Overview
Stakeholders in project management encompass individuals, groups, or organizations with a vested interest in project outcomes—both those directly involved and those impacted by the results. Recognizing and engaging these stakeholders effectively is paramount; their needs and expectations profoundly influence project direction and success. Moreover, employing strategic analysis and tailored communication is essential to address these influences. By prioritizing stakeholder engagement, project managers can navigate complexities and drive projects towards successful outcomes.
Introduction
Understanding the dynamics of stakeholders is crucial in project management, as these individuals and groups hold significant sway over a project's success. From team members to external clients, their varying interests and levels of influence can shape the trajectory of any initiative. This article delves into the intricacies of stakeholder identification, analysis, and management, offering strategies that empower project managers to engage effectively with all parties involved. But how can one navigate the complexities of stakeholder relationships to ensure alignment and support throughout the project lifecycle?
Define Stakeholders in Project Management
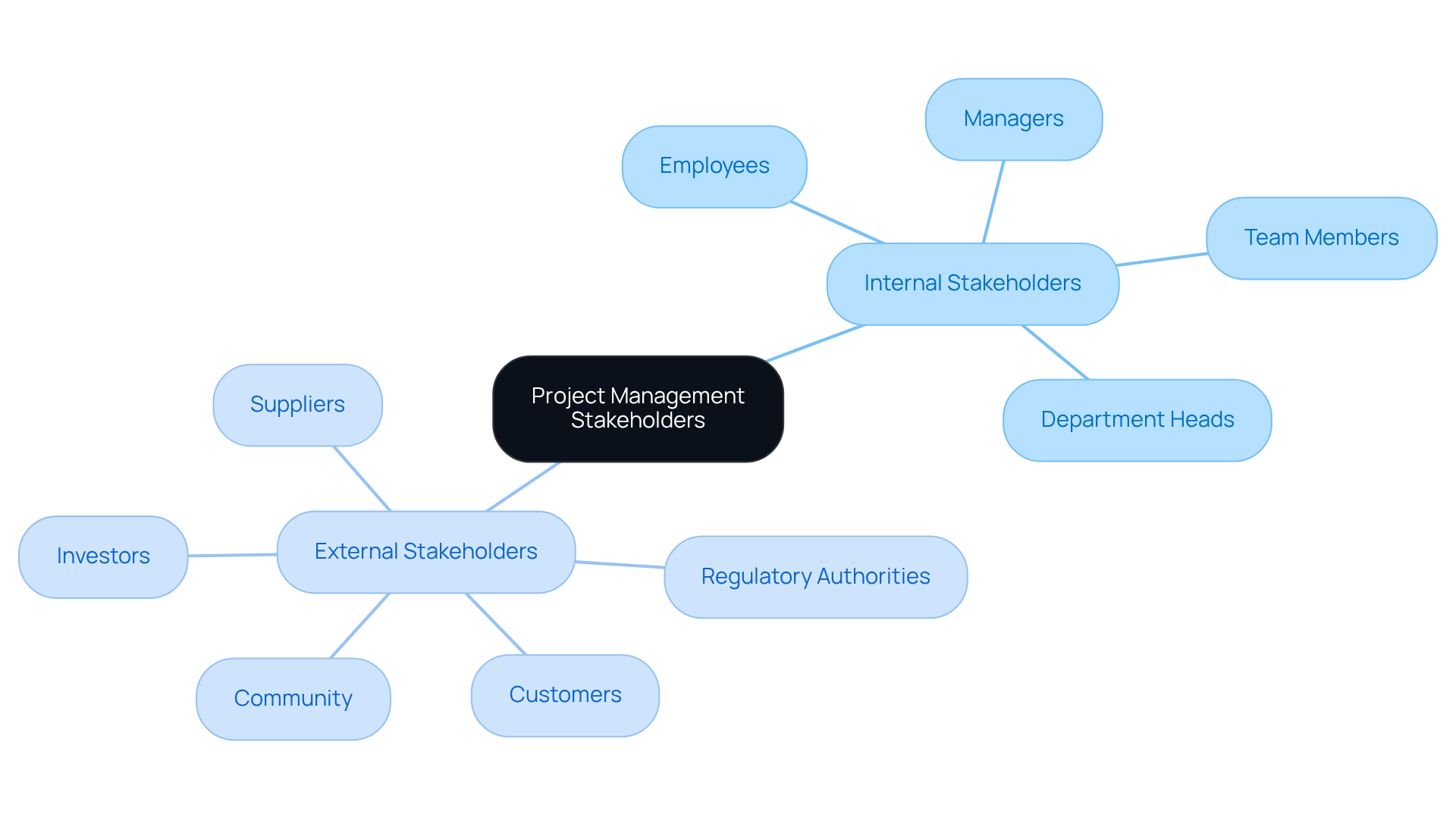
In the management of initiatives, the stakeholder in project management definition refers to individuals, groups, or organizations with a vested interest in the outcomes of an endeavor. They may be directly involved in the initiative or affected by its results. Stakeholders encompass team members, customers, suppliers, investors, and even the broader community.
