Introduction
The Accounts Payable Turnover ratio is a crucial financial metric for assessing a company's payment practices and cash flow health. In industries experiencing growth and transformation, such as healthcare and semiconductor manufacturing, managing this ratio becomes even more critical.
CFOs need to review expenditures, align them with strategic priorities, and establish a solid financial foundation. This article will cover the definition and importance of the accounts payable turnover ratio, how to calculate it, how to interpret the results, factors affecting the ratio, benefits of improving it, best practices for managing accounts payable turnover, common mistakes to avoid, and real-world examples of the ratio in action. By understanding and optimizing this ratio, companies can enhance their liquidity, foster sustainable growth, and maintain a competitive edge in their industries.
Understanding Accounts Payable Turnover: Definition and Importance
The Accounts Payable Turnover ratio is an essential financial metric for gauging the effectiveness of a company's payment practices. This ratio sheds light on the rate at which a firm settles its debts with suppliers and vendors, highlighting the fluidity of its accounts payable system.
For financial leaders, mastering this ratio is paramount—it not only signals the health of the company's cash flow but also surfaces potential for optimizing payment cycles. In industries such as healthcare and semiconductor manufacturing, which are experiencing significant growth and transformation, managing this ratio becomes even more critical.
The velocity of payables in these sectors can influence operational efficiency and the ability to capitalize on market opportunities. Therefore, it is advisable for CFOs to undertake a comprehensive review of all expenditures, aligning them with strategic priorities.
This scrutiny extends beyond a simple cost-cutting exercise; it involves a deep dive into the company's financial landscape, considering both outflows and potential revenue streams. Establishing a solid foundation for financial operations, such as opening a dedicated business bank account and choosing an appropriate accounting method, is also crucial. These steps ensure a clear demarcation between business and personal finances, simplifying tax filings and enhancing the transparency of financial reporting. By meticulously managing accounts payable and leveraging a robust financial infrastructure, companies stand to improve their liquidity, foster sustainable growth, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Calculating Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio
To determine a company's efficiency in managing its debts to suppliers, the accounts payable turnover ratio serves as a critical metric. This ratio is derived by dividing total purchases by the average accounts payable for a given period.
The total purchases figure can be sourced directly from the income statement, which reflects all company expenditures for goods and services. On the other hand, the average accounts payable is calculated by taking the sum of the starting and ending balances of accounts payable within the period and dividing by two, offering a fair representation of the company's short-term debt levels during that time frame.
This ratio is especially relevant considering the strategic objectives of large departments, such as collecting the right amount of tax and ensuring the right financial support is provided. As organizations strive to maintain robust financial practices, the application of accrual accounting—where transactions are recorded at the point of occurrence regardless of cash movement—highlights the importance of accurate and timely financial metrics. In the context of a rapidly transforming healthcare industry and expanding semiconductor industry, the ability to manage and analyze financial obligations is paramount for sustainability and compliance with financial regulations.
Interpreting Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio Results
Understanding the accounts payable turnover ratio is crucial for a company's financial diagnostics. It's a reflection of how promptly a business settles its debts with suppliers, which can be an indicator of its cash flow health.
A high ratio suggests efficient cash management, signaling that the company is quick to clear its dues, which can foster trust and favorable terms with vendors. Conversely, a low ratio might reveal potential bottlenecks, hinting at cash flow challenges or a reliance on extended payment terms that could strain vendor relationships.
This metric is part of a suite of financial ratios that provide a standardized way to evaluate a business's financial statements. By expressing financial data as percentages, these ratios allow for meaningful comparisons across companies and industries, leveling the playing field for analysis. They are indispensable in financial analysis, guiding critical business decisions, and evaluating a company's financial wellbeing. As such, a keen grasp of these ratios is essential for discerning the subtleties in a company's financial narrative, from historical performance to current fiscal health and future prospects.
