Overview
Stakeholders in project management are defined as individuals or groups with a vested interest in the project's outcome, encompassing team members, customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies. Effective stakeholder management is not just beneficial; it is crucial for project success. This approach fosters collaboration, minimizes resistance, and aligns project goals with the needs and expectations of all involved parties. Consequently, it enhances overall project performance.
Moreover, understanding the diverse roles of stakeholders allows project managers to tailor their strategies effectively. By acknowledging the unique perspectives and contributions of each group, project leaders can cultivate a more inclusive environment that drives success.
In addition, consider the impact of robust stakeholder engagement on project outcomes. Research indicates that projects with proactive stakeholder management are significantly more likely to meet their objectives. This highlights the necessity for project managers to prioritize stakeholder relationships.
Ultimately, the call to action is clear: invest in stakeholder management strategies to ensure project success. By doing so, you not only enhance collaboration but also pave the way for achieving desired results in your projects.
Introduction
In the intricate world of project management, stakeholders play a pivotal role, influencing outcomes and shaping success. From team members and clients to regulatory bodies, understanding the diverse array of stakeholders is essential for any project manager aiming to navigate the complexities of engagement and communication.
As organizations strive to align their objectives with stakeholder interests, the need for effective management strategies becomes increasingly clear. This article delves into the significance of stakeholder analysis, identification techniques, and the integration of technology, offering insights on how to foster collaboration, mitigate risks, and ultimately drive project success.
Through a comprehensive exploration of these themes, it becomes evident that prioritizing stakeholder engagement is not just beneficial—it's imperative for achieving sustainable outcomes in today's dynamic project landscape.
Understanding Stakeholders: Definition and Importance
In the realm of stakeholder definition within project management, participants encompass a diverse range of individuals and groups who possess a vested interest in the outcome of the initiative. This includes team members, customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies—essentially anyone who can influence or be influenced by the initiative. Recognizing and understanding these involved parties is crucial for grasping stakeholder definition in project management, as their support and active engagement can significantly impact the initiative's success.
Efficient management of these stakeholders, as outlined in stakeholder definition project management, not only addresses their needs and expectations but also fosters collaboration and minimizes resistance throughout the project lifecycle. Engaging internal participants through regular updates and collaborative workshops is vital for aligning project goals with organizational objectives. Recent studies indicate that strong alignment among participants mitigates risks, enhances communication, and cultivates trust, leading to more seamless execution and improved outcomes.
For instance, a case study on organizational and initiative-level participant awareness illustrates how consistent analysis of stakeholder involvement can enhance management practices and results. This research revealed that fostering a culture of awareness ensures that participant needs are met throughout the lifecycle, ultimately contributing to successful outcomes.
Moreover, the statistic that over 1 billion children in at least 185 nations were affected by school closures due to the global pandemic underscores the critical role of collaboration in adapting to challenges across various sectors. As project management evolves, particularly with the integration of AI technologies that automate tasks and enhance workflows, these innovations are essential for boosting stakeholder involvement by facilitating communication and collaboration.
Furthermore, the client involvement process at Transform Your Small/Medium Business, which begins with a comprehensive business review, enables the identification of underlying issues and the development of strategic plans to reinforce competitive advantages. This methodology not only streamlines decision-making but also provides real-time analytics through our client dashboard to continuously monitor business performance. As Emmanuel Acquah aptly states, "Strong participant alignment reduces risks, enhances communication, and builds trust, ensuring smoother execution and better results."
The importance of effective stakeholder involvement remains pivotal in achieving sustainable success.
