Introduction
The due diligence process is of utmost importance in any business transaction, requiring a comprehensive analysis of a company's financial health to uncover potential risks. This article explores the role of due diligence in transactions, key steps in conducting financial due diligence, a comprehensive case study, the benefits and challenges of financial due diligence, and best practices for effective due diligence. By following these insights, CFOs can ensure a thorough evaluation that safeguards the financial integrity of their organizations and facilitates successful negotiations.
Conducting a comprehensive due diligence process is paramount in any business transaction. Rather than a cursory review, an in-depth analysis of the company's financial health is required to uncover any potential risks that might not be immediately apparent.
A meticulous examination of financial statements, assets, customer base, and industry trends is essential. As underscored by experts, one must never underestimate the necessity of a proper valuation.
Engaging the expertise of a qualified business appraiser or valuation professional ensures that the business's worth is accurately assessed—a critical step that forms the linchpin of negotiation. Owners who rely solely on a gut feeling or arbitrary figures when selling may shortchange themselves or dissuade buyers with overstated valuations. An accurate assessment, grounded in concrete data, guarantees that the selling price reflects the true value, guarding against financial compromise.
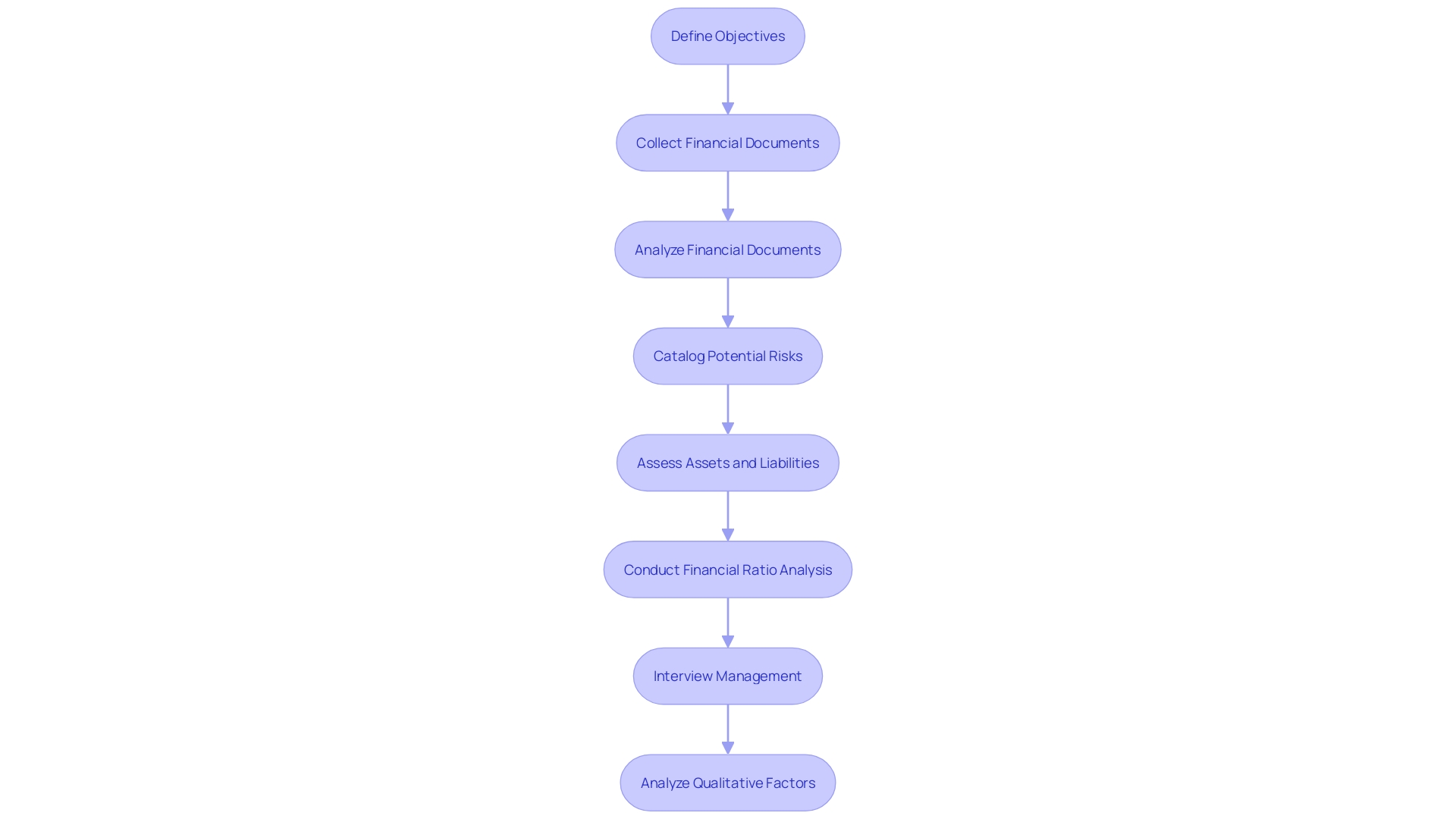
Financial due diligence is an investigative art that transcends a mere audit to encompass a full spectrum analysis of an organization's inner workings. This meticulous process kicks off with a laser-focused definition of due diligence objectives that position the evaluation within clear goalposts.
