Overview
A stakeholder analysis in project management serves as a systematic approach for identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing individuals or groups affected by or interested in a project. This process is essential for ensuring successful outcomes. Effective stakeholder management can significantly reduce project delays and enhance collaboration. Consequently, these efforts lead to improved financial performance and higher project completion rates. It is imperative for project managers to recognize the importance of engaging stakeholders early and consistently to maximize project success.
Introduction
In the intricate world of project management, stakeholder analysis stands out as a pivotal tool that can determine a project's success or failure. By systematically identifying and assessing the various individuals and groups invested in a project, managers gain a deeper understanding of the diverse needs and expectations that influence outcomes. This proactive approach not only minimizes risks and enhances collaboration but also drives significant improvements in project efficiency and financial performance.
As organizations increasingly acknowledge the importance of stakeholder engagement, the ability to categorize and prioritize these relationships becomes essential. From primary stakeholders directly impacted by project decisions to secondary ones whose influence can sway outcomes, understanding these dynamics is crucial for steering projects toward success in an ever-evolving landscape.
Define Stakeholder Analysis in Project Management
A stakeholder analysis in project management is a systematic method for identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing individuals or groups with an interest in or who are impacted by an endeavor. Understanding stakeholder analysis is essential for managers, as it highlights the needs, expectations, and potential effects of interested parties on outcomes. By classifying these parties according to their influence and interest, teams can create focused involvement strategies that ensure concerns are addressed and support is secured throughout the initiative lifecycle.
The importance of effectively managing interested parties is underscored by research indicating that it can lead to a 40% decrease in delays. This emphasizes the critical role of stakeholder analysis in project management, which serves to boost efficiency and success, ultimately positively impacting financial performance.
For instance, a well-organized communication strategy tailored for various interest groups can significantly enhance transparency and cooperation. One case study demonstrated that by specifying information delivery methods—such as monthly board meetings for executives and email newsletters for external stakeholders—projects fostered a collaborative environment that supported their goals. This approach not only enhanced participant involvement but also resulted in a 15% increase in completion rates, showcasing its financial benefits.
Looking ahead to 2025, the continuous development of engagement techniques highlights the necessity for improved documentation and prioritization, which are crucial for success in participant capitalism. As Simon Mainwaring wisely noted, companies must recognize that shareholders should also view themselves as participants in the broader social context. This perspective emphasizes the significance of stakeholder analysis in project management, aligning objectives with the needs of all parties involved, ultimately leading to cost savings and potential revenue growth for organizations.
Explain the Importance of Stakeholder Analysis
Understanding stakeholder analysis in project management is crucial for several compelling reasons. First, it identifies essential participants whose influence can dictate the success or failure of an initiative. By grasping their interests and concerns, managers can devise tailored communication strategies that keep stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the initiative's lifecycle.
Moreover, effective stakeholder analysis significantly reduces risks by anticipating potential conflicts and addressing them proactively. This foresight not only leads to smoother execution but also enhances stakeholder satisfaction, which is vital for success. Recent research indicates that organizations prioritizing stakeholder involvement experience a notable improvement in outcomes, with successful initiatives adhering to budgets and schedules more reliably.
In fact, program oversight expenses typically range between 7% and 11% of a program's overall cost, underscoring the financial implications of efficient stakeholder engagement in mitigating risks. Furthermore, a case study titled 'Management Performance and Challenges' reveals that only a small fraction of firms successfully complete all their initiatives, with significant financial losses linked to inadequate performance. This emphasizes the importance of effective initiative oversight techniques, including a thorough understanding of stakeholder analysis in project management.
Finally, involving stakeholders fosters teamwork and collaboration, which are essential for achieving goals and ensuring lasting success. As the demand for skilled leaders continues to rise, with approximately 88 million individuals expected to occupy roles related to project oversight by 2027, prioritizing stakeholder engagement becomes increasingly critical. Case studies have shown that initiatives with comprehensive stakeholder analysis are more likely to meet their objectives, illustrating the clear connection between stakeholder involvement and initiative performance.
Outline Key Components of Stakeholder Analysis
Crucial elements of interest group analysis in management are vital for guaranteeing success. These components include:
- Identification: Recognizing what constitutes a stakeholder analysis in project management involves identifying all potential participants, both internal and external, who may influence or be impacted by the initiative. A comprehensive list is essential for understanding stakeholder dynamics, ensuring that no critical voices are overlooked.
- Evaluation: Stakeholders are assessed according to their influence, interest, and potential effect on the initiative. Employing tools such as the power-interest grid enables managers to visualize the dynamics of involved parties effectively, which is essential for grasping the nuances of stakeholder analysis in project management.
