Overview
The article elucidates that Asset-Based Lending (ABL) represents loans secured by a borrower's assets, including accounts receivable, inventory, or equipment. This financing method empowers businesses to leverage their tangible assets effectively.
Particularly during economic downturns, ABL becomes crucial, offering flexible terms and reduced borrowing costs. This makes it an indispensable financing option for companies grappling with cash flow challenges.
By understanding ABL, businesses can navigate financial hurdles with greater confidence and resilience.
Introduction
Asset-Based Lending (ABL) stands as a pivotal financial strategy, especially for businesses navigating the uncertainties of economic fluctuations. By leveraging tangible assets such as accounts receivable and inventory, companies can secure funding that traditional loans may not provide, thereby enhancing their financial flexibility.
However, as the lending landscape evolves, what are the key features and benefits of ABL that render it a compelling choice for enterprises? Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their financial strategies and maintain operational resilience.
Define Asset-Based Lending (ABL)
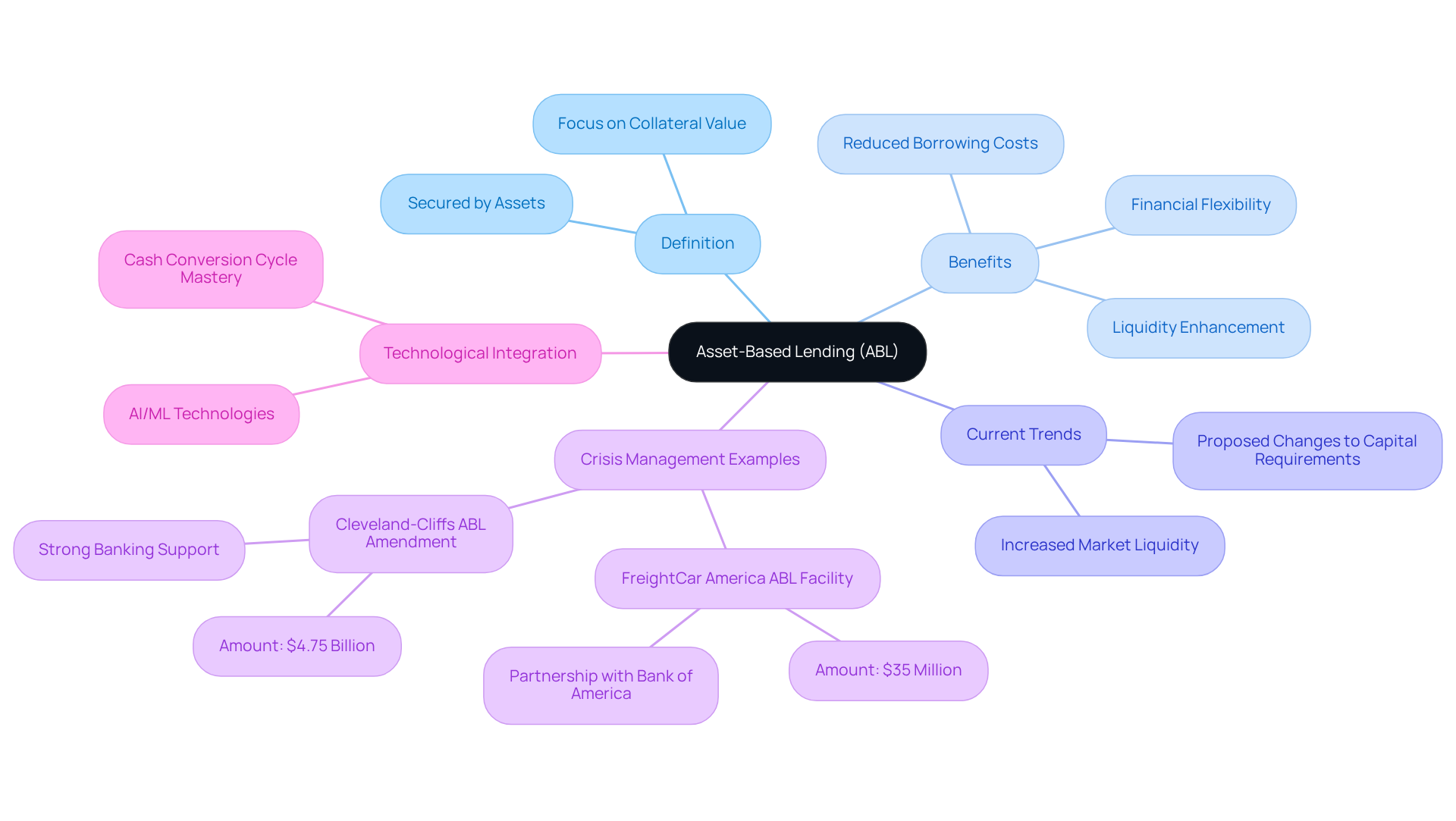
Asset-Backed Lending (ABL), which is encapsulated in the term 'abl facility meaning', represents a strategic financial arrangement where loans are secured by the borrower's assets, such as accounts receivable, inventory, or equipment. Unlike traditional loans that