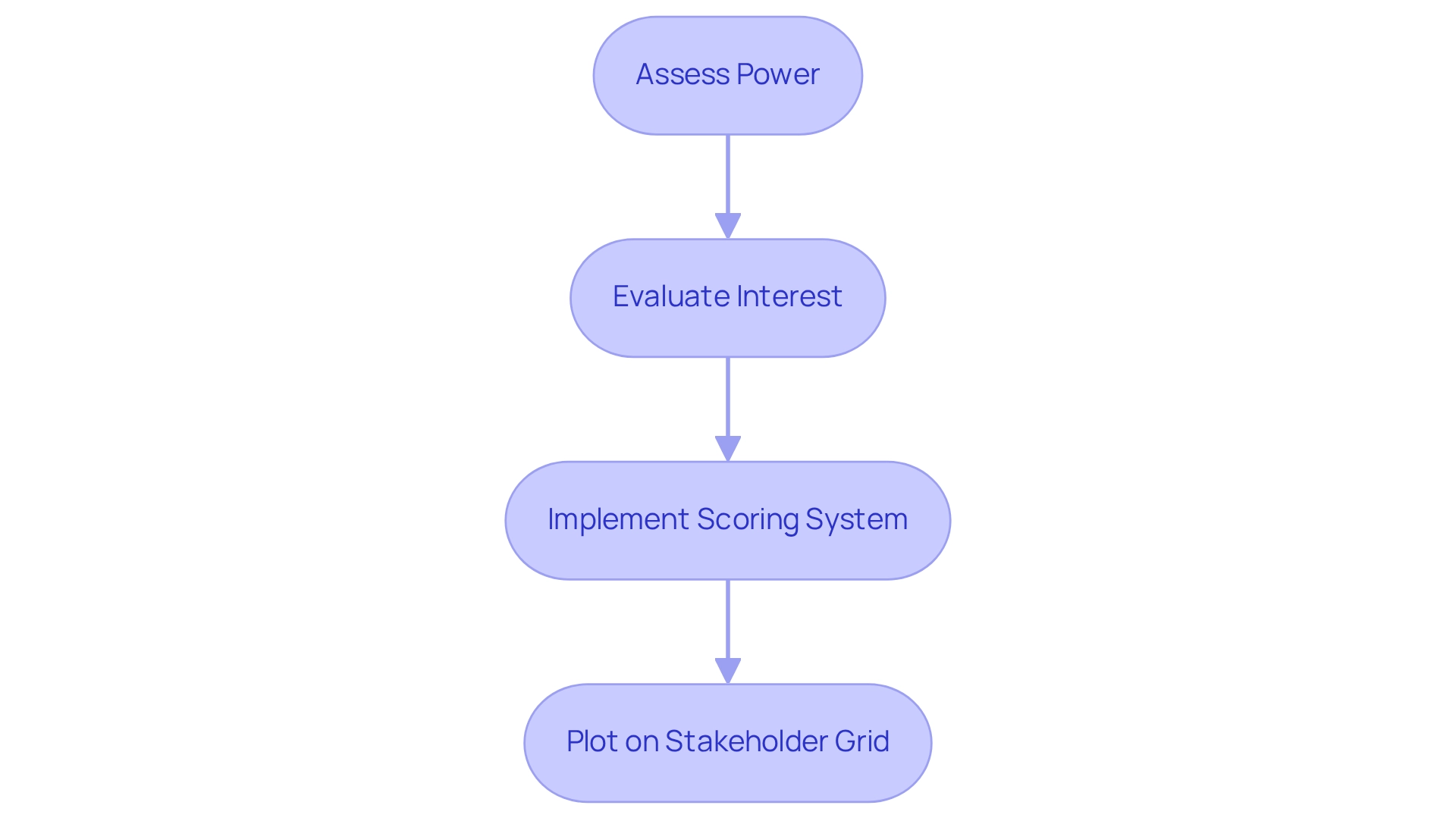
To effectively assess stakeholder power and interest, consider the following structured approach:
- Assess Power: Determine the degree of impact each participant has on the initiative. Key factors include their organizational position, available resources, and ability to significantly influence outcomes.
