Overview
This article delineates the essential steps in stakeholder management, pivotal for achieving effective engagement and ensuring project success. It underscores the significance of identifying stakeholders, analyzing their interests and influence, planning engagement strategies, and monitoring participation. These critical processes are bolstered by compelling case studies that highlight the necessity of proactive communication and tailored strategies in overcoming challenges and fostering collaboration. By implementing these strategies, organizations can navigate complexities and enhance their collaborative efforts.
Introduction
In the realm of project management, the significance of stakeholders is paramount. These individuals and groups, each with their distinct interests and influence, form the backbone of any successful initiative. Understanding who these stakeholders are and how to effectively engage them is crucial for aligning project goals with their expectations.
As organizations increasingly recognize the impact of stakeholder management on project outcomes, the necessity for structured approaches has never been more evident. From identifying key players to analyzing their interests, planning engagement strategies, and monitoring effectiveness, the journey to mastering stakeholder management is both intricate and essential.
This article explores the critical steps and real-world applications that can empower project managers to navigate this complex landscape and enhance project success.
1. Name: Understanding Stakeholders: The Foundation of Effective Management
Stakeholders encompass a diverse array of individuals and groups engaged in an initiative or organization, each possessing the potential to influence or be influenced by outcomes. Recognizing the various types of interested parties—internal entities such as employees and management, alongside external groups including customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies—is crucial for the of these entities. This understanding lays the groundwork for aligning objectives with participant expectations and interests.
By precisely identifying stakeholders, managers can implement to develop targeted engagement and communication approaches that significantly enhance success rates. Notably, studies indicate that 87% of senior leaders grasp the , underscoring the necessity for robust participation from upper leadership to avert failures. The lack of is cited as a primary reason for initiative failures, as illustrated in the case study titled 'Understanding of Project Practices by Senior Managers.'
Furthermore, the —initiative, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closure—provide a framework for understanding how participant oversight integrates within the broader administration process. Additionally, with 79% of high-performing organizations utilizing PM software tool training, it becomes evident that . In this context, the significance of [stakeholder management processes](https://smbdistress.com/services) is paramount, as it not only propels success but also cultivates a collaborative environment conducive to achieving strategic objectives.
2. Step 1: Identifying Your Stakeholders
To effectively identify interested parties, it is crucial to begin by who may be affected by or have the capacity to influence the project. This is a key step in the . Utilize a range of techniques such as brainstorming sessions, participant questionnaires, and environmental assessments to gather . A is essential; therefore, creating a is advised.
This register should outline each participant's role, interests, and level of influence on the initiative, ensuring that no one is overlooked. As aptly states,
By communicating with interested parties early and frequently, you can ensure that they fully understand what you are doing and recognize the advantages of your initiative.
This can lead to active support when necessary.
Moreover, understanding the importance of is essential for obtaining ongoing participation and support throughout the initiative's lifecycle. Recent instances, such as an offshore wind initiative that employed multi-dimensional and geographical mapping techniques, emphasize the effectiveness of various participant involvement methods. Furthermore, the case study titled 'Creating a Participatory Process' illustrates the importance of and treating them as equals, fostering inclusivity and empowering marginalized populations, thus enhancing the overall effectiveness of community initiatives.
Such comprehensive approaches not only enhance participation but also lay the groundwork for throughout the project's lifecycle.
3. Step 2: Analyzing Stakeholder Interests and Influence
Upon identifying the involved parties, the critical next step in is to effectively analyze their interests and influence. This analysis is often facilitated by employing tools such as the , which classifies stakeholders into four distinct categories:
- High Power, High Interest
- High Power, Low Interest
- Low Power, High Interest
- Low Power, Low Interest
This strategic categorization is essential for prioritizing , ensuring that those wielding significant influence over the initiative receive the necessary attention and communication.
As one expert notes,
I’ve found these : Current position on the project, Level of influence in the organization, Specific interests and concerns, Potential impacts on their role or department, and Historical relationship with similar initiatives.
This comprehensive approach emphasizes the significance of understanding and incorporates to guide decision-making processes. For instance, case studies demonstrate that recognizing involved parties in the 'Fourth Quadrant'—those with low power and low interest—can lead to maintaining and a responsive approach, aligning communications with their limited influence.