primarily assess cash flow, the ABL facility meaning emphasizes the intrinsic value of the collateral provided. This approach empowers companies, particularly small to medium-sized enterprises, to secure funding based on the tangible worth of their assets, illustrating the abl facility meaning as a versatile financing option crucial during financial strain. Current trends indicate that proposed adjustments to financial requirements could bolster liquidity within the asset-backed lending sector, which highlights the abl facility meaning and encourages more businesses to embrace this financing method.
Noteworthy instances of ABL in crisis management include FreightCar America, which successfully secured a $35 million ABL credit facility, illustrating the abl facility meaning of enhancing financial flexibility and supporting growth strategies. Michael Riordan, CFO of FreightCar America, expressed enthusiasm about the partnership with Bank of America, highlighting that this arrangement marks a significant milestone in their extensive refinancing efforts, thereby improving their capacity to meet operational funding needs and optimize borrowing costs. Financial experts assert that the meaning of the ABL facility not only fulfills working capital demands but also reduces borrowing expenses, making it an attractive option for enterprises navigating challenging economic climates.
Furthermore, the integration of expert advice and the application of AI/ML technologies can significantly enhance ABL efficiency, particularly in mastering the cash conversion cycle and improving overall organizational performance.
Context and Importance of ABL in Business Financing
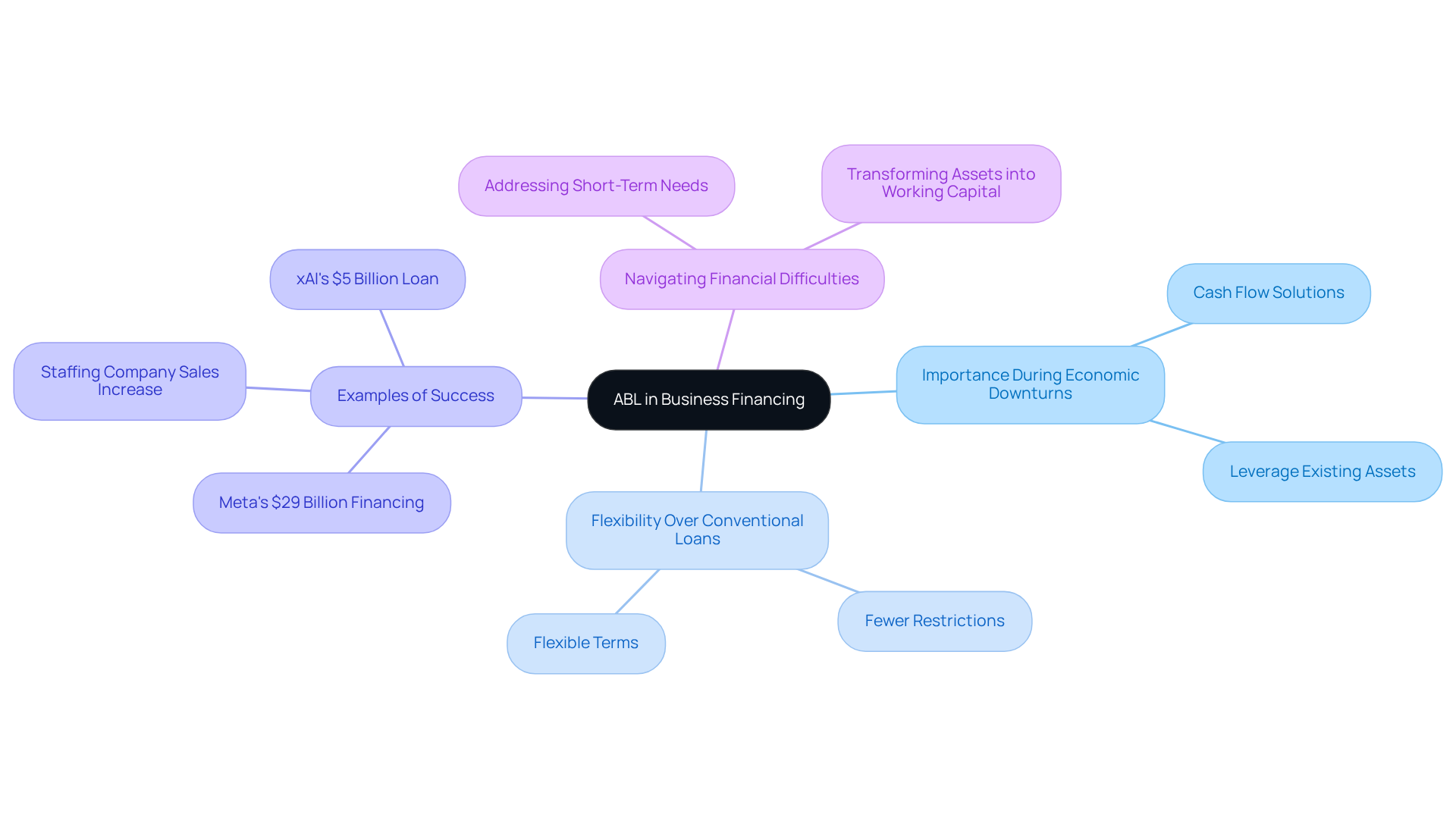
The ABL facility meaning has emerged as a crucial financing option for enterprises, particularly during economic downturns or periods of uncertainty. In 2025, a considerable portion of enterprises are grappling with cash flow issues, making the ABL facility meaning an appealing choice to leverage current resources for essential financing. This approach is particularly advantageous for businesses with significant inventories or receivables, as it helps them understand the ABL facility meaning while transforming these assets into working capital.
The term 'ABL facility meaning' typically refers to loans that offer fewer restrictions than conventional loans, featuring more flexible terms and fewer covenants. For instance, a large staffing company successfully doubled its borrowing capacity from $1 million to $2.5 million through ABL, resulting in over $5 million in increased sales.
Moreover, during recent economic fluctuations, companies like Meta secured a $29 billion financing package for data center expansion, which highlights the ABL facility meaning in facilitating growth amidst financial challenges. As traditional lenders tighten their criteria, understanding the ABL facility meaning stands out as a viable solution for businesses aiming to navigate financial difficulties and sustain operations.