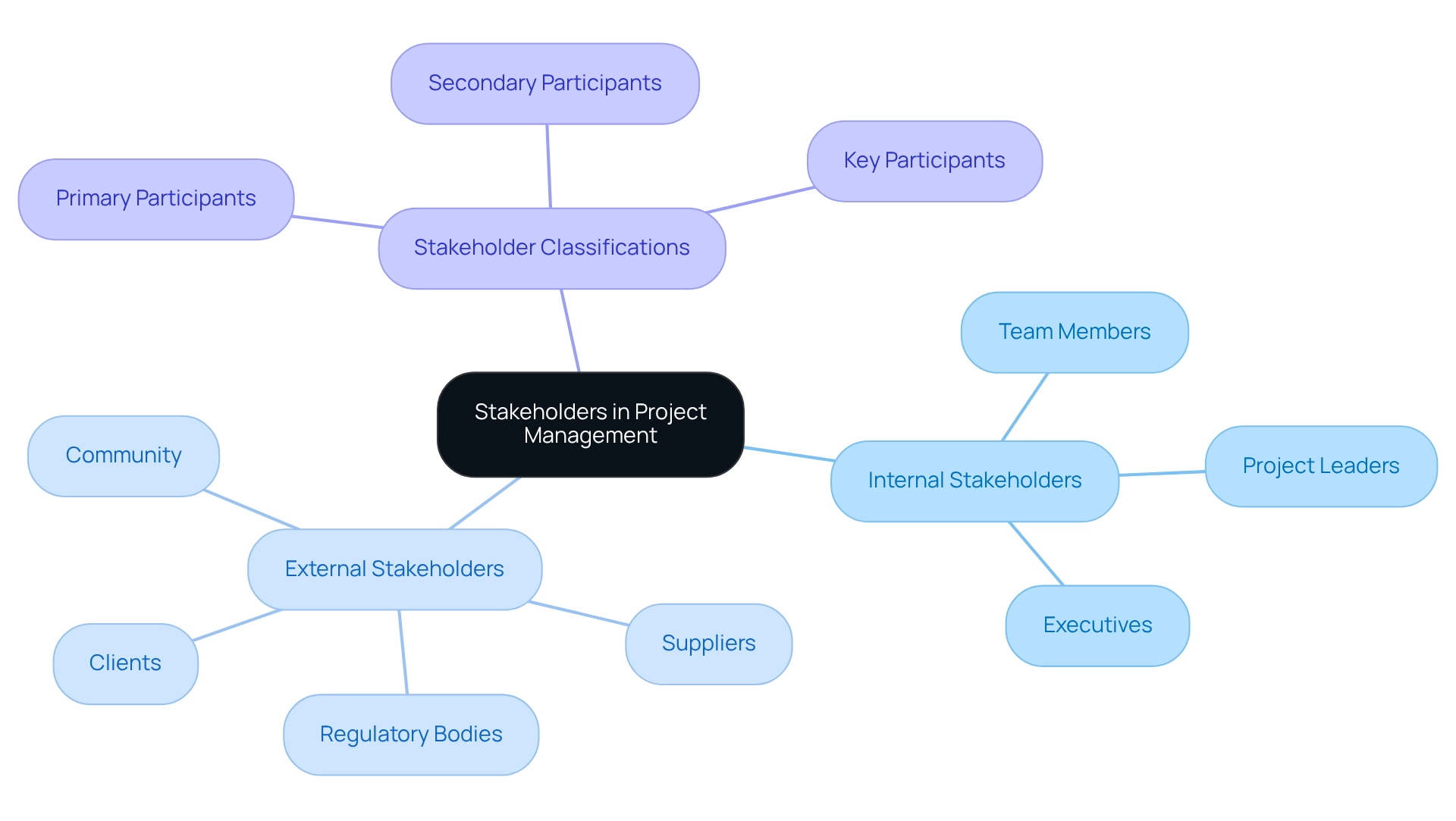
Types of Stakeholders in Project Management
In project management, stakeholders can be broadly categorized into two distinct groups: internal and external. Internal participants encompass team members, project leaders, and executives who are directly involved in the implementation of initiatives. Conversely, external parties include clients, suppliers, regulatory bodies, and the community, all of whom may be impacted by the outcomes of these initiatives.
Moreover, stakeholders can be classified as primary, secondary, or key participants based on their degree of influence and interest in the endeavor. Key participants are those whose interests are directly affected by the initiative, while secondary participants may experience a non-direct impact. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective stakeholder management, as it allows managers to tailor their communication and engagement strategies accordingly.
Recent trends in stakeholder categorization underscore the importance of recognizing the varying levels of influence and interest among individuals. For instance, a study revealed that approximately 70% of initiatives involve both primary and secondary participants, highlighting the necessity for managers to balance these diverse needs and expectations. Furthermore, different parties may evaluate the costs of the initiative in various ways and at different times, adding complexity to the management of interests.
Expert insights suggest that successful management of stakeholders demands a nuanced approach. As Deborah Vogwell aptly stated, "It is essential that managers find the appropriate balance between participant involvement and separation of the initiative from outside influence to ensure delivery within budget and schedule while also enhancing benefits for the client and his participants." This balance is vital for executing initiatives on time and within budget while maximizing advantages for all involved parties.
Furthermore, understanding both supporters and detractors of the initiative is key to aligning it with the needs of stakeholders. Case studies illustrate the significant role of customers as external participants. Although they may not directly influence company decisions, their collective purchasing behavior and feedback can profoundly affect a company's success.
Focusing on customer interests, such as product quality and availability, is essential for fostering business growth and enhancing customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of both internal and external stakeholders, along with their classifications, is critical for navigating the complexities of managing initiatives and grasping the stakeholder definition in project management to ensure successful outcomes. Effective management of stakeholders involves recognizing both internal and external groups, as well as their varying levels of power and interest in the project.