Involving interested parties in this quadrant is vital for stakeholder management, as they can still affect views of the initiative. Moreover, instances of , such as energy initiatives, healthcare facility planning, and education policy reforms, illustrate how these strategies can be effectively executed in various contexts. The recent offshore wind initiative showcased sophisticated participant mapping methods, incorporating geographical mapping and relationship network diagrams, thus improving consultation and involvement strategies.
Ultimately, employing a straightforward 1-5 scoring system within stakeholder management can further enhance the evaluation of each participant's . This offers a solid framework for engagement, ensuring that all individuals are effectively assessed and involved.
4. Step 3: Planning Effective Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
Developing an is essential for successful in project management. This plan should clearly outline the stakeholder management steps, specifying how with various parties, detailing the methods, frequency, and tailored messages for each group according to their specific interests and influence. Observing and evaluating through a comprehensive is a key aspect of the stakeholder management steps, allowing essential participants to align on priorities and understand the situation beyond mere numbers. This leads to deeper insights into the business's challenges and opportunities.
Recent insights from PwC indicate that utilizing visual tools such as dashboards and infographics can enhance comprehension and retention of information by up to 70%. These methods are particularly beneficial in communications with interested parties. Incorporating feedback mechanisms, including surveys and regular check-ins, is crucial in the stakeholder management steps, allowing for ongoing involvement and the flexibility to adjust strategies as necessary. A case study on active listening and responsiveness highlights that participants appreciate when their concerns are genuinely acknowledged.
Leaders who prioritize stakeholder management steps not only reinforce support but also mitigate potential misunderstandings and resistance. As Raghunath Reddy Koilakonda observes, 'In conclusion, the stakeholder management steps involving interested parties are complicated,' which underscores the significance of a well-organized method. Furthermore, identifying and planning to address can facilitate real-time analytics for .
Participating in gatherings such as the CFO Summit London 2024, showcasing presentations from prominent firms, can offer valuable insights into current trends and strategies in management. Ultimately, nurturing a cooperative environment that highlights trust and openness is essential for the stakeholder management steps of interested parties.
5. Step 4: Implementing and Monitoring Stakeholder Engagement
The successful execution of hinges on consistent effort and adherence to the established plan. To keep interested parties informed and actively engaged, it is essential to follow stakeholder management steps that include:
- Regular updates
- Open communication channels
is equally vital in the stakeholder management steps; this encompasses:
- in meetings
- Collecting feedback
- Evaluating
All of which are directly connected to project milestones and interaction activities.
Recent metrics indicate that an alpha for .7, underscoring the importance of quantitatively measuring engagement. As Justin Lagac aptly stated, "Having lets you measure the success of initiatives and ensure your investments are being directed in the right places." Furthermore, strategies for tracking participant satisfaction have evolved, allowing organizations to better gauge retention rates and calculate ROI based on costs and benefits.
For instance, the Community Integration Measure assessed feelings of belonging among older African Americans participating in research and revealed a significant connection between community involvement and overall well-being. This case study demonstrates how effective strategies for involving interested parties can strengthen community connections and enhance participant results. Recent developments in monitoring participant involvement now include that provide deeper insights into interaction patterns and participant sentiments, enabling organizations to make proactively.
Such insights emphasize the necessity of making adjustments based on monitoring outcomes as part of the stakeholder management steps to enhance participation and proactively address emerging issues.