Key Features and Mechanics of Asset-Based Lending
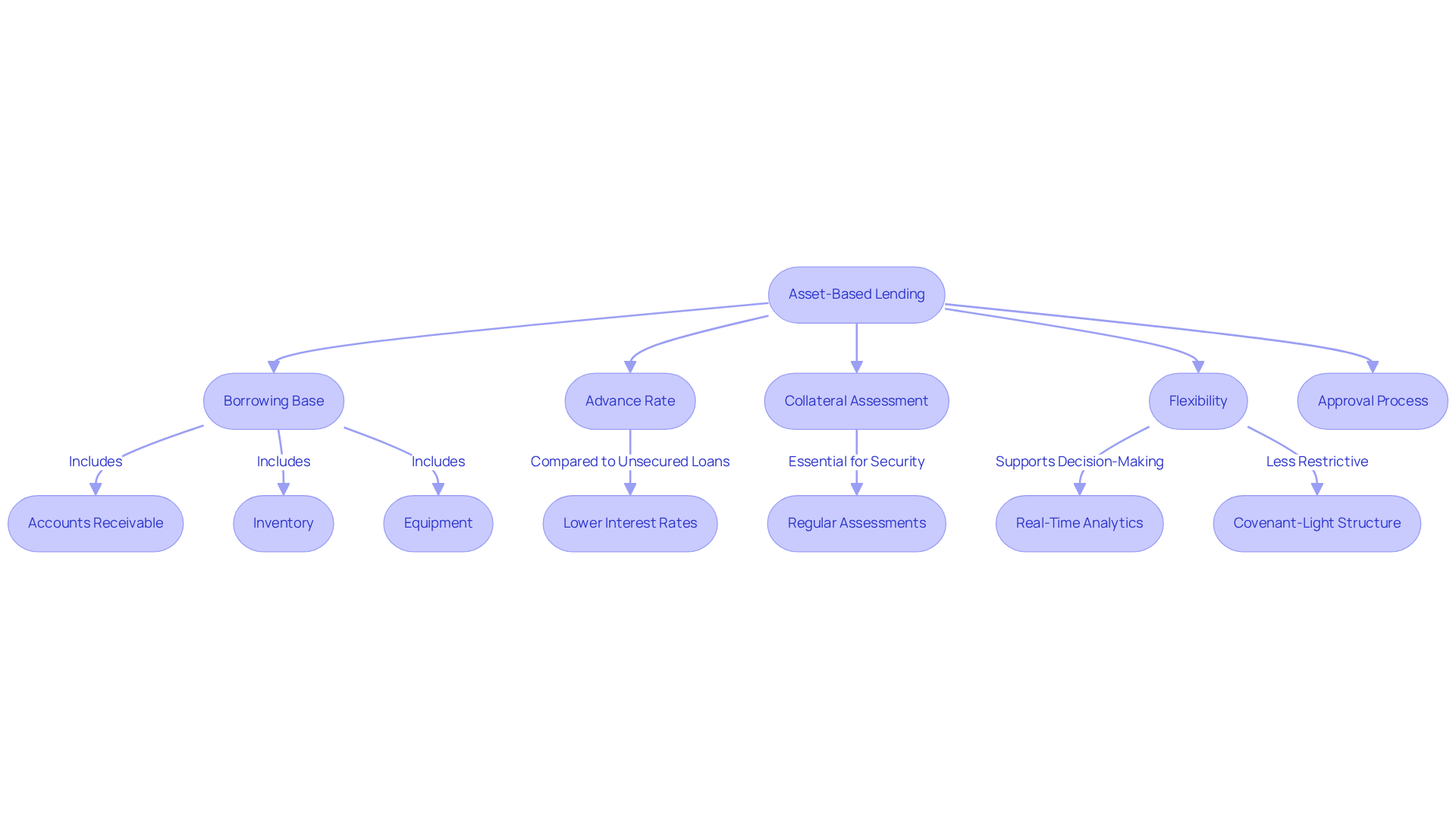
The mechanics of Asset-Based Lending (ABL) exhibit distinct features that help in understanding the ABL facility meaning, differentiating it from traditional lending. The ABL facility meaning is centered around the borrowing base, which is determined by the value of resources pledged as collateral, including accounts receivable, inventory, and equipment. Lenders typically advance a percentage of this value, referred to as the advance rate, which ranges from 80-90% for receivables and 50-70% for inventory. Regular collateral assessments are essential to understanding the ABL facility meaning, ensuring that loans remain adequately secured and enabling lenders to adjust borrowing limits in response to fluctuations in asset values.