The subsequent step is a thorough collection of financial documents such as balance sheets, income statements, tax filings, and binding contracts. These materials then become subject for a nuanced analysis, sifting through them to pinpoint the company's fiscal performance, profitability contours, and liquidity streams.
Each potential risk is then cataloged, from pending legal entanglements and compliance conundrums, to the specter of obscured liabilities. Turning the magnifying glass onto assets and liabilities grants a quantifiable measure of the firm's resources and obligations, taking into consideration the granularity of intellectual property, inventory, and even real estate holdings.
A financial ratio analysis ensues, cutting through the data to unveil insights into the organizational stability, operating efficacy, and the caliber of profitability. Delving deeper still, interviews with management draw out the strategic underpinnings and possible hurdles intrinsic to the company's financial systems. As important as quantifiable data is, due diligence reaches beyond, venturing into the qualitative territory. This aspect scrutinizes market trajectories, competitive ecosystems, and industry-specific regulations. The culmination of these steps is synthesized into a comprehensive report, sagely advising on the advisable steps forward, replete with a sober assessment of any attendant risks.
Navigating the waters of corporate mergers and acquisitions requires a multifaceted approach to due diligence—a mission critical for the success of any deal. Take, for example, the case of ABC Corporation setting its sights on acquiring a promising, yet smaller player, XYZ Corporation, a software development start-up with considerable market potential.
In the throes of this significant transaction, the onus falls on ABC Corporation's CFO to embark on a meticulous analysis beyond the obvious robust revenue growth and solid customer base of XYZ Corporation. Due diligence unfolds as a comprehensive investigation that goes beyond typical financial audits, probing into XYZ’s IT infrastructure, data architecture, and how data is stored, protected, and analyzed.
The CFO must also pay heed to the organization and alignment of XYZ’s various departments. In doing so, the assessment brings to light not just the strengths of the start-up, but also potential risks like unresolved legal battles and impending lawsuits, which cannot be ignored.
As Darshil Shah, an investment banking pro, elucidates, the reasons behind M\&A may be diverse, but the process is rife with complexities requiring strategic insights and methodical steps. The expanse of due diligence spans assessing financial statements, assets, debts, and cash flows, to the more granular like compliance with environmental regulations, tax laws, and evaluation of legal liabilities. The role of external professionals—lawyers, accountants, and brokers—is paramount, each bringing unique value to the table. Their expertise is a safeguard, preventing the common pitfalls of inadequate planning and underestimated risk assessments. In this maneuver, the CFO must present the board with more than just numbers; it demands a narrative that marries financial health with strategic foresight, embedding recommendations that ensure not just the acquisition, but also its harmonious integration into the company’s long-term vision.
Venturing into mergers and acquisitions (M\&A) is akin to navigating a financial minefield, with the proper due diligence as your indispensable map. At its core, the due diligence process scrutinizes the enterprise value of a business, a critical metric gauging its worth.
This assessment isn't merely a review of basic financial statements; rather, it's a meticulous evaluation that takes into account EBITDA, Free Cash Flow, and nuanced factors specific to the industry. In painting a true picture of financial health, recognizing and adjusting for sporadic events, non-operational expenditures, and potential accounting oversights is essential—a feat achieved by Quality of Earnings (QOE) reports.
M\&A activities serve as strategic maneuvers, whether they're carried out for synergy creation, geographical expansion, or market vertical consolidation. Yet, the buyer's or seller's perspectives often dictate the mechanics of the transaction process.
For sellers, each phase of the sell-side M\&A journey is punctuated by the application of deep, yet swift, financial analysis, much like the way security researchers scan for vulnerabilities—quickly identifying glaring issues for further inspection. The ultimate benefits?
Risk identification becomes systematic, thus steering clear of future liabilities. Decision-makers are conferred with nuanced insights that propel strategic moves rooted in a profound understanding of financial standings. This arms them with the edge needed for more incisive negotiations. However, this comprehensive due diligence is not without its tribulations. The process is labor-intensive and demands a level of expertise that spans across accounting, legal, and financial domains. Furthermore, no matter the diligence, a residual risk of undiscovered issues lurks, demanding consistent vigilance and reassessment, as echoed by industry leaders who suggest that ownership and control are crucial elements that need protection throughout transaction proceedings.
Effective financial due diligence extends far beyond mere financial statement analysis—it's a comprehensive evaluation of a company’s various dimensions, from regulatory adherence to IT system integrity. These measures lead to the identification of latent risks, ensuring the company you're scrutinizing is vetted across every relevant sector. A meticulous investigation into financial health examines financial statements, liabilities, liquidity, and forward-looking projections.
Legal and regulatory compliance is equally crucial, with a focus on industry-specific regulations, assessment of tax obligations, and perusal of legal liabilities such as partnerships and licensing agreements. A successful due diligence process entails the formation of a specialized team, where financial, legal, and sector-specific expertise converge. Team members work collaboratively, maintaining confidentiality while keeping stakeholders informed—a practice that engenders transparency and fortifies trust.