- Prioritization: Stakeholders are classified into categories such as high power/high interest or low power/high interest. This classification aids in assessing the degree of involvement necessary, ensuring that those with the most influence receive appropriate attention. For instance, case studies utilizing the power-interest grid demonstrate how recognizing and prioritizing participants can align communication strategies with their needs, ultimately enhancing the probability of success.
- Engagement Approach: Creating customized communication and involvement plans for each interested party group is essential. This approach guarantees that the interests of involved parties are addressed, ensuring their backing is maintained throughout the lifecycle of the initiative. Effective engagement strategies can lead to a 10% increase in employee retention within the tech sector, showcasing the concrete advantages of a well-executed analysis.
Incorporating feedback from interested parties not only improves decision-making but also leads to more informed results. Efficient initiative oversight significantly depends on managing different elements of participant interactions; thus, grasping these factors is crucial for leaders seeking to assist companies in overcoming obstacles and attaining lasting development.
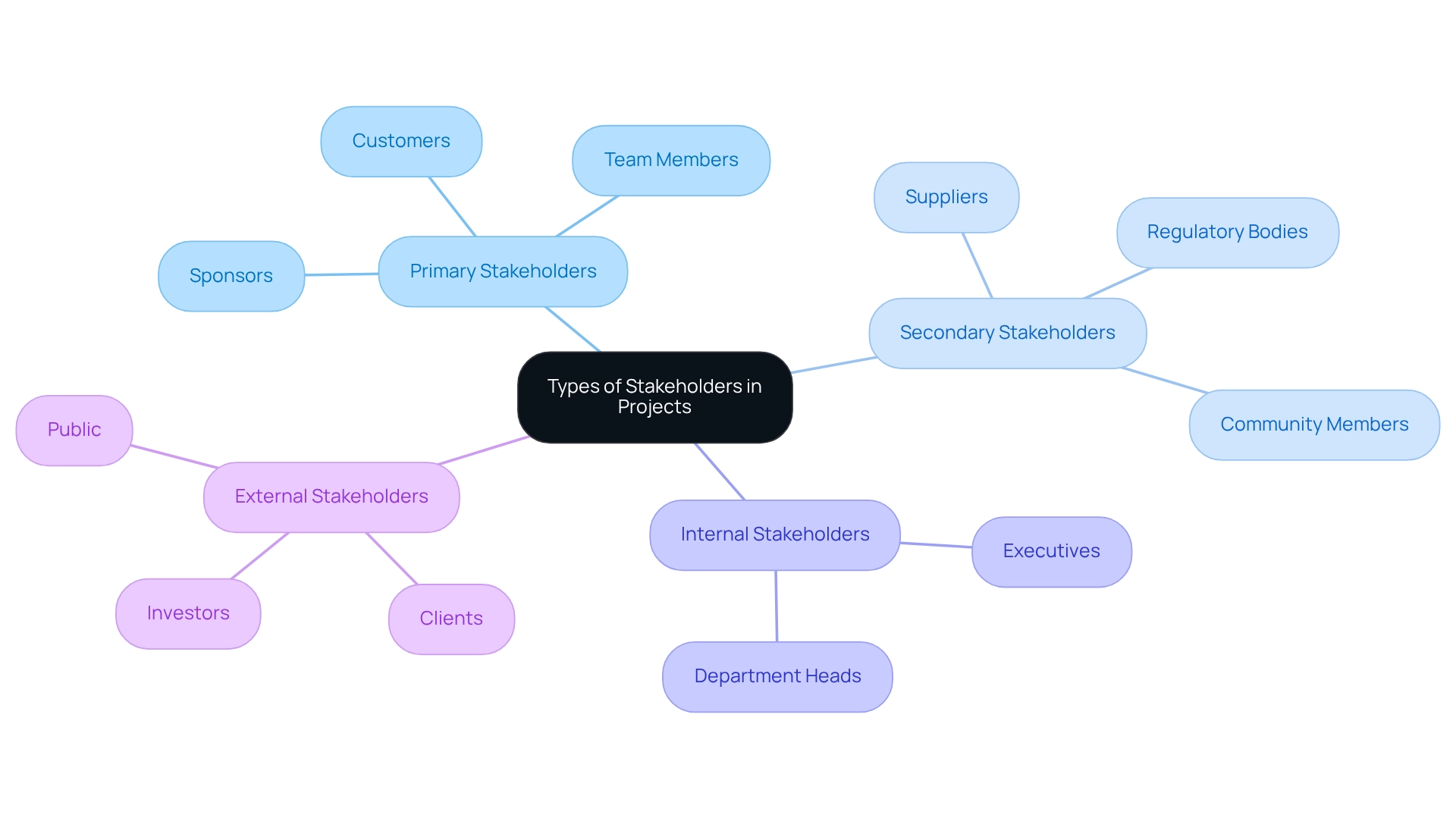
Identify Types of Stakeholders in Projects
In project management, stakeholders can be categorized into several distinct types, each playing a crucial role in the project's success:
- Primary Stakeholders: These are individuals or groups directly impacted by the initiative, including customers, team members, and sponsors. Their needs and feedback are essential for initiative alignment and success.
