Introduction
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a critical financial metric that quantifies the total spend required to convert potential prospects into actual customers. It encompasses all expenses related to sales and marketing activities, including promotional efforts, employing sales personnel, creating marketing materials, and investing in marketing technologies.
In this article, we will explore the importance of CAC for businesses and how it impacts their financial health and growth potential. We will also delve into the factors that affect CAC, strategies to optimize it, and key metrics for measuring the effectiveness of customer acquisition tactics. Join us as we provide practical advice and solutions for CFOs to manage CAC and drive sustainable customer growth.
What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)?
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) quantifies the total spend to convert potential prospects into actual customers. A critical financial barometer, CAC is computed by totaling every dime spent on sales and marketing endeavors, from promotional activities and employing sales personnel, to creating marketing materials and investing in marketing technologies.
A pivotal reason to determine CAC is to perform a 'Financial Health Check.' If acquiring a customer costs more than the revenue they're projected to generate over their lifetime (Customer Lifetime Value or CLTV), it's effectively a loss-making undertaking for each new customer acquired.
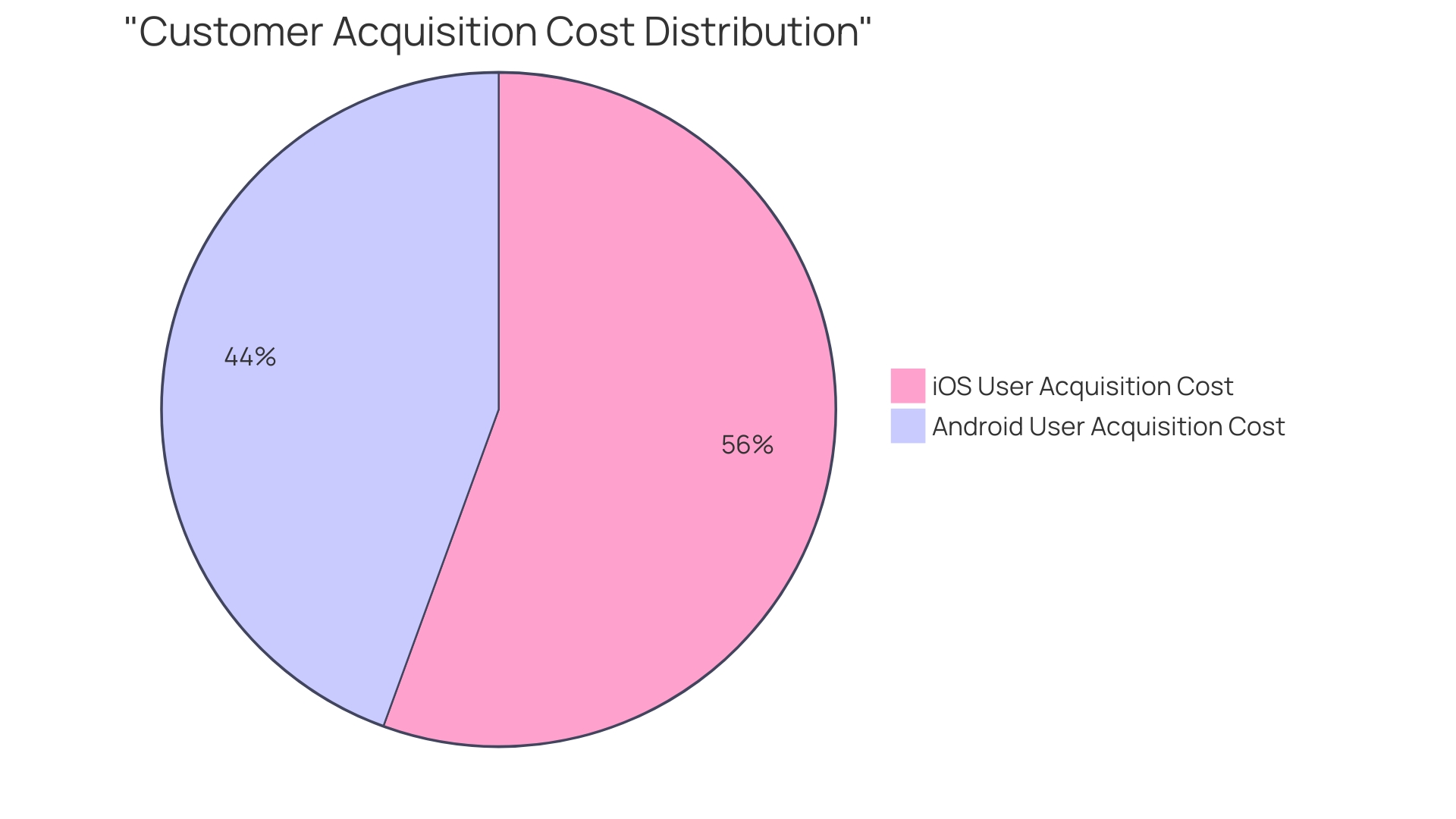
Recognizing CAC also enables smarter 'Resource Allocation,' as it provides insights on how best to distribute marketing and sales budgets. Moreover, from a 'Growth Perspective,' maintaining a proportionate CAC ensures that a company can widen its clientele base while carefully managing its capital reserves. Analyzing app user acquisition costs reveals a stark disparity in expenses based on the operating system, with historically lower costs for Android users compared to iOS, influenced by the larger Android user base in various regions, including Latin America, Europe, and Asia.
Why is CAC Important for Businesses
To remain competitive and financially healthy, companies must be vigilant in managing their Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC). CAC is more than just a financial metric; it encapsulates the efficiency of marketing efforts, translating into the costs associated with converting prospects into customers.
This number reflects the aggregate expense of activities like advertising, staff salaries, content creation, and marketing tools. A keen understanding of CAC not only indicates the direct return on marketing investments but also serves as a broader measure of corporate sustainability.
The criticality of CAC analysis comes to the forefront when weighed against Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV). A CAC that eclipses CLTV suggests that a business is operating at a loss with each new customer, signaling an unsustainable growth model.