Understanding who these participants are is vital for success, as their needs and expectations significantly influence the initiative's direction and outcomes. For example, a program manager must take into account the interests of both internal parties, such as team members, and external entities, including clients and regulatory bodies, to ensure alignment and support throughout the initiative lifecycle.
Identify Types of Stakeholders and Their Roles
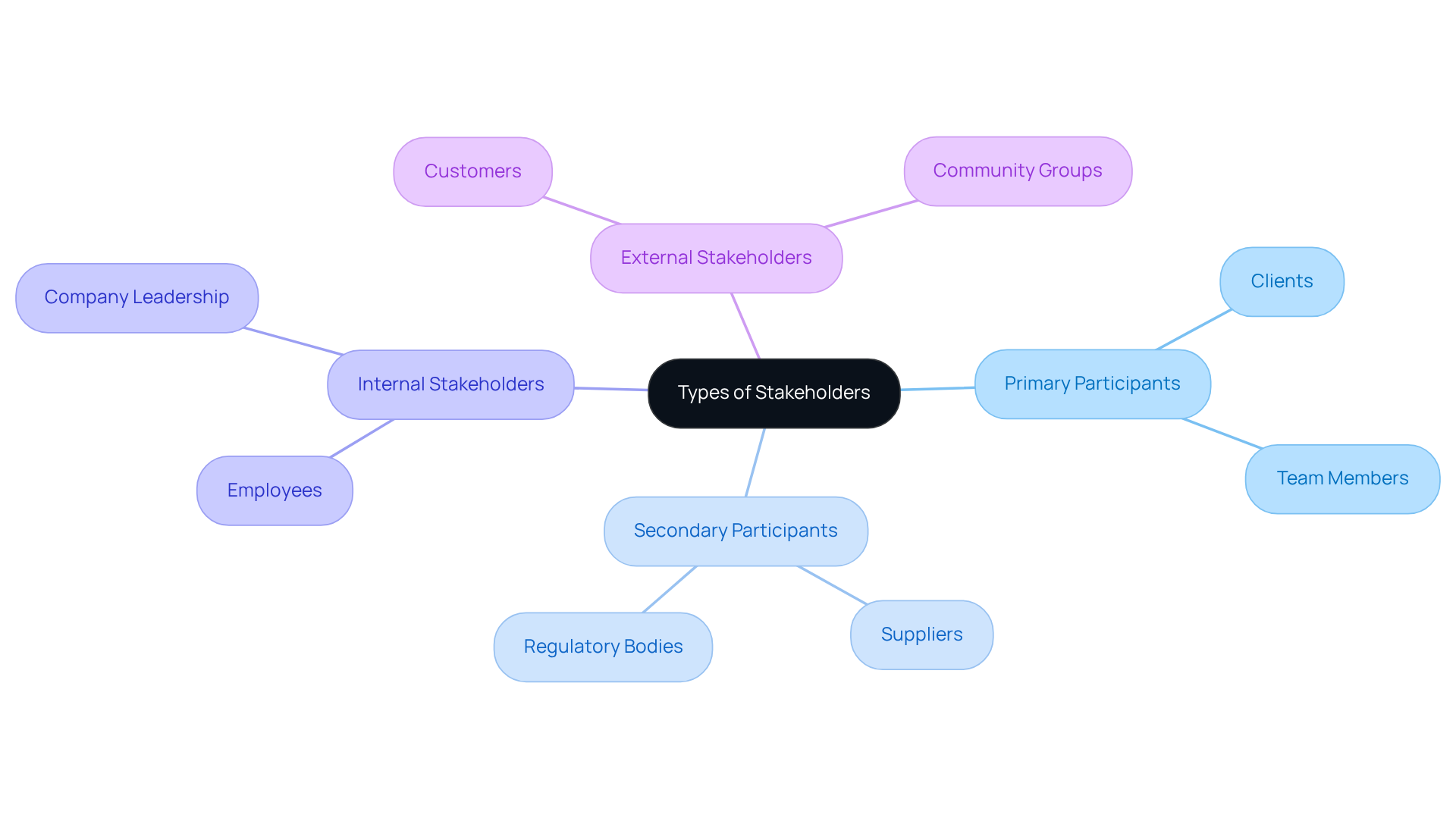
Participants can be classified into two primary categories: primary and secondary participants.
- Primary participants are those who are directly impacted by the initiative, such as clients and team members.