This adaptability provides organizations with a flexible financing solution that evolves alongside their operational needs, thereby supporting a streamlined decision-making process. For example, companies with substantial accounts receivable can leverage their invoices to secure immediate capital, illustrating the ABL facility meaning in supporting operational cash flow and growth initiatives. Moreover, the incorporation of real-time analytics through client dashboards allows businesses to monitor their financial health continuously, ensuring that decisions are data-driven and timely.
While ABL features a streamlined approval process and generally lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans, it is crucial to recognize that these rates are often higher than those of traditional loans due to the increased risk for lenders. The application process for ABL underscores the necessity of testing hypotheses to optimize financial strategies and operational frameworks.
Types of Collateral Used in ABL
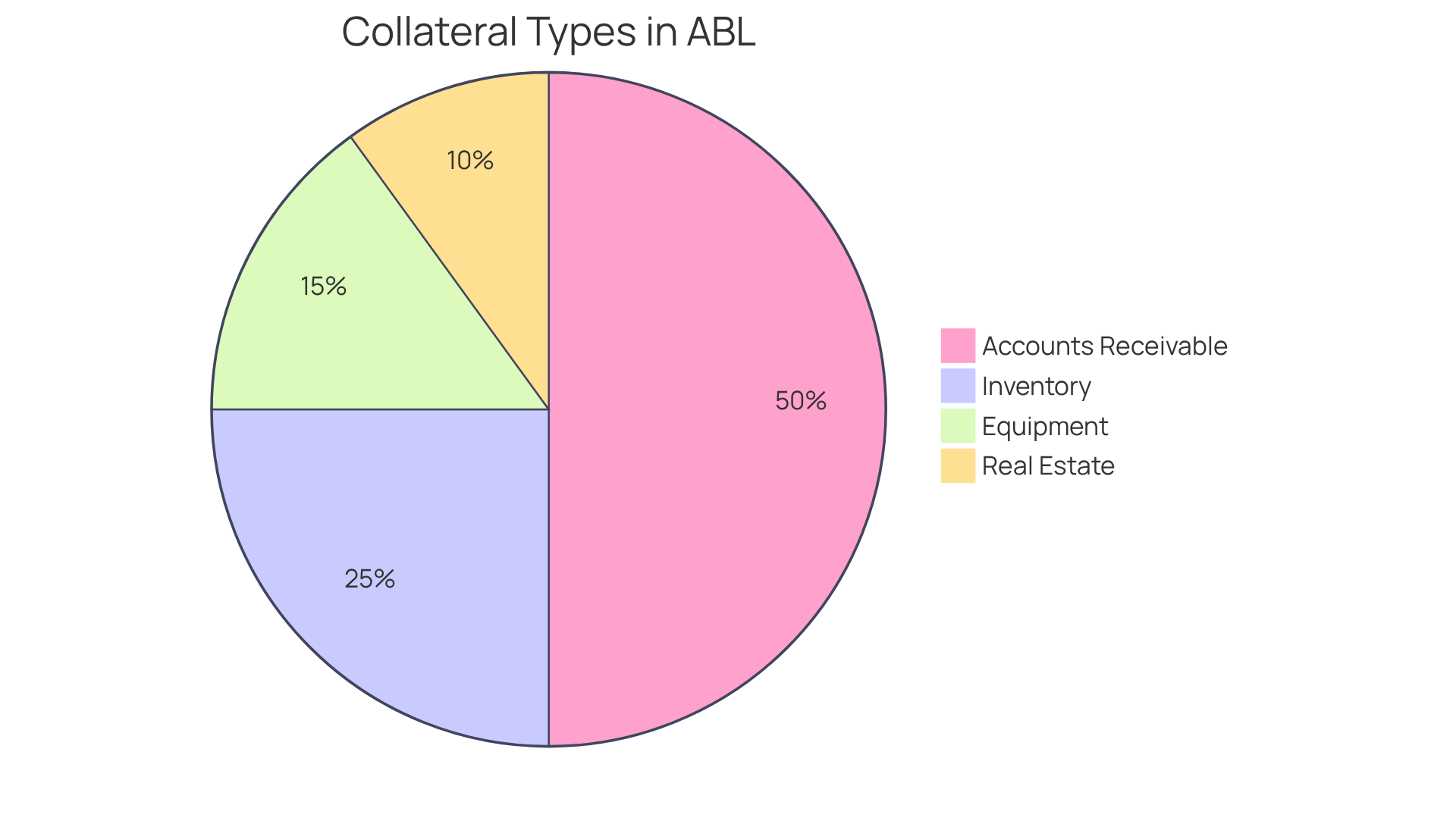
In asset-based lending (ABL), the abl facility meaning refers to the diverse range of collateral that can be utilized to secure loans, with accounts receivable emerging as a crucial resource. The primary types of collateral include:
-
Accounts Receivable: Outstanding invoices owed by customers represent a readily convertible asset into cash. In 2025, accounts receivable financing is expected to constitute a substantial share of ABL transactions, indicating its significance in offering liquidity for enterprises. Financial experts emphasize that the faster a resource can be transformed into cash, the greater the advance rate lenders are willing to provide, rendering accounts receivable especially appealing.