This disparity necessitates a decisive review and reallocation of resources to ensure marketing initiatives are not only effective but also economically viable. Moreover, global market analysis reveals noteworthy discrepancies based on customer demographics: iOS users tend to carry higher acquisition costs compared to their Android counterparts, largely due to the global distribution and sheer number of Android users, particularly in regions like Latin America, Europe, and Asia. Enveloping this data within the CAC framework enables businesses to adapt strategies that are cognizant of regional market dynamics and the distinct behaviors of user segments. In sum, CAC provides a quantified narrative of marketing success and operational health. By meticulously tracking and scrutinizing this crucial cost metric, enterprises can blueprint a path to fiscal prudence and scalable customer growth.

Factors Affecting Customer Acquisition Cost
Determining customer acquisition costs (CAC) is integral, especially as these expenses can vary depending on the industry, marketing strategies, and more. Crucially, factors such as the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, customer lifetime value, competitive landscape, retention rates, and sales team proficiency play a significant role.
For instance, the global cost to acquire app users on Android has historically been lower than on iOS, due to the greater volume of Android users worldwide, particularly in regions like Latin America, Europe, and Asia. Additionally, the concept of post-acquisition value (PAV), representing the net present value of a customer's revenue after acquisition excluding CAC, is invaluable.
It enables a company to gauge ongoing customer contributions and informs investment decisions for acquiring new customers. As Sean Ellis, the progenitor of Growth Hacking, indicated, achieving a certain threshold in customer feedback can signal product-market fit, a crucial precursor to bolstering CAC efforts. Moreover, with giants like Amazon, defining their success through relentless innovation and customer-centric strategies, understanding and enhancing customer value has never been more imperative in the competitive e-commerce sector.
Calculating Customer Acquisition Cost
Calculating Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is pivotal for a company's financial health and strategic planning. To discern this vital figure, tally all costs related to the procurement of new customers which encapsulates advertising, marketing campaigns, sales team expenses, and the deployment of technology tools.
A precise understanding of CAC is not just a number—it's a reflection of the enterprise's spending efficiency in its growth endeavors. According to a thorough analysis, app user acquisition costs exhibit noticeable disparities between the iOS and Android operating systems.
