Overview
The stakeholder model of strategic management underscores the critical importance of acknowledging the interests of all parties impacted by an organization's actions, rather than merely concentrating on shareholder value.
Companies that embrace this model not only enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs but also bolster their reputation and cultivate stronger relationships through corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Consequently, this approach leads to sustainable growth and a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Introduction
In a landscape where corporate responsibility is increasingly scrutinized, stakeholder theory emerges as a pivotal framework for organizations striving to balance diverse interests. This approach emphasizes the necessity of considering not just shareholders but all parties affected by business actions, including:
- employees
- customers
- the community
As companies navigate the complexities of 2025, the integration of stakeholder theory into corporate strategies is proving essential for enhancing operational efficiency and fostering sustainable growth. By prioritizing stakeholder relationships and aligning business objectives with broader societal values, organizations can:
- mitigate risks
- improve performance
- ultimately thrive in a competitive marketplace.
Defining Stakeholder Theory: Core Concepts and Principles
The stakeholder model of strategic management asserts that organizations must account for the interests of all parties impacted by their actions, extending beyond mere shareholder concerns. This encompasses employees, customers, suppliers, and the broader community. In 2025, the adoption of the stakeholder model of strategic management has become increasingly prevalent, with studies indicating that companies embracing this model experience enhanced operational efficiency and reduced costs associated with employee turnover and theft.
Corporations that neglect the interests of involved parties often face significant resistance, leading to inflated operating costs due to idle time, replacement costs, thefts, and vandalization.
The importance of the stakeholder model of strategic management is closely tied to (CSR), which serves as a framework for businesses to create value for all involved parties. A strong commitment to CSR not only fosters positive stakeholder relationships but also correlates with improved overall performance. In fact, organizations that effectively integrate sustainability into their core strategies are better positioned to meet market expectations and enhance their brand reputation.
A notable case study highlights how companies prioritizing sustainability have successfully built public trust, while those that overlook these commitments risk reputational damage and loss of consumer loyalty.
With a focus on streamlined decision-making and real-time analytics, our team supports a shortened decision-making cycle throughout the turnaround process, allowing your team to take decisive action to preserve your organization. Our client dashboard plays a crucial role in this process by providing real-time analytics that continually diagnose your organization's health. This guarantees that lessons from the turnaround process are put into practice to create strong, enduring relationships.
The stakeholder model of strategic management emphasizes the interconnectedness of various parties, which can significantly enhance decision-making processes. Recent advancements in this area highlight the importance for companies to adopt the stakeholder model of strategic management, acknowledging that long-term success depends on the welfare of all parties involved. Expert opinions reinforce this notion, suggesting that CSR provides a global standard of social responsibility, fostering employee loyalty and enhancing corporate reputation.
As Hart O. Awa states, 'CSR provides a global standard of social responsibilities, builds social welfare beyond profitability, develops employee loyalty and company reputation, and ultimately serves as a building block for corporate sustainability and competitive advantage.' In summary, the stakeholder model of strategic management has a profound influence on corporate social responsibility, shaping the way companies operate in today's complex environment. As organizations navigate the challenges of 2025, embracing the theory of interested parties, alongside continuous business performance monitoring and relationship-building through real-time analytics, will be crucial for achieving sustainable growth and maintaining competitive advantage.
Applying Stakeholder Theory in Project Management: Strategies for Success
In the management of initiatives, the stakeholder model of strategic management is essential for attaining successful results. Strategies such as party mapping, engagement plans, and effective communication serve as critical components. By identifying essential participants and thoroughly understanding their needs and expectations, managers can tailor their approaches in alignment with the stakeholder model of strategic management, ensuring alignment with participant interests.
Engaging participants during the planning stage not only improves results but also enables the recognition of possible risks and opportunities that might otherwise remain overlooked. Statistics indicate that 44% of initiatives fail due to a lack of alignment between business and initiative objectives, highlighting the necessity of participant engagement. Conversely, organizations that utilize formal management methodologies, which frequently incorporate engagement strategies, experience a 59% success rate in delivering initiatives on schedule. This correlation emphasizes the significance of incorporating participant viewpoints into the stakeholder model of strategic management for effective planning and execution.
Moreover, maintaining open lines of communication is vital for fostering trust and collaboration among involved parties in the stakeholder model of strategic management. This trust is essential for success, as it encourages participants to share insights and feedback that can greatly impact the direction of the initiative. A case study titled "Engagement ROI: Quantifying the Value of Involvement" illustrates this point by demonstrating how measuring engagement metrics can enhance plans and improve relationships, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Current trends in participant mapping and engagement strategies emphasize the need for a proactive approach. By utilizing , managers can effectively assess participant dynamics and adjust their strategies accordingly. This adaptability is essential in today's fast-paced business environment, where the expectations of interested parties are continually evolving.