Regular updates are crucial as they provide stakeholders with real-time insights into the due diligence outcomes. These are complemented by seeking specialty advice when confronting complex issues, underscoring the importance of a valuation that accurately represents your business's worth, a point stressed by industry experts. Proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges round out the process, equipping decision-makers to navigate negotiations confidently and secure the most advantageous deal possible.
In conclusion, the due diligence process plays a crucial role in any business transaction, providing a comprehensive analysis of a company's financial health and uncovering potential risks. By following key steps in conducting financial due diligence, CFOs can ensure a thorough evaluation and mitigate the possibility of financial compromise.
A case study exemplifies the importance of due diligence in mergers and acquisitions, where a meticulous analysis beyond financial audits is required. This includes assessing the IT infrastructure, data architecture, and potential legal risks of the target company.
The involvement of external professionals, such as lawyers, accountants, and brokers, is vital in achieving adequate planning and risk assessments. Financial due diligence offers various benefits, including a true assessment of enterprise value, nuanced insights for strategic decision-making, and systematic risk identification.
However, challenges such as the labor-intensive nature of the process and the possibility of undiscovered issues require consistent vigilance and reassessment throughout the transaction. To conduct effective due diligence, CFOs should adopt best practices that go beyond financial statement analysis.
This includes evaluating regulatory compliance, assessing tax obligations, and forming a specialized team with diverse expertise. Maintaining transparency through regular updates and seeking specialty advice for complex issues are crucial. Additionally, proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges empower decision-makers to negotiate confidently and secure advantageous deals. In summary, the due diligence process is a critical component of successful business transactions. By adhering to best practices and conducting comprehensive financial due diligence, CFOs can safeguard the financial integrity of their organizations and make informed decisions that align with their long-term vision.
Understanding the Role of Due Diligence in Transactions
Conducting a comprehensive due diligence process is paramount in any business transaction. Rather than a cursory review, an in-depth analysis of the company's financial health is required to uncover any potential risks that might not be immediately apparent.
A meticulous examination of financial statements, assets, customer base, and industry trends is essential. As underscored by experts, one must never underestimate the necessity of a proper valuation.
Engaging the expertise of a qualified business appraiser or valuation professional ensures that the business's worth is accurately assessed—a critical step that forms the linchpin of negotiation. Owners who rely solely on a gut feeling or arbitrary figures when selling may shortchange themselves or dissuade buyers with overstated valuations. An accurate assessment, grounded in concrete data, guarantees that the selling price reflects the true value, guarding against financial compromise.
Financial due diligence is an investigative art that transcends a mere audit to encompass a full spectrum analysis of an organization's inner workings. This meticulous process kicks off with a laser-focused definition of due diligence objectives that position the evaluation within clear goalposts.
The subsequent step is a thorough collection of financial documents such as balance sheets, income statements, tax filings, and binding contracts. These materials then become subject for a nuanced analysis, sifting through them to pinpoint the company's fiscal performance, profitability contours, and liquidity streams.
Each potential risk is then cataloged, from pending legal entanglements and compliance conundrums, to the specter of obscured liabilities. Turning the magnifying glass onto assets and liabilities grants a quantifiable measure of the firm's resources and obligations, taking into consideration the granularity of intellectual property, inventory, and even real estate holdings.
A financial ratio analysis ensues, cutting through the data to unveil insights into the organizational stability, operating efficacy, and the caliber of profitability. Delving deeper still, interviews with management draw out the strategic underpinnings and possible hurdles intrinsic to the company's financial systems. As important as quantifiable data is, due diligence reaches beyond, venturing into the qualitative territory. This aspect scrutinizes market trajectories, competitive ecosystems, and industry-specific regulations. The culmination of these steps is synthesized into a comprehensive report, sagely advising on the advisable steps forward, replete with a sober assessment of any attendant risks.

Navigating the waters of corporate mergers and acquisitions requires a multifaceted approach to due diligence—a mission critical for the success of any deal. Take, for example, the case of ABC Corporation setting its sights on acquiring a promising, yet smaller player, XYZ Corporation, a software development start-up with considerable market potential.
In the throes of this significant transaction, the onus falls on ABC Corporation's CFO to embark on a meticulous analysis beyond the obvious robust revenue growth and solid customer base of XYZ Corporation. Due diligence unfolds as a comprehensive investigation that goes beyond typical financial audits, probing into XYZ’s IT infrastructure, data architecture, and how data is stored, protected, and analyzed.
The CFO must also pay heed to the organization and alignment of XYZ’s various departments. In doing so, the assessment brings to light not just the strengths of the start-up, but also potential risks like unresolved legal battles and impending lawsuits, which cannot be ignored.