- Secondary Stakeholders: This group encompasses those indirectly affected by the initiative, such as suppliers, regulatory bodies, and community members. While they may not be directly involved, their influence can significantly impact results.
- Internal Stakeholders: Comprising members within the organization, such as executives and department heads, internal stakeholders are essential for resource allocation and strategic direction.
- External Stakeholders: Entities outside the organization, including clients, investors, and the public, fall into this category. Their perceptions and satisfaction can influence initiative viability and organizational reputation.
Understanding stakeholder analysis in project management is essential for managers, as it enables them to customize engagement strategies efficiently. For instance, a case study concerning a distribution firm emphasized the significance of key participants when a manager realized that the sponsor's lack of evident dedication was obstructing advancement. By involving the sponsor in a weekend testing session, the team reignited motivation and underscored the initiative's significance, ultimately steering it back on track.
Moreover, effective oversight of involved parties is a continuous process of developing connections. Engaging employees, satisfying customers, and securing investor confidence are key to transforming challenges into opportunities. Significantly, merely 34% of underperformers offer comparable training in engagement with interested parties, demonstrating how effective management of these relationships can distinguish successful initiatives from those that face difficulties.
Consequently, managers can enhance their strategies and improve overall success by understanding stakeholder analysis in project management, which involves classifying interested parties and their influence. As PMI indicates, "Projects should begin with the assumption that recognizing a variety of interested parties and interacting with them in a consistent and structured way will enhance project success." This underscores the necessity of a structured approach to stakeholder engagement, tailored to the unique needs of each stakeholder category.
Conclusion
Stakeholder analysis is crucial for successful project management, systematically identifying, assessing, and prioritizing the various individuals and groups involved. This process illuminates the diverse needs and expectations of stakeholders, equipping project managers with essential insights to develop tailored engagement strategies. By effectively categorizing stakeholders, project teams can minimize risks, enhance collaboration, and ultimately drive improved project outcomes.
Moreover, the significance of stakeholder analysis is underscored by its impact on project efficiency and financial performance. Proactive engagement with stakeholders can lead to substantial reductions in project delays and increases in completion rates. As organizations navigate the complexities of stakeholder capitalism, understanding the dynamics of these relationships becomes vital. Aligning project objectives with stakeholder interests fosters collaboration and can yield potential cost savings and revenue growth.
In conclusion, effective stakeholder analysis serves as a cornerstone of successful project management. By prioritizing stakeholder engagement, project managers establish a solid foundation for project execution that aligns with the needs of all parties involved. As the demand for skilled project managers continues to grow, the ability to navigate stakeholder relationships will be an increasingly critical competency, ensuring that projects not only meet their goals but also contribute to long-term organizational success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stakeholder analysis in project management?
Stakeholder analysis is a systematic method for identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing individuals or groups who have an interest in or are impacted by a project. It helps managers understand the needs, expectations, and potential effects of these parties on project outcomes.
Why is stakeholder analysis important for managers?
Stakeholder analysis is essential for managers as it allows them to create focused involvement strategies that address concerns and secure support throughout the project lifecycle. It can lead to improved project efficiency and success, ultimately affecting financial performance positively.
How does effective stakeholder management impact project delays?
Research indicates that effectively managing interested parties can lead to a 40% decrease in project delays, highlighting the critical role of stakeholder analysis in enhancing project efficiency.
What role does communication play in stakeholder management?
A well-organized communication strategy tailored for different interest groups enhances transparency and cooperation. For example, using specific information delivery methods for various stakeholders can foster a collaborative environment and support project goals.
Can you provide an example of successful stakeholder communication?
One case study showed that specifying information delivery methods—such as monthly board meetings for executives and email newsletters for external stakeholders—led to increased participant involvement and a 15% rise in project completion rates.
What is the significance of engagement techniques in stakeholder analysis?
The ongoing development of engagement techniques emphasizes the need for improved documentation and prioritization, which are crucial for success in participant capitalism and aligning project objectives with the needs of all stakeholders.
How does stakeholder analysis contribute to cost savings and revenue growth?
By aligning project objectives with the needs of all parties involved, stakeholder analysis can lead to cost savings and potential revenue growth for organizations, as it encourages a broader perspective on stakeholder involvement.