Expert opinions in the field suggest that a strong engagement strategy, according to the stakeholder model of strategic management, not only reduces risks but also propels success, making it a crucial focus for managers in 2025. Furthermore, using well-known management software such as Jira can enable adaptable management, further improving participant engagement. With the typical program manager in Europe earning approximately $95,000 each year, and UK-based professionals earning $114,000, the need for skilled managers highlights the significance of efficient engagement strategies in achieving success.
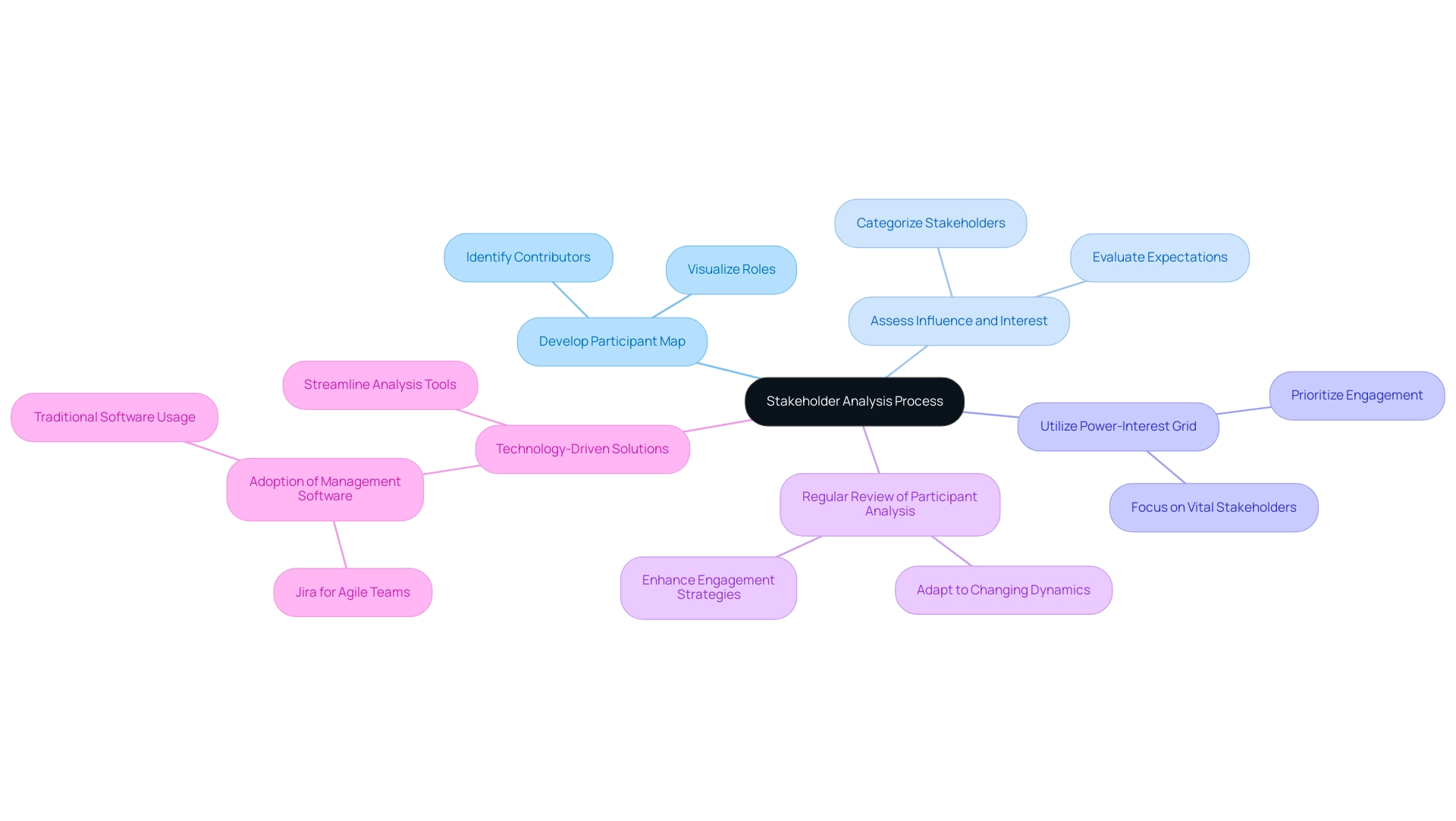
Identifying and Analyzing Stakeholders: Key Steps and Tools
Identifying and analyzing interested parties is a critical process fundamental to the stakeholder model of strategic management, involving several essential steps. Initially, developing a detailed participant map allows managers to visualize the different contributors involved and their specific roles. This map must include an assessment of each participant's influence and interest levels, effectively categorized using the stakeholder model and tools like the power-interest grid.
