Overview
The key methods in stakeholder management include integrative and relational approaches, which focus on creating shared value and nurturing trust-based relationships through ongoing communication. The article supports this by highlighting how effective stakeholder management leads to improved project outcomes and competitive advantages, emphasizing the importance of understanding diverse stakeholder motivations and employing tailored strategies for engagement.
Introduction
In the intricate world of business, stakeholder management emerges as a pivotal process that can make or break an organization’s success. This multifaceted discipline involves identifying, analyzing, and engaging various parties—ranging from employees and customers to investors and the community—who have a vested interest in a company's operations.
As businesses navigate the complexities of modern challenges, particularly during times of change or crisis, the need for effective stakeholder management becomes increasingly critical. With a focus on aligning strategies with stakeholder priorities, organizations can not only enhance their project success rates but also foster collaboration and mitigate conflicts.
By exploring the dynamics of stakeholder engagement, the article delves into essential methodologies, power dynamics, and the tools necessary for conducting effective stakeholder analysis, ultimately providing a comprehensive guide for organizations striving to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
Understanding Stakeholder Management: An Overview
The ideally uses identification and analysis methods to ensure effective oversight of individuals or groups vested in a business's operations or outcomes. These parties encompass a wide range of entities, including employees, customers, suppliers, investors, and the broader community. The importance of efficient participant oversight cannot be overstated; it ensures alignment with the entity’s goals, especially during times of change or crisis.
Mark Webb, Managing Director at Future Purchasing, emphasizes this point:
Aligning strategies with is not optional—it’s critical for success.
Furthermore, entities with attain an impressive project success rate of 92%, in contrast to only 33% for those that underperform. Significantly, 46% of organizations emphasize proper project planning to accomplish their objectives, indicating the growing complexity of project oversight due to new technologies and changing customer expectations.
By understanding the diverse motivations and influences of stakeholders, ideally uses collaboration and conflict resolution methods to devise strategies that drive more successful outcomes. The project governance landscape is set to benefit from automation, generative AI, and data analytics, as highlighted in the case study titled "Adapting to Project Management Trends for 2024." This study encourages organizations to adopt AI-powered project coordination tools, such as those included in our promotional guide, "Revolutionizing Operations With AI & Machine Learning - An Operators Guide," available now for $399.
These tools improve strategy and implementation, ensuring successful project outcomes. Additionally, real-time analytics allow for continuous business performance monitoring, aiding CFOs in making informed decisions. In 2024, Space will be hosting a webinar centered on impact, which will serve as a platform for discussing these essential topics and .
Key Methods in Stakeholder Management: Integrative vs. Relational
The ideally uses to manage interested parties. The stakeholder management approach ideally uses integrative methods and collaborative decision-making methods that prioritize the creation of shared value by aligning the interests of involved parties with organizational goals, fostering mutual benefits. This contrasts with the stakeholder management approach, which ideally uses relational and engagement methods that focus on nurturing through ongoing communication.
Effective management of relationships with interested parties is critical; organizations that excel in this regard can achieve competitive advantages in areas such as risk management, reputation enhancement, adaptation, and innovation. For instance, a restaurant chain facing financial challenges might implement an integrative approach by collaborating with suppliers on cost-saving initiatives, while also strengthening ties with loyal customers to ensure their continued patronage.
The Engagement Stakeholder Advisory Group (ESAG) comprised:
- Two patients/consumers
- Three healthcare payers
- Three practicing clinicians
- Two policy-makers
- One regulator
- Two representatives from the pharmaceutical and diagnostic industry
This diverse composition emphasizes the significance of categorizing involved parties based on their potential for threat and cooperation, which can significantly enhance value creation. A recent study emphasized this categorization, illuminating the significance of tailored approaches. As mentioned by a senior manager at Zeta, 'Following the philosophy of our parent company, we honor our partners and have a good reputation for integrity and transparency.'