- Evaluate Interest: Assess the level of interest each participant has in the initiative. This assessment should reflect their potential gains or losses associated with the project's success or failure.
- Implement a Scoring System: Develop a scoring system (e.g., 1-5) for both power and interest. This quantification assists in precisely mapping participants on the stakeholder management power interest grid, which enables clearer analysis.
- The stakeholder management power interest grid is essential for analyzing project dynamics. Plot on the stakeholder management power interest grid: Position each participant according to their scores on the grid. This visual depiction clarifies their relative significance and aids in prioritizing interaction strategies effectively.
Integrating real-time analytics into this organized method can greatly improve involvement from those with an interest. By consistently tracking interest groups and power dynamics through a client dashboard, informed choices can be made that maintain business health and promote success. A systematic method for involving interested parties is essential, as research shows that 50% of a company’s value frequently comes from merely 15-20 significant roles. This underscores the significance of effective participant engagement in driving project success. Moreover, in the technology industry, establishing trust with involved parties has been demonstrated to enhance employee retention by 10%. This illustrates how assessing participant interest can directly affect organizational culture and performance. As Meredith G. Malinawan, PMP, states, "These steps will guide you in effectively managing your involved parties and ensuring that your endeavor meets their expectations and influence." By following these steps, you can ensure that your project aligns with the expectations of interested parties and maximizes its chances of success.
Develop Tailored Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
To create effective customized engagement strategies, use the stakeholder management power interest grid to consider the following approaches based on influence and interest:
- High Power, High Interest: Engage these parties closely by scheduling regular meetings, providing detailed updates, and involving them in decision-making processes. This proactive method encourages cooperation and guarantees their insights are included in development. Best practices include actively soliciting their feedback and ensuring their concerns are addressed promptly.
- High Power, Low Interest: Maintain their satisfaction with periodic updates. Keep them informed of major developments without overwhelming them with excessive details, ensuring they feel valued while not burdened.
- Low Power, High Interest: Keep these individuals informed and engaged through newsletters, updates, and opportunities for feedback. Their perspectives can be instrumental in refining project strategies and enhancing overall outcomes.
- Low Power, Low Interest: Monitor these parties with minimal effort. Offer general updates to keep them informed of key developments, ensuring they stay aware without needing significant involvement.
Statistics show that organizations thriving in managing relationships often face lower conflict resolution expenses, emphasizing the financial advantages of effective interaction. Moreover, it is significant that around 50% of a company's worth can arise from only 15-20 essential roles, highlighting the necessity of prioritizing interaction strategies based on the stakeholder management power interest grid for these individuals. A thorough business assessment at the beginning of client interactions can greatly improve the management of these key participants. By aligning essential participants and understanding the business context beyond mere figures, organizations can identify underlying issues and collaboratively create strategic plans that reinforce strengths. This process not only addresses weaknesses but also allows businesses to reinvest in their key strengths. A case study from iQuasar demonstrates the transformative power of involving interested parties. By keeping transparent communication and adjusting approaches, they effectively improved results and client satisfaction. This example strengthens the idea that customized interaction approaches can greatly influence project success rates, making it crucial for project managers to dedicate time and resources to comprehend and address the distinct requirements of their constituents.