This grid prioritizes interested parties based on their potential influence on the initiative, enabling managers to focus their engagement efforts on those most vital to the initiative's success.
Current best practices in mapping interested parties underscore the importance of understanding their expectations and motivations within the stakeholder model. Regularly reviewing participant analysis is essential, ensuring that teams remain adaptable to changing participant dynamics throughout the initiative's lifecycle. In 2025, data suggest that only 36% of teams in underperforming companies successfully complete initiatives, highlighting the urgent need for effective engagement strategies to enhance results.
Moreover, the stakeholder model of strategic management has gained traction, with numerous entities embracing technology-driven solutions to streamline the use of analysis tools. The popularity of management software like Jira, particularly among Agile-based teams, illustrates the shift towards more flexible and responsive methodologies. This trend is critical, as half of all Project Management Offices shut down within just three years, emphasizing the challenges faced in management and the necessity for efficient engagement with involved parties.
Furthermore, with 39% of desiring swift replies, entities must prioritize prompt interaction with involved parties to cultivate positive relationships. The statistic that only 40% of IBM initiatives achieve their objectives serves as a cautionary example of the consequences of inadequate participant management. As organizations navigate complex project environments, the ability to create and maintain an accurate interest group map will be paramount for achieving project objectives and adhering to the stakeholder model of strategic management, ensuring sustainable growth.
Stakeholder vs. Shareholder Models: Implications for Corporate Governance
of strategic management underscores the importance of addressing the interests of all parties involved, standing in stark contrast to the shareholder model, which primarily seeks to maximize shareholder value. This fundamental distinction carries significant implications for corporate governance practices. Organizations embracing the stakeholder model tend to engage in ethical decision-making and long-term strategic planning, recognizing the interconnectedness of various interests.
For instance, Haidilao, a prominent hot pot restaurant chain, exemplifies this model by prioritizing employee satisfaction and customer service. This approach has resulted in a low employee turnover rate and effective crisis management during a food-safety incident.
Conversely, companies that focus predominantly on shareholder interests may prioritize immediate financial returns, often at the expense of broader societal and environmental considerations. Such short-sightedness can lead to reputational damage and long-term sustainability challenges. The increasing shift towards participant governance reflects a growing recognition of the necessity for sustainable business practices that align with the stakeholder model, yielding benefits for all parties involved, including employees, customers, suppliers, and the community.
As one expert noted, "companies are increasingly acknowledging the importance of generating value for all parties involved, including shareholders, employees, customers, suppliers, and the community."
Current trends in corporate governance practices indicate a significant movement towards the stakeholder model, with many organizations recognizing the value of creating holistic value. Research suggests that efficiency can be achieved under both governance structures, provided that appropriate information is accessible. This insight reinforces the notion that governance involving all parties can be as effective as, if not more than, traditional shareholder-focused models, supporting the stakeholder model of strategic management.
Furthermore, sales strategies can be refined by understanding the needs of various parties, ensuring that all individuals involved in the purchasing process feel informed and valued. As companies navigate the complexities of modern markets, the implications of adopting a governance framework become increasingly clear: it fosters resilience, enhances trust, and ultimately drives sustainable growth.
Challenges in Implementing Stakeholder Theory: Navigating Complexities
Applying this theory presents numerous challenges for companies. A significant obstacle in the stakeholder model of strategic management is the balancing act required to address the competing interests of various parties, often resulting in conflicts and necessary trade-offs. In 2025, statistics indicate that nearly 60% of organizations grapple with alignment among interested parties, underscoring the importance of the stakeholder model of strategic management, particularly when short-term gains overshadow long-term sustainability.
This resistance can severely impede the adoption of sustainable practices, as involved parties may oppose initiatives that do not provide immediate benefits. Our technology-enabled turnaround and restructuring consulting services are specifically designed to assist organizations in navigating these challenges, streamlining operations, and ultimately achieving sustainable growth through transparency and collaboration.
Moreover, the lack of clear metrics for assessing value to interested parties complicates decision-making processes within the stakeholder model of strategic management. As noted by Commons, 'Industrial goodwill materializes through a process wherein emerging moral norms elevate the competitive landscape.' This highlights the necessity for entities to create frameworks that not only evaluate impact on interested parties but also align with the stakeholder model of strategic management and evolving moral and ethical standards.