- Conversely, secondary participants may not be directly engaged but can still affect or be affected by the initiative, including suppliers and regulatory bodies.
Moreover, interested parties can be categorized as internal (within the organization) or external (outside the organization). Understanding these categories aids project managers in efficiently customizing their interaction and involvement strategies, as outlined in the stakeholder in project management definition.
For instance, primary parties may require more frequent updates and involvement in decision-making, while secondary parties might need less direct engagement but still necessitate regular communication to keep them informed.
Conduct Stakeholder Analysis for Effective Engagement
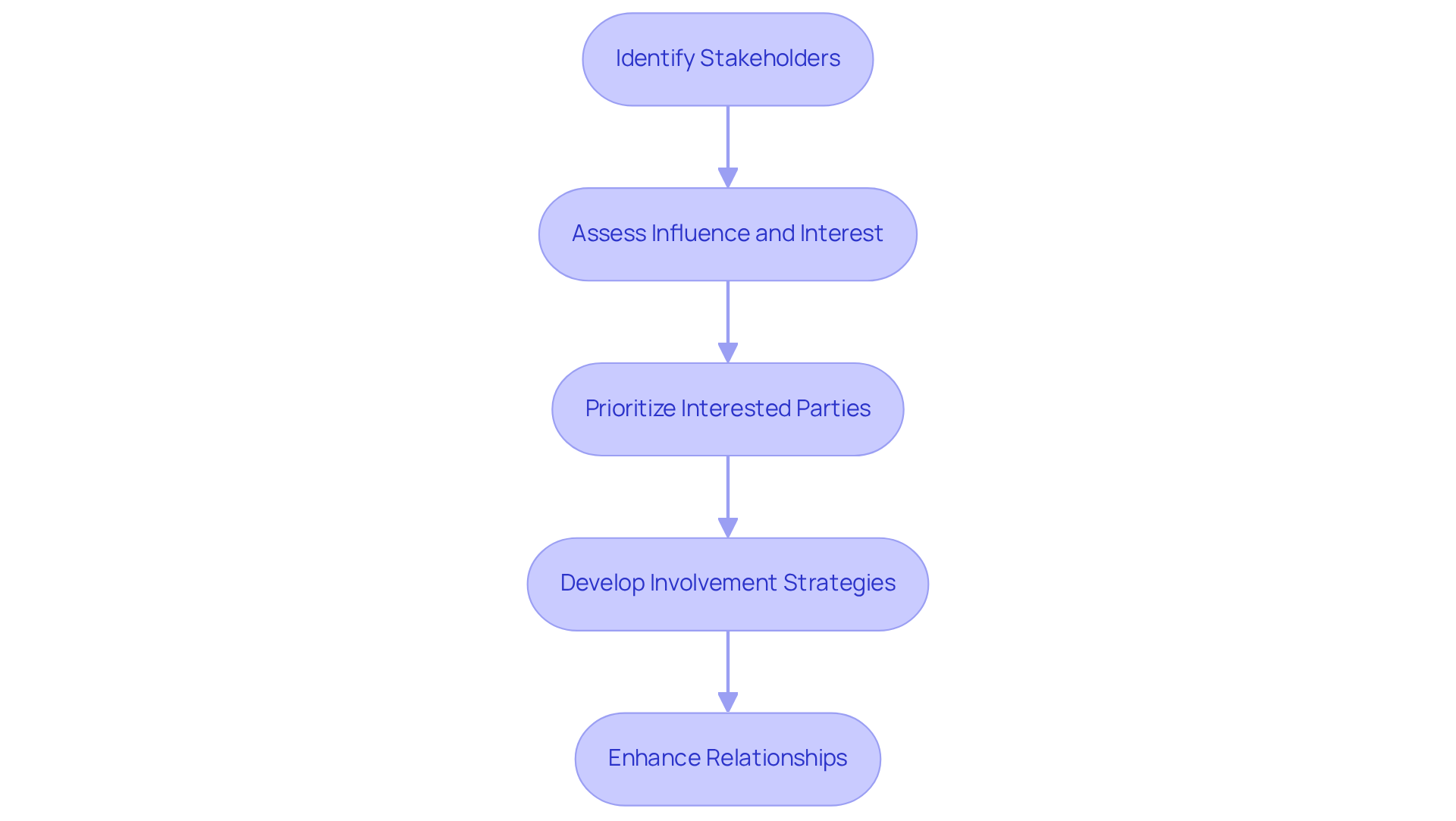
To conduct a stakeholder analysis effectively, follow these structured steps:
-
Identify Stakeholders: Compile a comprehensive list of individuals and groups that may be affected by or have an interest in the initiative. This encompasses internal participants like employees and managers, along with external ones such as suppliers and community organizations, which are all identified as stakeholders in project management definition.