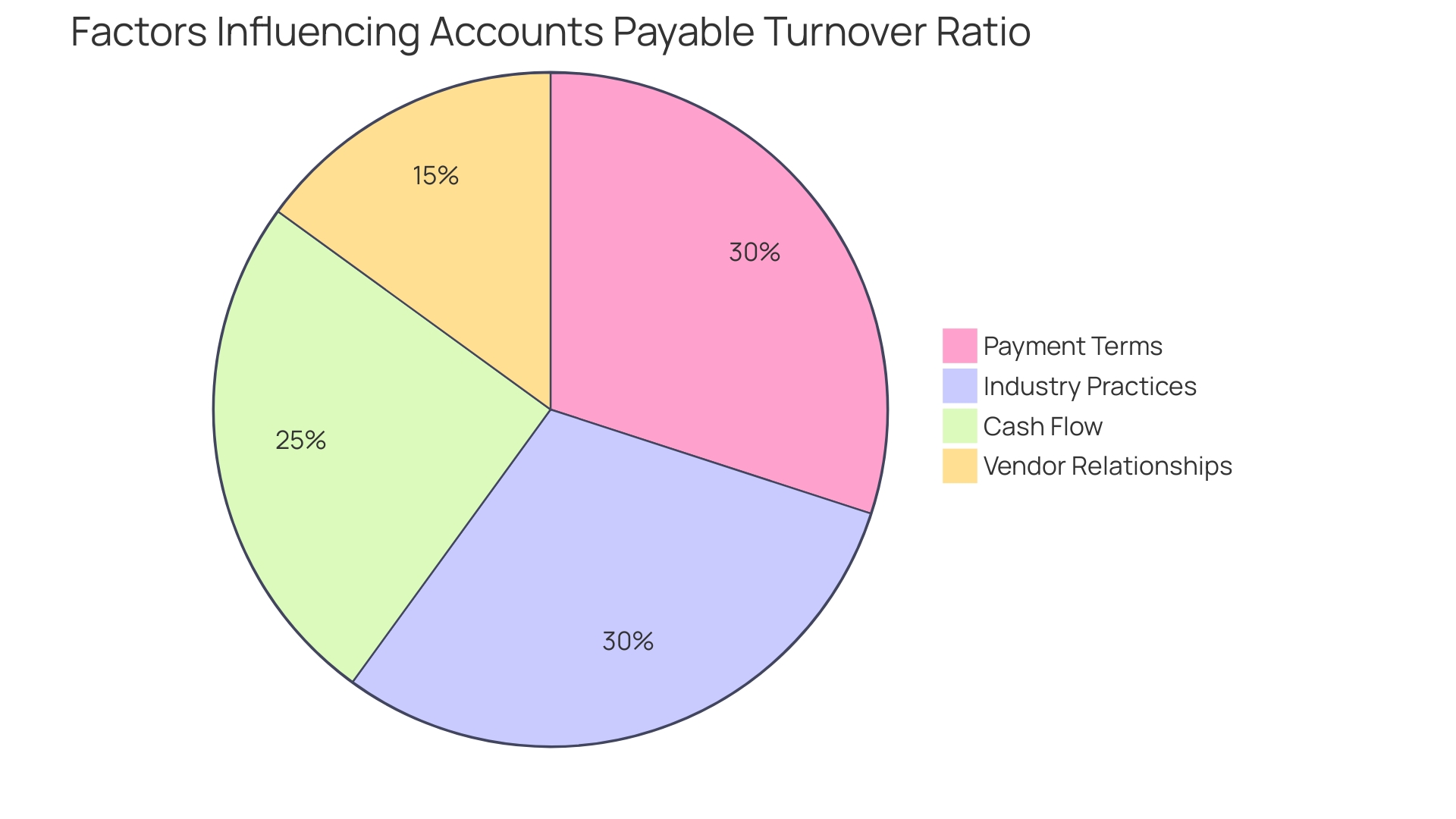
Factors Affecting Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio
The accounts payable turnover ratio, a critical financial metric, is influenced by several pivotal factors. Payment terms negotiated with suppliers play a significant role; extended periods for settling invoices could translate to a more modest turnover ratio. Cash flow, the lifeblood of any organization, must be robust to ensure suppliers are paid promptly, as faltering cash flows could diminish the ratio.
Vendor relationships are also crucial; cultivating strong ties with suppliers may yield advantageous payment terms and discounts, thereby enhancing the turnover ratio. Additionally, it's essential to contextualize the turnover ratio within the landscape of industry-specific payment practices, ensuring a meaningful comparison against industry benchmarks. With over 5 million businesses in the UK alone adhering to their financial obligations, it's evident that a well-managed turnover ratio is vital for fulfilling strategic objectives such as collecting the right taxes and providing financial support, ultimately contributing to the funding of public services like education and healthcare.
Benefits of Improving Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio
Enhancing the accounts payable turnover ratio is not just about paying bills; it's a strategic financial maneuver that yields multiple advantages. Firstly, it sharpens cash flow management by signifying efficient use of resources to settle dues with suppliers. This is critical in sectors like healthcare and semiconductors, where rapid transformation and technological advancements necessitate agile financial operations.
Secondly, it fosters robust vendor relationships, which are essential for securing favorable terms and discounts. As the industry evolves, these partnerships become crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and ensuring a resilient supply chain. Lastly, negotiating better payment terms directly contributes to cost reductions, bolstering overall fiscal health.
This aligns with strategic objectives of revenue services, aiming to collect rightful taxes and support financial stability, as seen in the UK, where over 5 million businesses benefit from efficient tax collection and support systems. An invoice, more than a request for payment, is integral to these processes, detailing transaction specifics and ensuring a seamless flow from service delivery to financial recompense. Understanding the essence of invoicing and accounting is paramount for small business owners to fit individual transactions into the broader financial narrative, thus maintaining a healthy cash flow and robust financial standing.
Best Practices for Managing Accounts Payable Turnover
To optimize accounts payable turnover, financial leaders should focus on the following strategies:
- Streamlining the accounts payable process is paramount.
By adopting a structured approach to invoice handling, including prompt receipt, approval, and settlement, organizations can reduce the likelihood of delays and inaccuracies. This practice not only enhances efficiency but also strengthens the financial health of the company by ensuring that transactions are recorded and managed effectively.