Our comprehensive financial assessments prioritize cash preservation, efficiency, and risk reduction, enabling organizations to uncover value and minimize expenses while ensuring effective management of interests.
To successfully navigate these complexities, entities must cultivate a culture of open communication and actively engage interested parties in the stakeholder model of strategic management during decision-making processes. This approach not only fosters trust but also encourages cooperation, aligning with the stakeholder model of strategic management and empowering organizations to address the concerns of interested parties more effectively. For instance, the 2023 PwC Corporate Directors Survey revealed that companies with a higher percentage of female directors were more likely to adopt inclusive models, suggesting that diverse perspectives can enhance corporate governance and engagement.
This case study illustrates how integrating diverse viewpoints within the stakeholder model of strategic management can lead to more effective management practices for all involved parties.
By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations can refine through the stakeholder model of strategic management, ultimately fostering sustainable growth and building with technology-enabled solutions. Contact us to discover how we can support your business in navigating stakeholder challenges.
Conclusion
In the corporate landscape of 2025, stakeholder theory stands out as a pivotal framework for organizations striving to align the interests of all parties involved—not solely shareholders. By prioritizing employees, customers, suppliers, and the wider community, businesses can significantly enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and cultivate sustainable growth. The incorporation of stakeholder theory into corporate strategies not only mitigates risks but also boosts overall performance, as evidenced by organizations that successfully align their objectives with societal values.
The practical application of stakeholder theory in project management highlights the critical importance of stakeholder mapping, engagement, and communication. By actively involving stakeholders during the planning phase, project managers can pinpoint potential risks and opportunities, ultimately leading to higher success rates in project delivery. This correlation between stakeholder engagement and project outcomes emphasizes the necessity of a proactive approach in today’s dynamic business environment.
However, the implementation of stakeholder theory is not without its challenges, including the need to balance competing interests and establish metrics for stakeholder value. Organizations must foster a culture of open communication and inclusive decision-making to effectively navigate these complexities. By addressing stakeholder concerns and integrating diverse perspectives, businesses can enhance their governance practices while building resilience and trust within their organizational frameworks.
Ultimately, embracing stakeholder theory is vital for organizations aiming to excel in a competitive marketplace. As businesses navigate the intricacies of modern economies, a steadfast commitment to stakeholder interests will be a defining factor in achieving sustainable success and nurturing long-term relationships that benefit all parties involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the stakeholder model of strategic management?
The stakeholder model of strategic management asserts that organizations must consider the interests of all parties affected by their actions, including employees, customers, suppliers, and the broader community, rather than focusing solely on shareholders.
Why has the stakeholder model become more prevalent in 2025?
Studies indicate that companies adopting the stakeholder model experience enhanced operational efficiency and lower costs related to employee turnover and theft, making it increasingly popular among organizations.
What are the consequences of neglecting stakeholder interests?
Corporations that ignore the interests of involved parties often face significant resistance, leading to increased operating costs due to idle time, replacement costs, theft, and vandalism.
How is the stakeholder model related to corporate social responsibility (CSR)?
The stakeholder model is closely tied to CSR, which provides a framework for businesses to create value for all parties involved. A strong commitment to CSR fosters positive stakeholder relationships and correlates with improved overall performance.
What benefits do organizations gain from integrating sustainability into their strategies?
Organizations that effectively integrate sustainability into their core strategies are better positioned to meet market expectations and enhance their brand reputation, ultimately building public trust and loyalty.
What role does real-time analytics play in the stakeholder model?
Real-time analytics support streamlined decision-making and allow organizations to monitor their health continuously, ensuring that lessons learned from turnaround processes are applied to strengthen relationships.
What strategies are essential for managing stakeholder initiatives?
Key strategies include party mapping, engagement plans, and effective communication, which help identify essential participants and align approaches with their needs and expectations.
How does participant engagement impact the success of initiatives?
Engaging participants during the planning stage improves results and helps identify potential risks and opportunities. Statistics show that 44% of initiatives fail due to misalignment between business and initiative objectives, while organizations using formal management methodologies achieve a 59% success rate in delivering initiatives on time.
Why is communication important in the stakeholder model?
Open lines of communication foster trust and collaboration among involved parties, encouraging them to share insights and feedback that can significantly influence the initiative's direction.
What current trends are emerging in participant engagement strategies?
Current trends emphasize a proactive approach using technology-driven consulting services to assess participant dynamics and adapt strategies to meet evolving expectations in a fast-paced business environment.
How does a strong engagement strategy contribute to success in the stakeholder model?
A robust engagement strategy reduces risks and enhances success, making it a crucial focus for managers in 2025, as highlighted by expert opinions in the field.