The costs associated with Android users have consistently been lower than those for iOS, attributed largely to Android's expansive global user base, especially in regions such as Latin America, Europe, and Asia. This distinction in costs is essential for tailoring resource allocation and underlines the significance of robust data analysis. Companies must be vigilant; if the CAC surpasses the Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV), resources are being eroded rather than utilized. Conversely, a balanced CAC indicates potential for scalable growth and operational efficiency, thereby securing financial longevity and competitive advantage.
Strategies to Optimize Customer Acquisition Cost
To bolster a company's profitability, a strategic focus on reducing Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC) is essential. Initiating with data analytics, it's crucial to understand that the global cost to acquire Android app users consistently undercuts that for iOS users due to the higher number of Android users worldwide; this is especially true in regions like Latin America, Europe, and Asia.
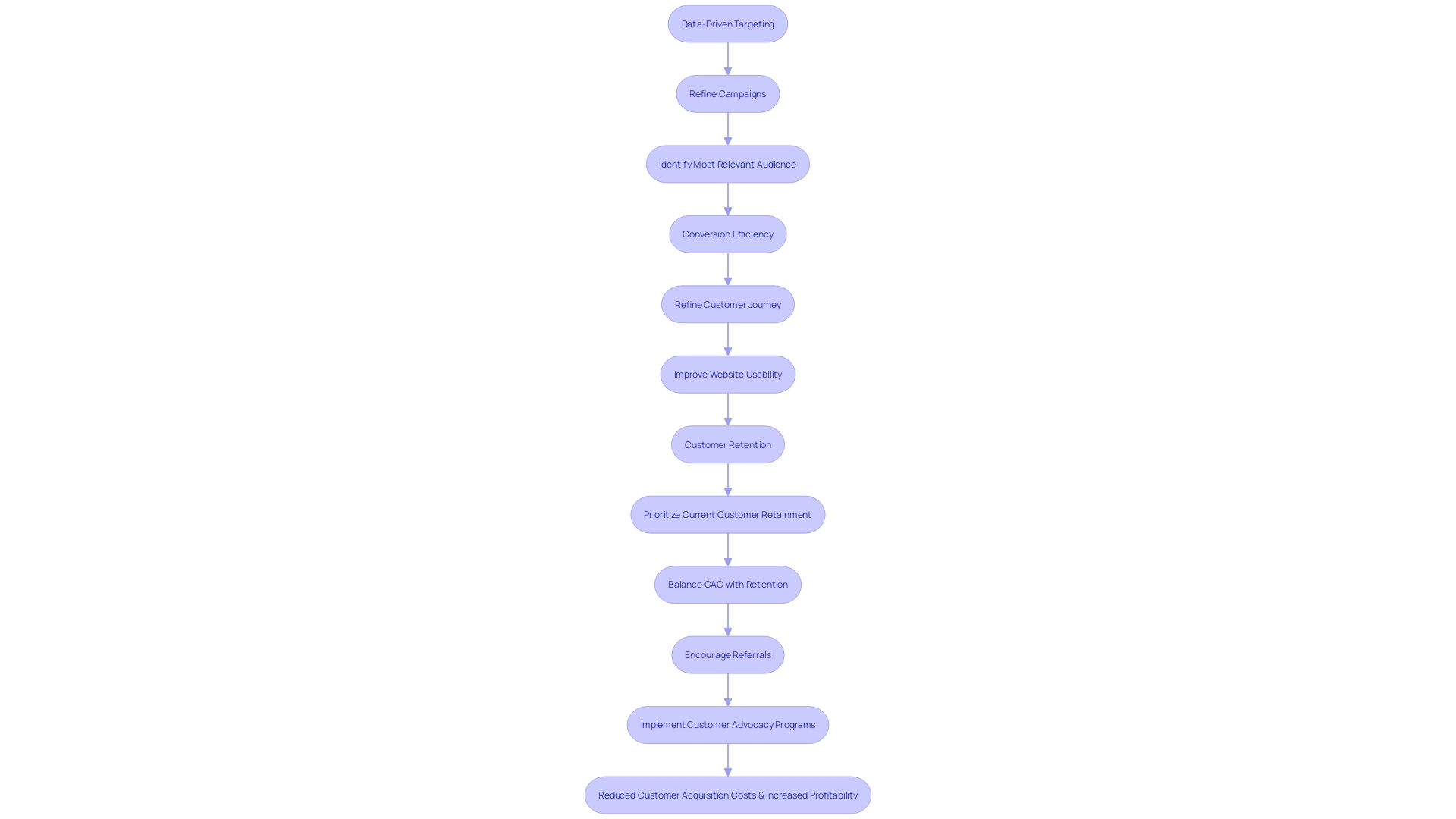
Recognizing that the differences between these operating systems can influence CAC, consider these tactics for optimization:
- Data-Driven Targeting: Tailor campaigns to your most relevant audience, boosting the possibility of engagement and reducing wasted outreach. - Conversion Efficiency: Streamline the customer journey by refining funnel efficiency and heightening website usability.