This philosophy is echoed in the Analytic-Deliberative Model used in (CER), which emphasizes the importance of integrating diverse perspectives in decision-making. The model facilitated a structured approach to participant engagement, ensuring that various viewpoints were considered, ultimately leading to better-informed decisions. Overall, grasping the subtleties of integrative versus relational interactions is crucial for entities striving to navigate today's intricate environments successfully.
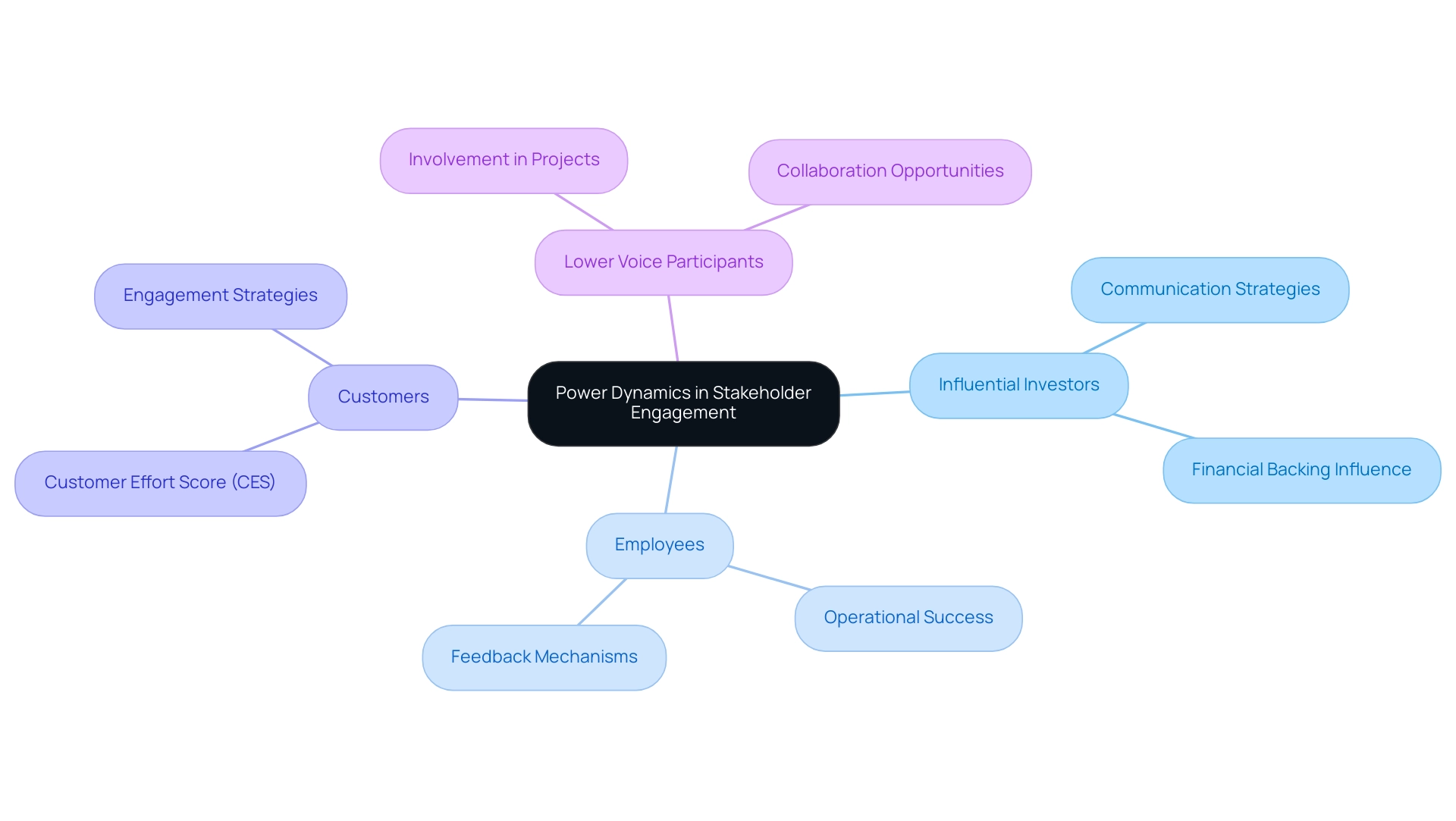
The Role of Power Dynamics in Stakeholder Engagement
Power dynamics are essential in managing interested parties, significantly influencing how they interact with the entity. Various participants wield different levels of power, influenced by their resources, expertise, and relationships with the organization. For example, organizations that adopt are .