As Darshil Shah, an investment banking pro, elucidates, the reasons behind M\&A may be diverse, but the process is rife with complexities requiring strategic insights and methodical steps. The expanse of due diligence spans assessing financial statements, assets, debts, and cash flows, to the more granular like compliance with environmental regulations, tax laws, and evaluation of legal liabilities. The role of external professionals—lawyers, accountants, and brokers—is paramount, each bringing unique value to the table. Their expertise is a safeguard, preventing the common pitfalls of inadequate planning and underestimated risk assessments. In this maneuver, the CFO must present the board with more than just numbers; it demands a narrative that marries financial health with strategic foresight, embedding recommendations that ensure not just the acquisition, but also its harmonious integration into the company’s long-term vision.
Venturing into mergers and acquisitions (M\&A) is akin to navigating a financial minefield, with the proper due diligence as your indispensable map. At its core, the due diligence process scrutinizes the enterprise value of a business, a critical metric gauging its worth.
This assessment isn't merely a review of basic financial statements; rather, it's a meticulous evaluation that takes into account EBITDA, Free Cash Flow, and nuanced factors specific to the industry. In painting a true picture of financial health, recognizing and adjusting for sporadic events, non-operational expenditures, and potential accounting oversights is essential—a feat achieved by Quality of Earnings (QOE) reports.
M\&A activities serve as strategic maneuvers, whether they're carried out for synergy creation, geographical expansion, or market vertical consolidation. Yet, the buyer's or seller's perspectives often dictate the mechanics of the transaction process.
For sellers, each phase of the sell-side M\&A journey is punctuated by the application of deep, yet swift, financial analysis, much like the way security researchers scan for vulnerabilities—quickly identifying glaring issues for further inspection. The ultimate benefits?
Risk identification becomes systematic, thus steering clear of future liabilities. Decision-makers are conferred with nuanced insights that propel strategic moves rooted in a profound understanding of financial standings. This arms them with the edge needed for more incisive negotiations. However, this comprehensive due diligence is not without its tribulations. The process is labor-intensive and demands a level of expertise that spans across accounting, legal, and financial domains. Furthermore, no matter the diligence, a residual risk of undiscovered issues lurks, demanding consistent vigilance and reassessment, as echoed by industry leaders who suggest that ownership and control are crucial elements that need protection throughout transaction proceedings.
Effective financial due diligence extends far beyond mere financial statement analysis—it's a comprehensive evaluation of a company’s various dimensions, from regulatory adherence to IT system integrity. These measures lead to the identification of latent risks, ensuring the company you're scrutinizing is vetted across every relevant sector. A meticulous investigation into financial health examines financial statements, liabilities, liquidity, and forward-looking projections.
Legal and regulatory compliance is equally crucial, with a focus on industry-specific regulations, assessment of tax obligations, and perusal of legal liabilities such as partnerships and licensing agreements. A successful due diligence process entails the formation of a specialized team, where financial, legal, and sector-specific expertise converge. Team members work collaboratively, maintaining confidentiality while keeping stakeholders informed—a practice that engenders transparency and fortifies trust.
Regular updates are crucial as they provide stakeholders with real-time insights into the due diligence outcomes. These are complemented by seeking specialty advice when confronting complex issues, underscoring the importance of a valuation that accurately represents your business's worth, a point stressed by industry experts. Proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges round out the process, equipping decision-makers to navigate negotiations confidently and secure the most advantageous deal possible.
In conclusion, the due diligence process plays a crucial role in any business transaction, providing a comprehensive analysis of a company's financial health and uncovering potential risks. By following key steps in conducting financial due diligence, CFOs can ensure a thorough evaluation and mitigate the possibility of financial compromise.
A case study exemplifies the importance of due diligence in mergers and acquisitions, where a meticulous analysis beyond financial audits is required. This includes assessing the IT infrastructure, data architecture, and potential legal risks of the target company.
The involvement of external professionals, such as lawyers, accountants, and brokers, is vital in achieving adequate planning and risk assessments. Financial due diligence offers various benefits, including a true assessment of enterprise value, nuanced insights for strategic decision-making, and systematic risk identification.
However, challenges such as the labor-intensive nature of the process and the possibility of undiscovered issues require consistent vigilance and reassessment throughout the transaction. To conduct effective due diligence, CFOs should adopt best practices that go beyond financial statement analysis.
This includes evaluating regulatory compliance, assessing tax obligations, and forming a specialized team with diverse expertise. Maintaining transparency through regular updates and seeking specialty advice for complex issues are crucial. Additionally, proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges empower decision-makers to negotiate confidently and secure advantageous deals. In summary, the due diligence process is a critical component of successful business transactions. By adhering to best practices and conducting comprehensive financial due diligence, CFOs can safeguard the financial integrity of their organizations and make informed decisions that align with their long-term vision.
Key Steps in Conducting Financial Due Diligence
Financial due diligence is an investigative art that transcends a mere audit to encompass a full spectrum analysis of an organization's inner workings. This meticulous process kicks off with a laser-focused definition of due diligence objectives that position the evaluation within clear goalposts.
The subsequent step is a thorough collection of financial documents such as balance sheets, income statements, tax filings, and binding contracts. These materials then become subject for a nuanced analysis, sifting through them to pinpoint the company's fiscal performance, profitability contours, and liquidity streams.