Identifying Stakeholders: Techniques and Strategies
Identifying interested parties is a multifaceted process that utilizes various techniques within stakeholder definition project management to ensure comprehensive engagement. Key methods, such as brainstorming sessions, participant mapping, and interviews, illuminate different aspects of participant dynamics. Notably, the Power/Interest Grid stands out as an effective tool, enabling managers to categorize individuals based on their influence and interest levels. This categorization facilitates targeted communication strategies, enhancing overall engagement.
Moreover, surveys and focus groups significantly enhance the identification process by gathering insights directly from potential participants regarding their concerns and expectations. This systematic approach is crucial for stakeholder definition project management, as it not only recognizes all relevant parties but also fosters a collaborative atmosphere that can lead to improved outcomes.
Recent studies indicate that 84.62% of program managers employ similar approaches to identify interested parties, underscoring the efficiency of these techniques across diverse initiatives. However, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of existing research, which primarily focuses on private corporate organizations. This focus may overlook nuances in public applications, suggesting that the applicability of these findings could vary and necessitating further exploration in public sector contexts.
A case study examining participant identification techniques in construction initiatives in Southwestern Nigeria revealed a preference among managers for brainstorming in group meetings over other methods, such as questionnaires and public hearings. This inclination to limit participant identification efforts could lead to considerable oversights, ultimately impacting project success.
As Lauren E. Petty noted, "These results demonstrate that genetic study of T2D in H/L populations can both help prevent a major health disparity through inclusion of this henceforth overlooked population and can also enable further discovery." This perspective emphasizes the importance of inclusive participant identification practices.
As we approach 2025, the efficiency of mapping strategies for involved parties continues to evolve, with successful instances illustrating how customized methods yield better results. The findings enable analysts to connect the statistical properties of the index with the weighting preferences of interested parties, allowing for the selection and modification of the index while achieving greater consistency. By employing these methods, organizations can ensure they not only recognize but also engage interested parties effectively, adhering to stakeholder definition project management and paving the way for sustainable success.
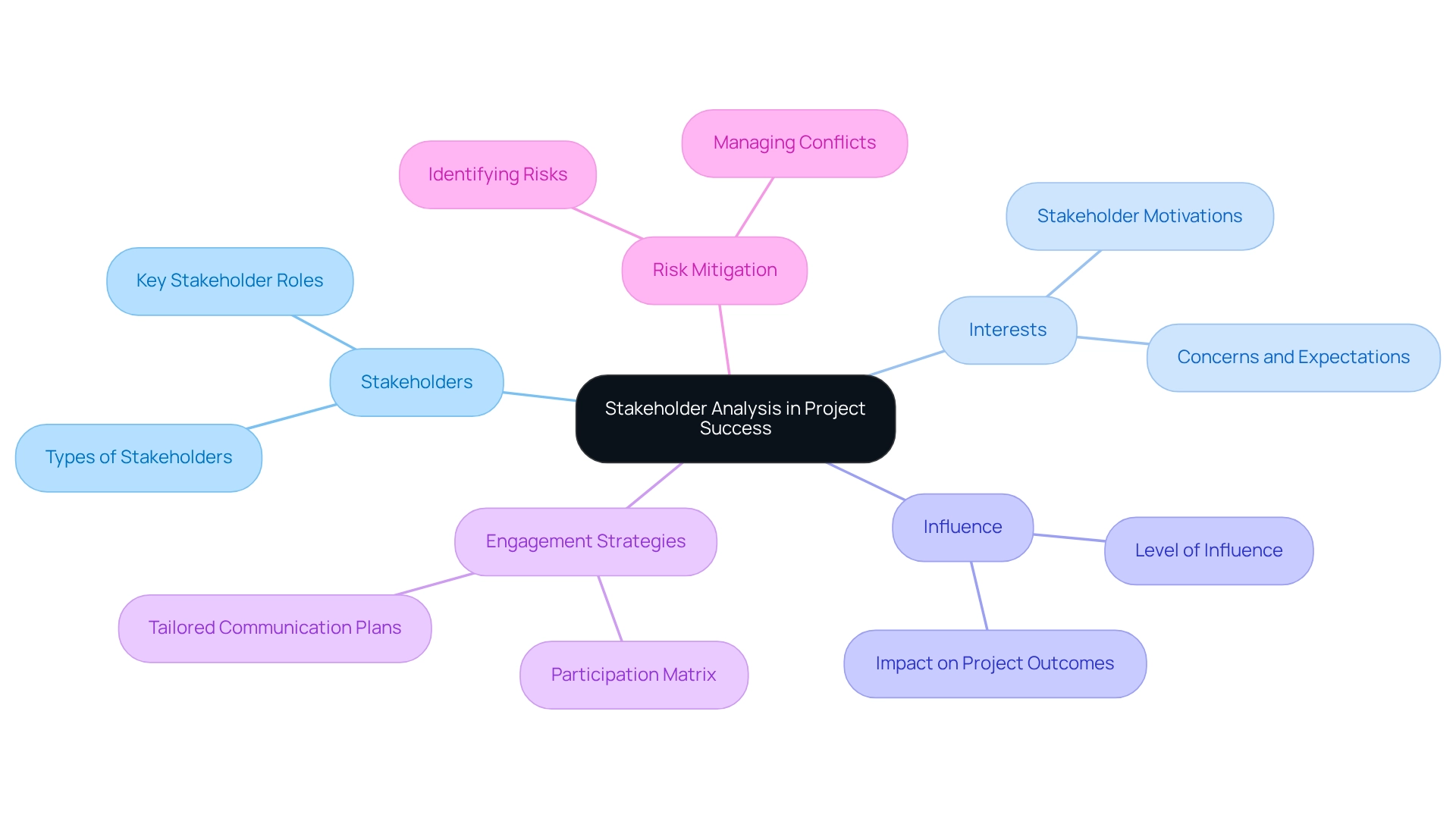
The Role of Stakeholder Analysis in Project Success
Analysis of interested parties represents a pivotal process in management, involving the assessment of interests, influence, and potential impact of various contributors on an initiative, as defined in stakeholder project management. This examination empowers managers to prioritize interested parties effectively and tailor their interaction strategies to align with the expectations of those involved in stakeholder project management. By understanding the motivations and concerns of these parties, managers can develop targeted communication plans that not only foster collaboration but also align with the stakeholder definition in project management, thereby mitigating risks associated with opposition from these groups.