-
Inventory: This includes goods held for sale, such as raw materials and finished products. Inventory can be liquidated if needed, offering companies an extra layer of financial security. In 2025, the retail sector experienced a notable increase in ABL financing, driven by the need to manage inventory volatility.
-
Equipment: Machinery and tools utilized in production hold intrinsic value and can be sold or financed. Equipment financing is frequently arranged to enable companies to utilize these assets for funding, particularly in sectors where equipment is essential for operations.
-
Real Estate: Properties owned by the company can serve as substantial collateral for securing larger loans. The worth of real estate frequently offers a solid basis for understanding the abl facility meaning, enabling companies to obtain substantial funding.
By strategically leveraging these assets, particularly accounts receivable, businesses can secure the necessary capital while maintaining operational flexibility. Case studies illustrate that companies with strong receivables have successfully utilized ABL to navigate cash flow challenges, ensuring they remain competitive in dynamic markets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, embracing Asset-Based Lending (ABL) can be a transformative strategy for businesses striving to maintain competitiveness in fluctuating markets. By leveraging existing assets, companies can secure necessary funding while optimizing their operational strategies. As financial landscapes continue to evolve, understanding and utilizing ABL will be crucial for businesses aiming to thrive amidst challenges. Taking the proactive step to explore ABL could very well unlock new growth avenues and ensure sustained success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Asset-Based Lending (ABL)?
Asset-Based Lending (ABL) is a financial arrangement where loans are secured by the borrower's assets, such as accounts receivable, inventory, or equipment, instead of primarily assessing cash flow.
How does ABL differ from traditional loans?
Unlike traditional loans that focus on cash flow, ABL emphasizes the intrinsic value of the collateral provided, allowing companies to secure funding based on the tangible worth of their assets.
Who can benefit from ABL?
ABL is particularly beneficial for small to medium-sized enterprises, as it provides a versatile financing option crucial during financial strain.
What are current trends in the ABL sector?
Current trends indicate proposed adjustments to financial requirements that could enhance liquidity within the asset-backed lending sector, encouraging more businesses to adopt this financing method.
Can you give an example of ABL in action?
An example is FreightCar America, which secured a $35 million ABL credit facility, demonstrating how ABL can enhance financial flexibility and support growth strategies.
What did Michael Riordan, CFO of FreightCar America, say about their ABL arrangement?
Michael Riordan expressed enthusiasm about the partnership with Bank of America, stating that it marks a significant milestone in their refinancing efforts, improving their capacity to meet operational funding needs and optimize borrowing costs.
What are the advantages of ABL for businesses?
ABL fulfills working capital demands, reduces borrowing expenses, and is an attractive option for enterprises navigating challenging economic climates.
How can technology improve ABL efficiency?
The integration of expert advice and the application of AI/ML technologies can significantly enhance ABL efficiency, particularly in mastering the cash conversion cycle and improving overall organizational performance.