Each potential risk is then cataloged, from pending legal entanglements and compliance conundrums, to the specter of obscured liabilities. Turning the magnifying glass onto assets and liabilities grants a quantifiable measure of the firm's resources and obligations, taking into consideration the granularity of intellectual property, inventory, and even real estate holdings.
A financial ratio analysis ensues, cutting through the data to unveil insights into the organizational stability, operating efficacy, and the caliber of profitability. Delving deeper still, interviews with management draw out the strategic underpinnings and possible hurdles intrinsic to the company's financial systems. As important as quantifiable data is, due diligence reaches beyond, venturing into the qualitative territory. This aspect scrutinizes market trajectories, competitive ecosystems, and industry-specific regulations. The culmination of these steps is synthesized into a comprehensive report, sagely advising on the advisable steps forward, replete with a sober assessment of any attendant risks.

Navigating the waters of corporate mergers and acquisitions requires a multifaceted approach to due diligence—a mission critical for the success of any deal. Take, for example, the case of ABC Corporation setting its sights on acquiring a promising, yet smaller player, XYZ Corporation, a software development start-up with considerable market potential.
In the throes of this significant transaction, the onus falls on ABC Corporation's CFO to embark on a meticulous analysis beyond the obvious robust revenue growth and solid customer base of XYZ Corporation. Due diligence unfolds as a comprehensive investigation that goes beyond typical financial audits, probing into XYZ’s IT infrastructure, data architecture, and how data is stored, protected, and analyzed.
The CFO must also pay heed to the organization and alignment of XYZ’s various departments. In doing so, the assessment brings to light not just the strengths of the start-up, but also potential risks like unresolved legal battles and impending lawsuits, which cannot be ignored.
As Darshil Shah, an investment banking pro, elucidates, the reasons behind M\&A may be diverse, but the process is rife with complexities requiring strategic insights and methodical steps. The expanse of due diligence spans assessing financial statements, assets, debts, and cash flows, to the more granular like compliance with environmental regulations, tax laws, and evaluation of legal liabilities. The role of external professionals—lawyers, accountants, and brokers—is paramount, each bringing unique value to the table. Their expertise is a safeguard, preventing the common pitfalls of inadequate planning and underestimated risk assessments. In this maneuver, the CFO must present the board with more than just numbers; it demands a narrative that marries financial health with strategic foresight, embedding recommendations that ensure not just the acquisition, but also its harmonious integration into the company’s long-term vision.
Venturing into mergers and acquisitions (M\&A) is akin to navigating a financial minefield, with the proper due diligence as your indispensable map. At its core, the due diligence process scrutinizes the enterprise value of a business, a critical metric gauging its worth.
This assessment isn't merely a review of basic financial statements; rather, it's a meticulous evaluation that takes into account EBITDA, Free Cash Flow, and nuanced factors specific to the industry. In painting a true picture of financial health, recognizing and adjusting for sporadic events, non-operational expenditures, and potential accounting oversights is essential—a feat achieved by Quality of Earnings (QOE) reports.
M\&A activities serve as strategic maneuvers, whether they're carried out for synergy creation, geographical expansion, or market vertical consolidation. Yet, the buyer's or seller's perspectives often dictate the mechanics of the transaction process.
For sellers, each phase of the sell-side M\&A journey is punctuated by the application of deep, yet swift, financial analysis, much like the way security researchers scan for vulnerabilities—quickly identifying glaring issues for further inspection. The ultimate benefits?
Risk identification becomes systematic, thus steering clear of future liabilities. Decision-makers are conferred with nuanced insights that propel strategic moves rooted in a profound understanding of financial standings. This arms them with the edge needed for more incisive negotiations. However, this comprehensive due diligence is not without its tribulations. The process is labor-intensive and demands a level of expertise that spans across accounting, legal, and financial domains. Furthermore, no matter the diligence, a residual risk of undiscovered issues lurks, demanding consistent vigilance and reassessment, as echoed by industry leaders who suggest that ownership and control are crucial elements that need protection throughout transaction proceedings.
Effective financial due diligence extends far beyond mere financial statement analysis—it's a comprehensive evaluation of a company’s various dimensions, from regulatory adherence to IT system integrity. These measures lead to the identification of latent risks, ensuring the company you're scrutinizing is vetted across every relevant sector. A meticulous investigation into financial health examines financial statements, liabilities, liquidity, and forward-looking projections.
Legal and regulatory compliance is equally crucial, with a focus on industry-specific regulations, assessment of tax obligations, and perusal of legal liabilities such as partnerships and licensing agreements. A successful due diligence process entails the formation of a specialized team, where financial, legal, and sector-specific expertise converge. Team members work collaboratively, maintaining confidentiality while keeping stakeholders informed—a practice that engenders transparency and fortifies trust.
Regular updates are crucial as they provide stakeholders with real-time insights into the due diligence outcomes. These are complemented by seeking specialty advice when confronting complex issues, underscoring the importance of a valuation that accurately represents your business's worth, a point stressed by industry experts. Proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges round out the process, equipping decision-makers to navigate negotiations confidently and secure the most advantageous deal possible.