This statistic underscores the importance of . In a restructuring scenario, leaders may prioritize communication with influential investors who can affect , while also addressing the concerns of employees—who may lack formal power but are integral to . This dual approach exemplifies effective , which ideally uses collaboration and involvement methods.
A notable example can be drawn from the telecom sector, where a company simplified its services, resulting in a reduced Customer Effort Score (CES). Such initiatives demonstrate that can lead to , ultimately contributing to . Moreover, entities that emphasize participant involvement often demonstrate increased and achieve enhanced long-term development, reflecting the stakeholder management approach that ideally uses collaborative and participatory methods.
By recognizing chances for cooperation and input, including involving lower voice and value participants in important projects, entities can improve their financial outcomes and manage the intricacies of relationships more effectively.
Conducting Effective Stakeholder Analysis: Tools and Techniques
Conducting effective is crucial for organizations aiming to enhance engagement and achieve successful outcomes. The ideally uses and surveys as key tools and techniques, with interviews serving a distinct purpose. Mapping of involved parties, particularly illustrated by , provides a three-dimensional view by integrating participants' attitudes with their power and interest.
This stakeholder management approach ideally uses strategic and prioritized methods to enhance engagement efforts. As noted, participant analysis often forms part of a communication plan, highlighting its importance in aligning messaging with participant needs. The stakeholder management approach ideally uses surveys and interviews to gather insights into participant concerns and expectations, while facilitating a deeper understanding of individual perspectives and motivations.
For example, a facing might utilize analysis of interested parties to assess sentiments among customers and employees alike, ensuring that their restructuring plan addresses the needs of both groups effectively. Organizations can develop a stakeholder management approach that ideally uses for analysis and relationship mapping, along with the OCMS Portal's Assessment Tool for built-in assessment surveys and autogenerated engagement plans, to foster strong relationships. As analysis of interested parties is an ongoing process, continuous reassessment and adaptation of these strategies are essential to remain responsive to evolving dynamics of involved entities.
Navigating Challenges in Stakeholder Management During Crises
Managing involved parties during crises introduces a host of unique challenges, from and pressing timelines. The pandemic has intensified these problems, resulting in delays in research results and participant communication deliverables, which entities must manage efficiently. It's essential for entities to demonstrate agility in their communication and involvement strategies.
Our team supports a shortened decision-making cycle throughout the turnaround process, empowering your team to take to preserve your business. Recent research indicates that 92% of entities plan to maintain online participant engagement moving forward, highlighting the value of adaptability in . For instance, during the financial fallout of a crisis, retail businesses may encounter significant backlash from customers worried about potential layoffs.
Proactively clarifying the reasoning behind essential decisions and involving interested parties in meaningful discussions can help mitigate negative sentiments. Moreover, we continually monitor the success of our plans through our client dashboard, providing to diagnose your continuously. This allows entities to update and adjust their strategies based on insights gained, thereby .
The complexities of engaging involved parties are further illustrated by the perspective that hybrid formats, while potentially beneficial, can be 'maybe' for some, as they are even more time-consuming and can create group dynamics that complicate communication. Furthermore, entities must remain vigilant and ready to adjust their strategies as situations evolve, ensuring their approach ideally uses to stay attuned to stakeholder concerns. Notably, research suggests that a of a company's narrative, as perceived timeliness correlates with credibility.
A significant example is the , where the company's initial denial and lack of transparency led to a catastrophic loss of trust, underscoring that effective crisis communication is vital for maintaining credibility. By adeptly addressing these challenges and operationalizing lessons learned, organizations can enhance trust and foster stronger relationships, even amidst the most tumultuous circumstances.