Monitor and Adjust Engagement Strategies
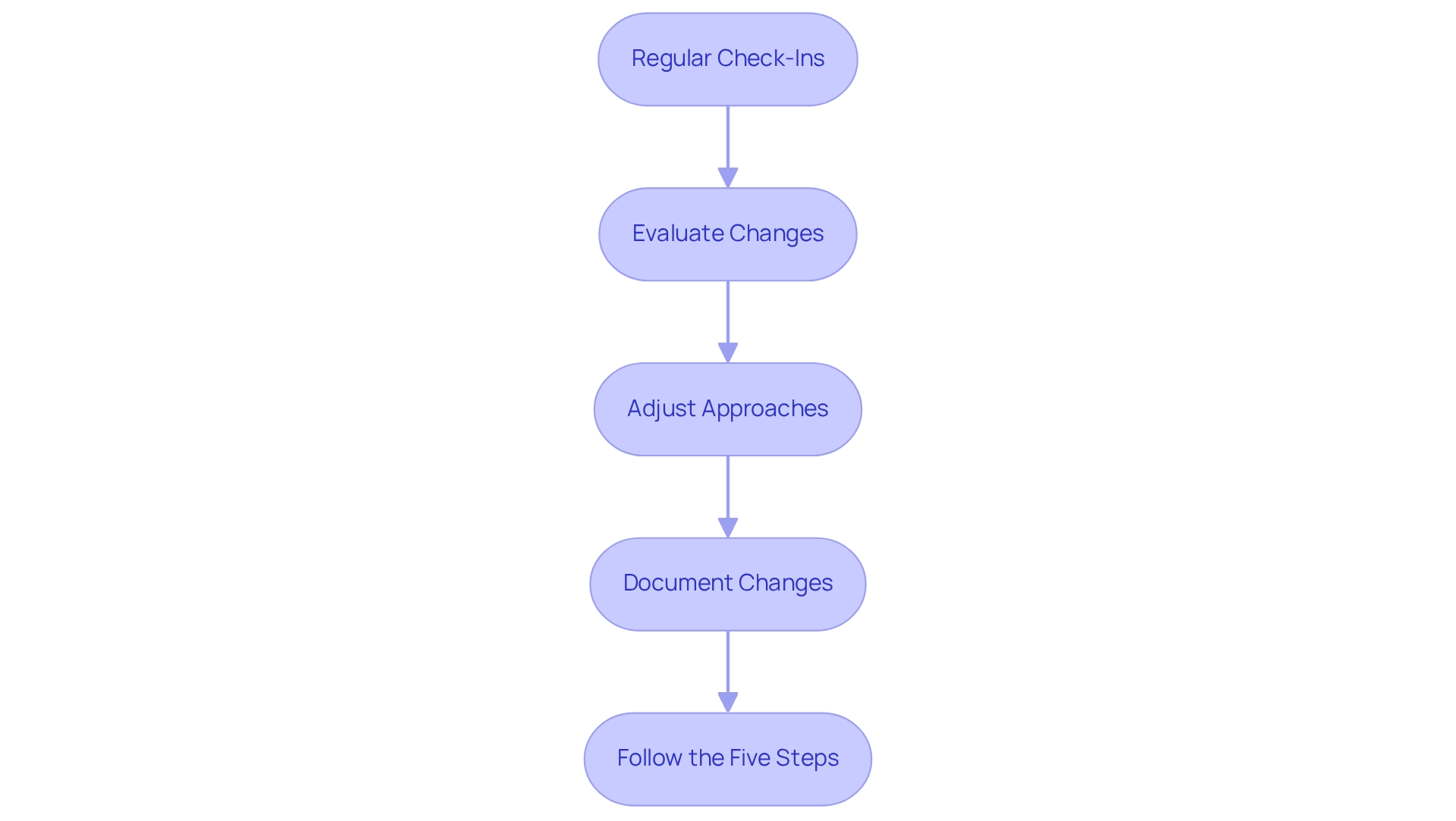
To effectively oversee and modify your interaction approaches, consider the following steps:
- Regular Check-Ins: Schedule consistent meetings with involved parties to assess their satisfaction and collect feedback on your engagement efforts. This practice is crucial, as regular evaluations can help refine strategies and priorities as needed.