In conclusion, the due diligence process plays a crucial role in any business transaction, providing a comprehensive analysis of a company's financial health and uncovering potential risks. By following key steps in conducting financial due diligence, CFOs can ensure a thorough evaluation and mitigate the possibility of financial compromise.
A case study exemplifies the importance of due diligence in mergers and acquisitions, where a meticulous analysis beyond financial audits is required. This includes assessing the IT infrastructure, data architecture, and potential legal risks of the target company.
The involvement of external professionals, such as lawyers, accountants, and brokers, is vital in achieving adequate planning and risk assessments. Financial due diligence offers various benefits, including a true assessment of enterprise value, nuanced insights for strategic decision-making, and systematic risk identification.
However, challenges such as the labor-intensive nature of the process and the possibility of undiscovered issues require consistent vigilance and reassessment throughout the transaction. To conduct effective due diligence, CFOs should adopt best practices that go beyond financial statement analysis.
This includes evaluating regulatory compliance, assessing tax obligations, and forming a specialized team with diverse expertise. Maintaining transparency through regular updates and seeking specialty advice for complex issues are crucial. Additionally, proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges empower decision-makers to negotiate confidently and secure advantageous deals. In summary, the due diligence process is a critical component of successful business transactions. By adhering to best practices and conducting comprehensive financial due diligence, CFOs can safeguard the financial integrity of their organizations and make informed decisions that align with their long-term vision.
Case Study: A Comprehensive Example of Financial Due Diligence
Navigating the waters of corporate mergers and acquisitions requires a multifaceted approach to due diligence—a mission critical for the success of any deal. Take, for example, the case of ABC Corporation setting its sights on acquiring a promising, yet smaller player, XYZ Corporation, a software development start-up with considerable market potential.
In the throes of this significant transaction, the onus falls on ABC Corporation's CFO to embark on a meticulous analysis beyond the obvious robust revenue growth and solid customer base of XYZ Corporation. Due diligence unfolds as a comprehensive investigation that goes beyond typical financial audits, probing into XYZ’s IT infrastructure, data architecture, and how data is stored, protected, and analyzed.
The CFO must also pay heed to the organization and alignment of XYZ’s various departments. In doing so, the assessment brings to light not just the strengths of the start-up, but also potential risks like unresolved legal battles and impending lawsuits, which cannot be ignored.
As Darshil Shah, an investment banking pro, elucidates, the reasons behind M\&A may be diverse, but the process is rife with complexities requiring strategic insights and methodical steps. The expanse of due diligence spans assessing financial statements, assets, debts, and cash flows, to the more granular like compliance with environmental regulations, tax laws, and evaluation of legal liabilities. The role of external professionals—lawyers, accountants, and brokers—is paramount, each bringing unique value to the table. Their expertise is a safeguard, preventing the common pitfalls of inadequate planning and underestimated risk assessments. In this maneuver, the CFO must present the board with more than just numbers; it demands a narrative that marries financial health with strategic foresight, embedding recommendations that ensure not just the acquisition, but also its harmonious integration into the company’s long-term vision.
Venturing into mergers and acquisitions (M\&A) is akin to navigating a financial minefield, with the proper due diligence as your indispensable map. At its core, the due diligence process scrutinizes the enterprise value of a business, a critical metric gauging its worth.
This assessment isn't merely a review of basic financial statements; rather, it's a meticulous evaluation that takes into account EBITDA, Free Cash Flow, and nuanced factors specific to the industry. In painting a true picture of financial health, recognizing and adjusting for sporadic events, non-operational expenditures, and potential accounting oversights is essential—a feat achieved by Quality of Earnings (QOE) reports.
M\&A activities serve as strategic maneuvers, whether they're carried out for synergy creation, geographical expansion, or market vertical consolidation. Yet, the buyer's or seller's perspectives often dictate the mechanics of the transaction process.
For sellers, each phase of the sell-side M\&A journey is punctuated by the application of deep, yet swift, financial analysis, much like the way security researchers scan for vulnerabilities—quickly identifying glaring issues for further inspection. The ultimate benefits?
Risk identification becomes systematic, thus steering clear of future liabilities. Decision-makers are conferred with nuanced insights that propel strategic moves rooted in a profound understanding of financial standings. This arms them with the edge needed for more incisive negotiations. However, this comprehensive due diligence is not without its tribulations. The process is labor-intensive and demands a level of expertise that spans across accounting, legal, and financial domains. Furthermore, no matter the diligence, a residual risk of undiscovered issues lurks, demanding consistent vigilance and reassessment, as echoed by industry leaders who suggest that ownership and control are crucial elements that need protection throughout transaction proceedings.
Effective financial due diligence extends far beyond mere financial statement analysis—it's a comprehensive evaluation of a company’s various dimensions, from regulatory adherence to IT system integrity. These measures lead to the identification of latent risks, ensuring the company you're scrutinizing is vetted across every relevant sector. A meticulous investigation into financial health examines financial statements, liabilities, liquidity, and forward-looking projections.