- Customer Retention: Prioritize the retention of current customers, as fostering their loyalty stretches Customer Lifetime Value and balances out CAC. - Encourage Referrals: Utilize the strength of word-of-mouth by implementing programs that reward customer advocacy.
Evaluating financial health is imperative when considering CAC. If the costs generated in acquiring a new customer exceed the revenue they bring (Customer Lifetime Value or CLTV), then the company's growth model may be unsustainable.
This understanding of CAC provides a metric for resource allocation, facilitating strategic decisions for marketing investments. Automation and regular data monitoring, to identify trends and tweak strategies, play pivotal roles in making cost-effective decisions and maintaining financial health and resource optimization. Businesses on the brink of marketing investments should assess whether they have attained product-market fit, a cornerstone for growth. As elucidated by Sean Ellis, reaching a point where 40% of users would miss your product significantly indicates a level of market fit. It's from this foundation that one can build robust and strategic marketing initiatives to lower CAC and foster long-term profitability.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Customer Acquisition
To gauge the impact of customer acquisition tactics, businesses must delve into pivotal metrics that reveal the yield of marketing and sales endeavors. Evaluating Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is fundamental; it encapsulates the total earnings a customer contributes throughout their association with the company.
Scrutinizing the Payback Period reveals the duration required for the company to recuperate the Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) from a new customer. Monitoring the Customer Churn Rate is crucial; it reflects the proportion of customers ceasing to patronize the business's offerings during a specific timeframe.
Assessing Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) is equally vital, as it measures the revenue spawned by each advertising dollar. Lastly, tracking the Conversion Rate - the ratio of prospective to actual customers - offers insight into the efficacy of marketing interactions.
Amidst the e-commerce fervor, examining Customer Post-Acquisition Value (PAV) emerges as a key metric. PAV, the net present value of a customer's revenue contributions post-acquisition minus the CAC, enables an accurate forecast of a customer's lifetime value. By meticulously calculating PAV, organizations determine the prudent sum to invest in acquiring a customer, informed by the expected customer value over time. Grasping these metrics, coupled with an understanding of Product-Market Fit (PMF) as evidenced by customers' anticipated disappointment in a product's absence, businesses can refine their strategies to prioritize customer segments. This informs where to allocate marketing resources proficiently, aiming to amplify growth and ensure optimum investment returns.

Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and managing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is crucial for businesses to maintain financial health and drive sustainable growth. By analyzing CAC in relation to Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV), companies can make informed resource allocation decisions and assess their growth model's viability. To optimize CAC, businesses should focus on data-driven targeting, improving conversion efficiency, prioritizing customer retention, and leveraging customer referrals.
These strategies can reduce costs and increase profitability. Measuring the effectiveness of customer acquisition tactics requires tracking metrics such as Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), Payback Period, Customer Churn Rate, Return on Ad Spend (ROAS), and Conversion Rate. Additionally, considering Customer Post-Acquisition Value (PAV) allows for accurate forecasting of a customer's lifetime value and informed investment decisions.
By managing and optimizing CAC, businesses can drive sustainable customer growth, maintain financial prudence, and secure a competitive advantage. CFOs should prioritize understanding CAC and implementing strategies to maximize its effectiveness. With a data-driven approach and a focus on customer value, businesses can thrive and succeed in the dynamic world of customer acquisition.