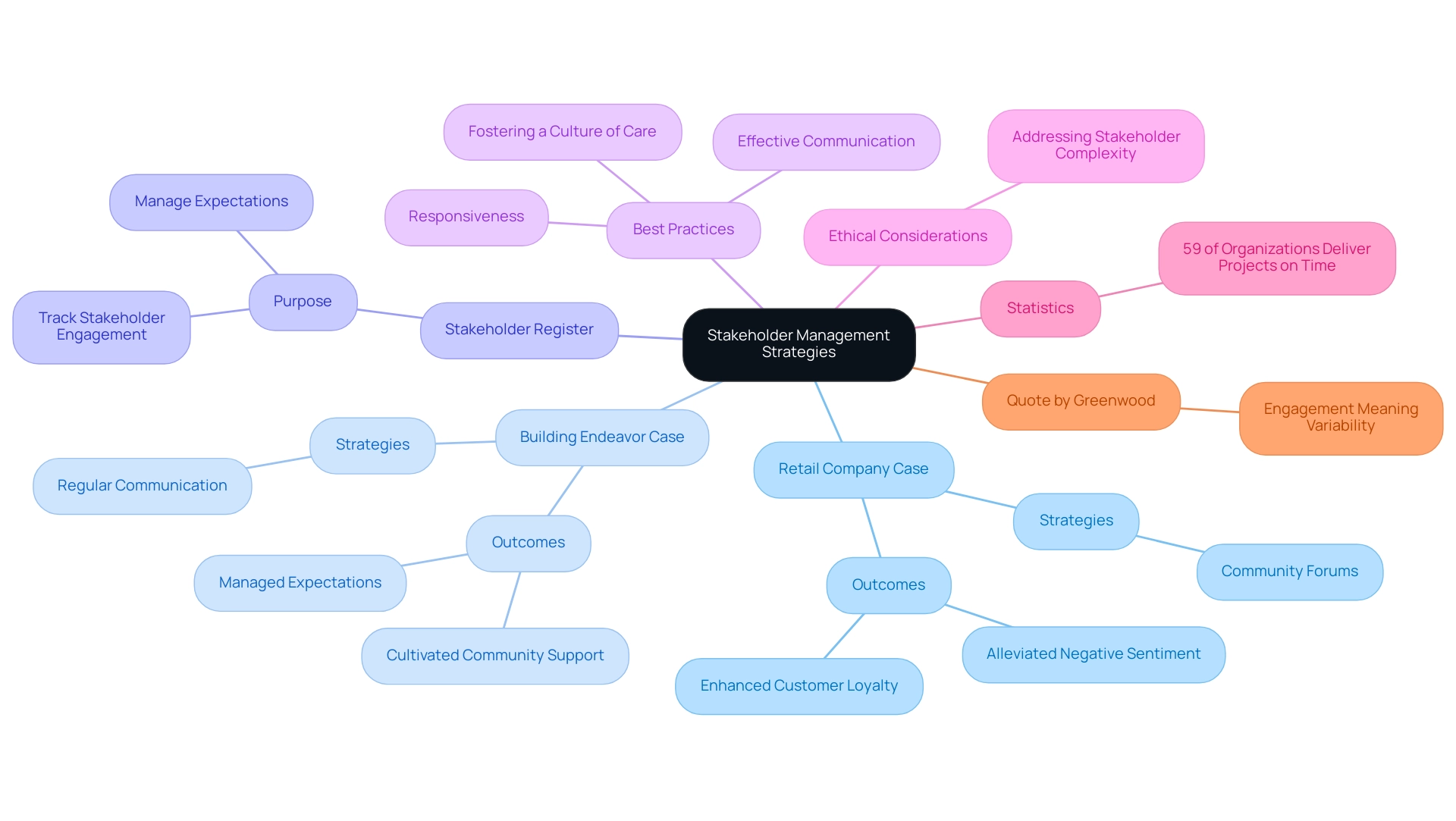
6. Real-World Applications: Case Studies in Stakeholder Management
An examination of recent case studies on successful highlights . A notable retail company, for instance, faced significant public backlash following a product recall. In response, they organized community forums, proactively inviting feedback from interested parties.
This strategy not only alleviated negative sentiment but also enhanced customer loyalty, showcasing the power of open dialogue and responsiveness. Likewise, a building endeavor demonstrated by ensuring regular communication with local inhabitants and officials about progress and possible disturbances. This approach helped manage expectations and cultivate .
Moreover, the participant register acts as an essential resource for managers to monitor participant involvement and handle expectations efficiently, emphasizing the significance of steps in participant oversight. These cases demonstrate that by , applying customized involvement strategies, and ensuring , organizations can achieve positive results for both participants and goals. Notably, statistics reveal that 59% of organizations using delivered projects on time, underscoring the effectiveness of structured approaches.
Greenwood aptly observes that the exaggerated portrayal of participant involvement yields an unclear truth: the involvement of contributors can signify various meanings to different individuals. Addressing is not only effective but also responsible.