Legal and regulatory compliance is equally crucial, with a focus on industry-specific regulations, assessment of tax obligations, and perusal of legal liabilities such as partnerships and licensing agreements. A successful due diligence process entails the formation of a specialized team, where financial, legal, and sector-specific expertise converge. Team members work collaboratively, maintaining confidentiality while keeping stakeholders informed—a practice that engenders transparency and fortifies trust.
Regular updates are crucial as they provide stakeholders with real-time insights into the due diligence outcomes. These are complemented by seeking specialty advice when confronting complex issues, underscoring the importance of a valuation that accurately represents your business's worth, a point stressed by industry experts. Proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges round out the process, equipping decision-makers to navigate negotiations confidently and secure the most advantageous deal possible.
In conclusion, the due diligence process plays a crucial role in any business transaction, providing a comprehensive analysis of a company's financial health and uncovering potential risks. By following key steps in conducting financial due diligence, CFOs can ensure a thorough evaluation and mitigate the possibility of financial compromise.
A case study exemplifies the importance of due diligence in mergers and acquisitions, where a meticulous analysis beyond financial audits is required. This includes assessing the IT infrastructure, data architecture, and potential legal risks of the target company.
The involvement of external professionals, such as lawyers, accountants, and brokers, is vital in achieving adequate planning and risk assessments. Financial due diligence offers various benefits, including a true assessment of enterprise value, nuanced insights for strategic decision-making, and systematic risk identification.
However, challenges such as the labor-intensive nature of the process and the possibility of undiscovered issues require consistent vigilance and reassessment throughout the transaction. To conduct effective due diligence, CFOs should adopt best practices that go beyond financial statement analysis.
This includes evaluating regulatory compliance, assessing tax obligations, and forming a specialized team with diverse expertise. Maintaining transparency through regular updates and seeking specialty advice for complex issues are crucial. Additionally, proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges empower decision-makers to negotiate confidently and secure advantageous deals. In summary, the due diligence process is a critical component of successful business transactions. By adhering to best practices and conducting comprehensive financial due diligence, CFOs can safeguard the financial integrity of their organizations and make informed decisions that align with their long-term vision.
Benefits and Challenges of Financial Due Diligence
Venturing into mergers and acquisitions (M\&A) is akin to navigating a financial minefield, with the proper due diligence as your indispensable map. At its core, the due diligence process scrutinizes the enterprise value of a business, a critical metric gauging its worth.
This assessment isn't merely a review of basic financial statements; rather, it's a meticulous evaluation that takes into account EBITDA, Free Cash Flow, and nuanced factors specific to the industry. In painting a true picture of financial health, recognizing and adjusting for sporadic events, non-operational expenditures, and potential accounting oversights is essential—a feat achieved by Quality of Earnings (QOE) reports.
M\&A activities serve as strategic maneuvers, whether they're carried out for synergy creation, geographical expansion, or market vertical consolidation. Yet, the buyer's or seller's perspectives often dictate the mechanics of the transaction process.
For sellers, each phase of the sell-side M\&A journey is punctuated by the application of deep, yet swift, financial analysis, much like the way security researchers scan for vulnerabilities—quickly identifying glaring issues for further inspection. The ultimate benefits?
Risk identification becomes systematic, thus steering clear of future liabilities. Decision-makers are conferred with nuanced insights that propel strategic moves rooted in a profound understanding of financial standings. This arms them with the edge needed for more incisive negotiations. However, this comprehensive due diligence is not without its tribulations. The process is labor-intensive and demands a level of expertise that spans across accounting, legal, and financial domains. Furthermore, no matter the diligence, a residual risk of undiscovered issues lurks, demanding consistent vigilance and reassessment, as echoed by industry leaders who suggest that ownership and control are crucial elements that need protection throughout transaction proceedings.
Effective financial due diligence extends far beyond mere financial statement analysis—it's a comprehensive evaluation of a company’s various dimensions, from regulatory adherence to IT system integrity. These measures lead to the identification of latent risks, ensuring the company you're scrutinizing is vetted across every relevant sector. A meticulous investigation into financial health examines financial statements, liabilities, liquidity, and forward-looking projections.
Legal and regulatory compliance is equally crucial, with a focus on industry-specific regulations, assessment of tax obligations, and perusal of legal liabilities such as partnerships and licensing agreements. A successful due diligence process entails the formation of a specialized team, where financial, legal, and sector-specific expertise converge. Team members work collaboratively, maintaining confidentiality while keeping stakeholders informed—a practice that engenders transparency and fortifies trust.
Regular updates are crucial as they provide stakeholders with real-time insights into the due diligence outcomes. These are complemented by seeking specialty advice when confronting complex issues, underscoring the importance of a valuation that accurately represents your business's worth, a point stressed by industry experts. Proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges round out the process, equipping decision-makers to navigate negotiations confidently and secure the most advantageous deal possible.
In conclusion, the due diligence process plays a crucial role in any business transaction, providing a comprehensive analysis of a company's financial health and uncovering potential risks. By following key steps in conducting financial due diligence, CFOs can ensure a thorough evaluation and mitigate the possibility of financial compromise.