-
Assess Influence and Interest: Evaluate each participant's level of influence over the initiative and their interest in its outcomes. Employing instruments such as the Power-Interest Grid can be advantageous, as this grid helps illustrate the stakeholder in project management definition by classifying participants according to their ability to affect the initiative and their degree of interest. Studies show that 85% of participants think involvement greatly influences their view of organizational openness, highlighting the significance of this evaluation. Furthermore, firms with efficient strategies for involving the stakeholder in project management definition are 40% more likely to finish tasks punctually and within financial limits, emphasizing the monetary advantages of managing involved parties.
-
Prioritize Interested Parties: Based on the influence and interest assessment, prioritize interested parties to determine who requires the most attention and engagement. High-power, high-interest participants, defined as stakeholders in project management definition, should be managed closely, as they can significantly influence success. On the other hand, low-power, low-interest parties may need less regular interaction, enabling resources to be allocated effectively. For example, in a study, the Contractor and Signaling systems provider were recognized as the most impactful participants, representing 40% of overall influence in their respective projects.
-
Develop Involvement Strategies: Customize your communication and involvement approaches based on each party's needs and priorities. For instance, high-power participants may benefit from regular updates and opportunities for input, while others might only need periodic information. Successful collaboration with relevant parties, which can be understood through the stakeholder in project management definition, can result in enhanced long-term financial outcomes, as firms that interact with these groups are 30% more likely to thrive with new products. Moreover, a case study revealed that robust participant involvement in the technology sector led to a 10% enhancement in employee retention, demonstrating its impact on company culture and human resources.
By following these steps, project managers can enhance relationships with interested parties, reflecting the stakeholder in project management definition, mitigate risks, and ultimately drive project success.
Implement Strategies for Stakeholder Management
To effectively manage stakeholders, consider the following strategies:
- Interact Consistently: Create a thorough plan outlining the frequency and methods for updates. Consistent communication not only fosters trust but also keeps interested parties informed, leading to a 35% increase in employee involvement due to clear messaging.
- Involve Interested Parties in Decision-Making: Actively engage key participants in the decision-making process. This participation greatly enhances buy-in and backing for projects, with research indicating that initiatives with robust involvement from interested parties succeed 83% of the time compared to just 32% for those lacking it.
- Be Transparent: Maintain openness by sharing both successes and challenges with interested parties. This transparency promotes trust and supports productive discussions, which is crucial as 70% of change efforts fail due to inadequate interaction and absence of involvement.
- Tailor Engagement Approaches: Acknowledge that various parties have differing needs. For example, executives may prefer concise summaries, while team members might require detailed information. Tailoring communication ensures clarity and resonance, enhancing overall involvement.
- Monitor and Adapt: Continuously assess the effectiveness of participant engagement strategies. Routine feedback cycles are essential for comprehending the needs of involved parties and adjusting methods accordingly, resulting in enhanced outcomes and decreased delays by up to 40% through improved coordination.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can significantly enhance the stakeholder in project management definition, which leads to improved project success rates and sustainable growth.
Conclusion
In project management, understanding the roles and definitions of stakeholders is crucial for the success of any initiative. Stakeholders, encompassing a diverse range of individuals and organizations, significantly impact project outcomes. Effectively identifying and engaging these parties ensures that their needs and expectations are met, leading to better alignment and support throughout the project lifecycle.
Key insights from the article highlight the importance of categorizing stakeholders into primary and secondary groups, as well as internal and external participants. Conducting a thorough stakeholder analysis allows project managers to assess influence and interest, prioritize engagement, and develop tailored communication strategies. By fostering consistent interaction, transparency, and adaptability, organizations can significantly enhance stakeholder relationships, ultimately driving project success.
The significance of effective stakeholder management cannot be overstated. By recognizing the diverse roles that stakeholders play and implementing best practices for engagement, project managers can not only mitigate risks but also unlock greater potential for collaboration and innovation. Embracing these strategies will lead to improved project outcomes and sustainable growth, reinforcing the vital role stakeholders play in the landscape of project management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a stakeholder in project management?
A stakeholder in project management refers to individuals, groups, or organizations with a vested interest in the outcomes of a project. They may be directly involved in the project or affected by its results.
Who can be considered stakeholders in a project?
Stakeholders can include team members, customers, suppliers, investors, and even the broader community.
Why is it important to identify stakeholders in a project?
Identifying stakeholders is vital for project success because their needs and expectations significantly influence the project's direction and outcomes.
What role does a program manager play in relation to stakeholders?
A program manager must consider the interests of both internal parties, such as team members, and external entities, including clients and regulatory bodies, to ensure alignment and support throughout the project lifecycle.