- Negotiating favorable payment terms with suppliers is a strategic move that can have a profound impact on a company's cash flow.
By aligning payment schedules with the organization's cash flow, CFOs can maintain a balance that supports operational needs while managing the accounts payable turnover ratio. 3.
Embracing technology is a game-changer for accounts payable management. Utilizing advanced accounting software and automation tools can simplify the entire process, from invoice processing to payment execution.
This reduces manual intervention, thereby minimizing the risk of errors and increasing overall efficiency. 4. Monitoring and analyzing payment trends is an insightful exercise that can reveal patterns and opportunities for improvement in cash flow management. By keeping a close eye on these trends, financial managers can make data-driven decisions to enhance the accounts payable process. It's important to note that these practices should be integrated with the broader financial operations of the organization. Ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance with regulatory standards is crucial for maintaining stakeholder trust and achieving long-term financial stability. Through these concerted efforts, CFOs can ensure that their accounts payable turnover is managed effectively, contributing to the robust financial management of their organization.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Accounts Payable Turnover Management
Optimizing accounts payable turnover is essential for maintaining a healthy cash flow and strong vendor relationships. To ensure efficient accounts payable management, it's critical to avoid these pitfalls:
1.
Delayed Payments: Procrastination in settling invoices can not only damage supplier relationships but also adversely affect your accounts payable turnover ratio. In the dynamic healthcare and semiconductor industries, where timeliness can be a competitive edge, prompt payments are particularly crucial.
- Inaccurate Data Entry: Precision in recording financial transactions is non-negotiable.
Mistakes in invoice or payment entry can skew your accounts payable turnover ratio, leading to misguided management decisions. It's essential to align practices with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) to maintain accuracy.
- Neglecting Vendor Relationships: Vendor partnerships are more than just transactional; they are strategic.
Overlooking these relationships can result in less favorable payment conditions and increased costs. In a sector where the Product Strength Index and Total Available Market (TAM) are pivotal, nurturing supplier ties can directly influence your financial position. 4. Lack of Communication: Clear and consistent communication with your team and suppliers is the linchpin of smooth accounts payable operations. Keeping all parties apprised of payment timelines and process updates is a fundamental aspect of business management, which, as history shows, has always been integral to financial success. By steering clear of these common errors and employing robust accounting software, businesses can streamline their financial management, ensuring they are well-equipped to handle the complexities of modern commerce.
Real-World Examples of Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio in Action
Consider the financial health of two hypothetical entities to understand the significance of the accounts payable turnover ratio. Company A boasts a ratio of 8, demonstrating its ability to clear dues with suppliers eight times annually.
This is indicative of a well-oiled cash management system and robust vendor relations – a testament to the organization's operational efficiency. On the other hand, Company B's turnover ratio stands at 2, signaling that it settles accounts with suppliers just twice a year.
This is a potential red flag, highlighting possible liquidity constraints or inefficiencies within their accounts payable procedures. The importance of maintaining a healthy cash flow cannot be overstated; it is the lifeblood of a business, ensuring its survival and prosperity.
A statement that encapsulates this is: 'Cash flow refers to the movement of cash in and out of your business and preventing cash shortages at any time in your business cycle is critical.' In terms of practical application, CFOs can scrutinize these ratios to pinpoint areas needing refinement, thereby bolstering the accounts payable turnover ratio and, by extension, the organization's financial robustness. To contextualize the impact of these ratios, it's crucial to recognize that the turnover ratio is not merely a number but a reflection of a company's operational heartbeat, affecting everything from tax obligations to the ability to invest in growth opportunities. The money collected from efficient operations is funneled into public services and the broader economy, underscoring the far-reaching implications of adept financial management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the accounts payable turnover ratio is a vital financial metric for assessing payment practices and cash flow health. It provides insights into how promptly a company settles debts with suppliers, indicating the fluidity of its accounts payable system.
To calculate the ratio, divide total purchases by average accounts payable for a given period. CFOs can interpret the results to make data-driven decisions and evaluate the company's financial wellbeing.
Payment terms, cash flow robustness, and vendor relationships influence the ratio. Optimizing the accounts payable turnover ratio offers several benefits.
It enhances cash flow management, fosters robust vendor relationships, and contributes to cost reductions. Streamlining processes, negotiating favorable payment terms, embracing technology, and monitoring payment trends are effective strategies for improvement.
Avoiding common mistakes like delayed payments, inaccurate data entry, neglecting vendor relationships, and lack of communication is essential for efficient accounts payable turnover management. Best practices and robust accounting software streamline financial operations. Real-world examples highlight the significance of the ratio. Higher ratios indicate operational efficiency and strong vendor relations, while lower ratios may suggest liquidity constraints or inefficiencies. Understanding and optimizing the accounts payable turnover ratio is crucial for companies seeking enhanced liquidity, sustainable growth, and maintaining a competitive edge. By implementing best practices and avoiding common mistakes in accounts payable turnover management, CFOs ensure effective financial operations for long-term success.