Conclusion
Effective stakeholder management is an essential component of modern business practices, intricately woven into the fabric of organizational success. By identifying, analyzing, and engaging stakeholders, businesses can align their strategies with stakeholder priorities, ultimately leading to enhanced project outcomes and collaboration. The integrative and relational approaches to stakeholder management offer valuable methodologies that foster shared value and trust-based relationships, making it imperative for organizations to understand and leverage these dynamics.
Power dynamics play a critical role in shaping stakeholder engagement, highlighting the importance of recognizing varying levels of influence among stakeholders. Organizations that adapt their engagement strategies accordingly benefit from improved operational efficiency and financial stability. Furthermore, the tools and techniques for conducting effective stakeholder analysis, such as stakeholder mapping and surveys, empower organizations to develop targeted strategies that respond to the evolving needs and concerns of their stakeholders.
Navigating the complexities of stakeholder management during crises presents additional challenges, yet it also offers opportunities for organizations to demonstrate agility and responsiveness. By maintaining open lines of communication and proactively addressing stakeholder concerns, companies can foster trust and credibility even in turbulent times. The lessons learned from managing stakeholder relationships during crises underscore the importance of adaptability and continuous engagement.
In summary, the ability to effectively manage stakeholders is not merely a tactical necessity but a strategic imperative that can significantly influence an organization's trajectory. By prioritizing stakeholder engagement and understanding the nuances of their relationships, businesses can position themselves for sustained success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the stakeholder management approach?
The stakeholder management approach uses identification and analysis methods to oversee individuals or groups involved in a business's operations or outcomes, including employees, customers, suppliers, investors, and the community.
Why is efficient stakeholder oversight important?
Efficient stakeholder oversight ensures alignment with an entity’s goals, especially during times of change or crisis, which is critical for success.
What is the project success rate for organizations with project oversight maturity?
Organizations with project oversight maturity achieve a project success rate of 92%, compared to only 33% for those that underperform.
What role does proper project planning play in organizational success?
Proper project planning is emphasized by 46% of organizations as essential to accomplishing their objectives, highlighting the complexity of project oversight due to new technologies and changing customer expectations.
How does understanding stakeholder motivations benefit organizations?
By understanding diverse stakeholder motivations, organizations can use collaboration and conflict resolution methods to create strategies that drive more successful outcomes.
What tools are suggested for improving project outcomes?
AI-powered project coordination tools, automation, generative AI, and data analytics are suggested for improving strategy and implementation in project management.
What is the significance of real-time analytics in business performance?
Real-time analytics allow for continuous business performance monitoring, helping CFOs make informed decisions.
What is the purpose of the upcoming webinar hosted by Space in 2024?
The webinar will focus on impact and serve as a platform for discussing essential topics related to stakeholder management and fostering community engagement.
What are the two main methods used in stakeholder management?
The two main methods are integrative methods, which focus on creating shared value by aligning interests, and relational methods, which emphasize nurturing strong, trust-based relationships through ongoing communication.
How can effective stakeholder relationship management provide competitive advantages?
Organizations that excel in managing relationships with stakeholders can achieve advantages in risk management, reputation enhancement, adaptation, and innovation.
What is the composition of the Engagement Stakeholder Advisory Group (ESAG)?
The ESAG includes two patients/consumers, three healthcare payers, three practicing clinicians, two policy-makers, one regulator, and two representatives from the pharmaceutical and diagnostic industry.
Why is categorizing stakeholders based on their potential for threat and cooperation important?
Categorizing stakeholders enhances value creation by allowing organizations to tailor their approaches based on the unique influences and motivations of different parties.
What model emphasizes integrating diverse perspectives in decision-making?
The Analytic-Deliberative Model used in Comparative Effectiveness Research (CER) emphasizes the importance of integrating diverse perspectives to ensure better-informed decisions.