A case study exemplifies the importance of due diligence in mergers and acquisitions, where a meticulous analysis beyond financial audits is required. This includes assessing the IT infrastructure, data architecture, and potential legal risks of the target company.
The involvement of external professionals, such as lawyers, accountants, and brokers, is vital in achieving adequate planning and risk assessments. Financial due diligence offers various benefits, including a true assessment of enterprise value, nuanced insights for strategic decision-making, and systematic risk identification.
However, challenges such as the labor-intensive nature of the process and the possibility of undiscovered issues require consistent vigilance and reassessment throughout the transaction. To conduct effective due diligence, CFOs should adopt best practices that go beyond financial statement analysis.
This includes evaluating regulatory compliance, assessing tax obligations, and forming a specialized team with diverse expertise. Maintaining transparency through regular updates and seeking specialty advice for complex issues are crucial. Additionally, proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges empower decision-makers to negotiate confidently and secure advantageous deals. In summary, the due diligence process is a critical component of successful business transactions. By adhering to best practices and conducting comprehensive financial due diligence, CFOs can safeguard the financial integrity of their organizations and make informed decisions that align with their long-term vision.
Best Practices for Effective Due Diligence
Effective financial due diligence extends far beyond mere financial statement analysis—it's a comprehensive evaluation of a company’s various dimensions, from regulatory adherence to IT system integrity. These measures lead to the identification of latent risks, ensuring the company you're scrutinizing is vetted across every relevant sector. A meticulous investigation into financial health examines financial statements, liabilities, liquidity, and forward-looking projections.
Legal and regulatory compliance is equally crucial, with a focus on industry-specific regulations, assessment of tax obligations, and perusal of legal liabilities such as partnerships and licensing agreements. A successful due diligence process entails the formation of a specialized team, where financial, legal, and sector-specific expertise converge. Team members work collaboratively, maintaining confidentiality while keeping stakeholders informed—a practice that engenders transparency and fortifies trust.
Regular updates are crucial as they provide stakeholders with real-time insights into the due diligence outcomes. These are complemented by seeking specialty advice when confronting complex issues, underscoring the importance of a valuation that accurately represents your business's worth, a point stressed by industry experts. Proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges round out the process, equipping decision-makers to navigate negotiations confidently and secure the most advantageous deal possible.
In conclusion, the due diligence process plays a crucial role in any business transaction, providing a comprehensive analysis of a company's financial health and uncovering potential risks. By following key steps in conducting financial due diligence, CFOs can ensure a thorough evaluation and mitigate the possibility of financial compromise.
A case study exemplifies the importance of due diligence in mergers and acquisitions, where a meticulous analysis beyond financial audits is required. This includes assessing the IT infrastructure, data architecture, and potential legal risks of the target company.
The involvement of external professionals, such as lawyers, accountants, and brokers, is vital in achieving adequate planning and risk assessments. Financial due diligence offers various benefits, including a true assessment of enterprise value, nuanced insights for strategic decision-making, and systematic risk identification.
However, challenges such as the labor-intensive nature of the process and the possibility of undiscovered issues require consistent vigilance and reassessment throughout the transaction. To conduct effective due diligence, CFOs should adopt best practices that go beyond financial statement analysis.
This includes evaluating regulatory compliance, assessing tax obligations, and forming a specialized team with diverse expertise. Maintaining transparency through regular updates and seeking specialty advice for complex issues are crucial. Additionally, proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges empower decision-makers to negotiate confidently and secure advantageous deals. In summary, the due diligence process is a critical component of successful business transactions. By adhering to best practices and conducting comprehensive financial due diligence, CFOs can safeguard the financial integrity of their organizations and make informed decisions that align with their long-term vision.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the due diligence process plays a crucial role in any business transaction, providing a comprehensive analysis of a company's financial health and uncovering potential risks. By following key steps in conducting financial due diligence, CFOs can ensure a thorough evaluation and mitigate the possibility of financial compromise.
A case study exemplifies the importance of due diligence in mergers and acquisitions, where a meticulous analysis beyond financial audits is required. This includes assessing the IT infrastructure, data architecture, and potential legal risks of the target company.
The involvement of external professionals, such as lawyers, accountants, and brokers, is vital in achieving adequate planning and risk assessments. Financial due diligence offers various benefits, including a true assessment of enterprise value, nuanced insights for strategic decision-making, and systematic risk identification.
However, challenges such as the labor-intensive nature of the process and the possibility of undiscovered issues require consistent vigilance and reassessment throughout the transaction. To conduct effective due diligence, CFOs should adopt best practices that go beyond financial statement analysis.
This includes evaluating regulatory compliance, assessing tax obligations, and forming a specialized team with diverse expertise. Maintaining transparency through regular updates and seeking specialty advice for complex issues are crucial. Additionally, proactive risk management and anticipation of challenges empower decision-makers to negotiate confidently and secure advantageous deals. In summary, the due diligence process is a critical component of successful business transactions. By adhering to best practices and conducting comprehensive financial due diligence, CFOs can safeguard the financial integrity of their organizations and make informed decisions that align with their long-term vision.