7. Overcoming Challenges in Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder coordination presents a multitude of challenges, including , inadequate involvement, and . Notably, studies indicate that nearly 50% of initiative failures stem from insufficient and oversight, underscoring the critical need for . For instance, a telecom firm simplified its service offerings, resulting in a substantial reduction in the Customer Effort Score (CES), exemplifying the impact of .
To navigate these obstacles, managers must prioritize steps through consistent communication and active listening. The case study titled 'Combatting Stakeholder Issues' exemplifies how meticulous engagement with stakeholders can assess their influence on initiatives and develop a to mitigate challenges. Implementing techniques such as conflict resolution workshops and participant feedback sessions can be invaluable in addressing concerns and fostering collaboration.
Moreover, while the role of artificial intelligence in participant engagement may be limited due to the necessity for high emotional intelligence, integrating management software can significantly enhance communication. This ensures that participants remain informed and engaged throughout the project lifecycle. By anticipating potential challenges and equipping themselves with strategic responses, project managers can improve and facilitate smoother project execution, ultimately leading to greater .
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective stakeholder management stands as a strategic necessity rather than a mere tactical endeavor. It is the cornerstone of successful project execution, aligning project goals with the diverse interests of all involved parties. As the landscape of project management continues to evolve, mastering the art of stakeholder engagement will remain paramount in achieving desired outcomes. By investing in these relationships and continuously refining engagement strategies, project managers can ensure that their projects not only meet expectations but also contribute positively to broader organizational goals.
The journey towards effective stakeholder management begins with:
- Recognizing stakeholders
- Analyzing their interests and influence
- Planning, implementing, and monitoring engagement strategies
Organizations that prioritize open dialogue and responsiveness not only mitigate risks but cultivate a supportive environment that drives project success. Therefore, the call to action is clear: embrace structured approaches to stakeholder management to transform potential setbacks into opportunities for building trust and loyalty.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are stakeholders in an organization?
Stakeholders are diverse individuals and groups engaged in an initiative or organization, each having the potential to influence or be influenced by its outcomes. They include both internal entities, such as employees and management, and external groups, such as customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies.
Why is it important to recognize different types of stakeholders?
Recognizing different types of stakeholders is crucial for stakeholder management processes, as it helps align objectives with participant expectations and interests, ultimately enhancing the success rates of initiatives.
How can managers effectively manage stakeholders?
Managers can effectively manage stakeholders by precisely identifying them and implementing targeted engagement and communication strategies. This approach significantly enhances the chances of success for initiatives.
What role does senior leadership play in stakeholder management?
Senior leadership plays a critical role in stakeholder management, as their robust participation is necessary to avoid initiative failures. Studies indicate that a lack of senior leadership involvement is a primary reason for such failures.
What are the five essential phases of the project management (PM) lifecycle?
The five essential phases of the PM lifecycle are initiative, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closure. These phases provide a framework for understanding how participant oversight integrates within the broader administration process.
How does training contribute to effective stakeholder management?
Effective training is vital for enhancing participant coordination capabilities. Research shows that 79% of high-performing organizations utilize PM software tool training to improve stakeholder management processes.
What is the importance of mapping out interested parties?
Mapping out interested parties is crucial for the stakeholder management process as it helps identify all potential individuals or groups who may be affected by or have the capacity to influence the project.
What techniques can be used to identify stakeholders?
Techniques for identifying stakeholders include brainstorming sessions, participant questionnaires, and environmental assessments to gather comprehensive insights.
What is a participant register and why is it important?
A participant register outlines each participant's role, interests, and level of influence on the initiative. It is important to ensure that no one is overlooked and to facilitate effective communication and engagement.
How can proactive communication with stakeholders benefit an initiative?
Proactive communication with stakeholders ensures they understand the initiative and recognize its advantages, which can lead to active support when necessary.
Why is long-term involvement with stakeholders essential?
Long-term involvement with stakeholders is essential for obtaining ongoing participation and support throughout the initiative's lifecycle, contributing to the overall success of the project.
What is the significance of inclusivity in stakeholder engagement?
Inclusivity in stakeholder engagement fosters empowerment among marginalized populations and enhances the overall effectiveness of community initiatives by attracting representatives from all interest groups and treating them as equals.