- Evaluate Changes: Stay vigilant to any shifts in influence or interest resulting from project developments or external factors. Updating your evaluations in real-time is essential for maintaining alignment with interested parties' expectations. Our team supports a shortened decision-making cycle throughout the turnaround process, allowing your team to take decisive action to preserve your business.
- Adjust Approaches: Utilize the feedback and evaluations to alter your involvement methods. This may involve increasing the frequency of communications or altering the format of updates to better cater to stakeholder preferences. We continually monitor the success of our plans through our client dashboard, which provides real-time business analytics to diagnose your business health continuously.
- Document Changes: Maintain a comprehensive record of any adjustments made to your involvement strategies, along with the rationale behind these changes. This documentation acts as a valuable asset for upcoming endeavors, ensuring lessons learned are not forgotten.
- Follow the Five Steps: Keep in mind that the involvement process comprises five essential steps: Identify, Analyse, Plan, Act, and Review. This organized method will assist in guaranteeing that your plans for the stakeholder management power interest grid are thorough and efficient. By following these practices, you can ensure that participant involvement remains efficient and aligned with objectives, ultimately aiding in sustainable growth and achievement. As Dr. Mike Clayton points out, the changing terminology and practices in the stakeholder management power interest grid, as emphasized in the PMI’s PMBOK Guide, demonstrate the significance of adjusting to their needs. Additionally, the Project Management Institute's emphasis on stakeholder engagement illustrates the shift in project management practices, reinforcing the need for continuous improvement in engagement strategies.
Conclusion
Effectively managing stakeholder dynamics is crucial for project success. The Power-Interest Grid framework provides a robust approach for categorizing stakeholders based on their influence and interest levels. By identifying stakeholders, assessing their power and interest, and developing tailored engagement strategies, project managers can prioritize interactions that maximize project outcomes. This structured process of monitoring and adjusting these strategies ensures that stakeholder engagement remains relevant and effective throughout the project lifecycle.
In summary, a proactive and strategic approach to stakeholder management not only fosters collaboration and mitigates risks but also enhances the likelihood of achieving project goals. Organizations that invest in understanding their stakeholders and tailoring their engagement efforts are better positioned to navigate the complexities of project management. Ultimately, the commitment to refining stakeholder relationships is an investment in the overall success and sustainability of projects, reinforcing the idea that stakeholder engagement is a vital component of effective project management practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the stakeholder management power interest grid?
The stakeholder management power interest grid is a strategic tool used to classify participants based on their degree of power (influence) and level of interest in an initiative, helping managers prioritize engagement strategies.
How is the stakeholder management power interest grid segmented?
The grid is divided into four quadrants: 1. High Power, High Interest - crucial stakeholders requiring active management. 2. High Power, Low Interest - stakeholders to be kept satisfied with minimal interaction. 3. Low Power, High Interest - stakeholders to be informed and engaged for valuable insights. 4. Low Power, Low Interest - stakeholders needing minimal monitoring and communication.
What benefits does utilizing the stakeholder management power interest grid provide?
It allows managers to effectively prioritize engagement strategies and allocate resources where they will have the greatest impact, leading to critical adjustments and enhancements that improve overall project results.
What steps should be followed to recognize participants in the stakeholder management power interest grid?
The steps include: 1. Brainstorming to create a list of potential participants. 2. Categorizing participants into internal and external groups. 3. Researching existing documentation to ensure a comprehensive list. 4. Validating the list with team members and other involved parties. 5. Documenting a detailed register of interested parties, including their names, roles, interests, and contact information.
Why is it important to validate the list of stakeholders?
Validating the list ensures that no important participants are overlooked, as unknown contributors can lead to project failure. This process helps to enhance participant management and improve project outcomes.
How can organizations enhance their processes using the stakeholder management power interest grid?
By applying best practices in identifying and managing participants, organizations can improve their processes, leading to better outcomes and sustainable growth through effective stakeholder engagement.