Utilizing tools such as matrices and influence diagrams significantly enhances the stakeholder project management process, facilitating a structured approach to categorizing individuals based on their level of influence and interest. For instance, a case study titled 'Defining Stakeholder Participation' underscores the effectiveness of a participation matrix in clarifying roles and engagement levels throughout the lifecycle of the initiative. This clarity aids in managing communication expenses and ensures that interested parties are appropriately engaged, thus minimizing the risk of disputes during execution within the framework of stakeholder project management.
Recent findings underscore the significance of stakeholder definition in project management when analyzing involved parties to determine outcomes. According to IBISWorld, initiatives that adopt the stakeholder project management approach, which encompasses comprehensive interest group analysis, are statistically more likely to succeed, given that they account for the diverse interests and influences that can affect risk. Expert insights emphasize that overseeing and shaping stakeholder definition in project management is essential for achieving success in initiatives, as highlighted by the Project Management Institute (PMI), which asserts that 'the management team must … oversee and then shape those expectations to ensure a successful initiative.'
By prioritizing interested parties based on their potential influence, managers can enhance the likelihood of favorable results, ultimately driving sustainable growth for the organization, guided by a clear stakeholder definition in project management.
Effective Communication Strategies for Stakeholder Engagement
Effective communication strategies, as outlined in the stakeholder definition project management, are essential for engaging interested parties and ensuring project success. Regular updates, transparent reporting, and active listening form the backbone of these strategies. By utilizing a variety of communication channels—such as emails, meetings, and social media—organizations can effectively reach diverse audiences, ensuring that everyone is informed and engaged.
Creating strong feedback systems is especially crucial, as they enable involved parties to express their concerns and suggestions, promoting a collaborative atmosphere. This two-way communication not only improves satisfaction among involved parties but also aligns objectives with their expectations. Indeed, firms that thrive in involving interested parties highlight the stakeholder definition project management, as they are 40% more probable to finish assignments punctually and within financial limits, underscoring the essential function of efficient communication in management.
Adapting communication to the particular requirements and choices of involved parties, in line with the stakeholder definition in project management, is essential for sustaining their involvement and backing during the lifecycle of the initiative. For example, recent progress in digital tools has changed how participants interact, shifting from conventional methods such as workshops to more effective online platforms. A case study titled 'Facilitating Stakeholder Engagement through Digital Tools' illustrates how these tools enhance accessibility to information, improve feedback loops, and add new value to the communication process, ultimately leading to more successful project outcomes, particularly in relation to stakeholder definition project management.
Integrating expert perspectives into communication pathways can further enhance involvement strategies. As Angela Rodgers points out, "it’s crucial to consistently evaluate your communication with interested parties so that you can enhance your strategy, concentrate your efforts on the most effective channels and messages, and implement your insights in future interactions." Consistent evaluation of communication efficiency enables organizations to concentrate their efforts on the most influential channels and messages, ensuring that participant involvement remains a priority.
By adopting these effective communication techniques, companies can greatly enhance satisfaction among interested parties and achieve greater success. Furthermore, metrics on communication quality and stakeholder satisfaction can offer insights into the ROI of engagement strategies, highlighting the significance of effective communication in stakeholder definition project management.
Challenges in Stakeholder Management and How to Address Them
In the realm of stakeholder management within project management, numerous challenges frequently emerge, such as conflicting interests, communication breakdowns, and resistance to change. These obstacles can significantly impede success if not proactively addressed. To effectively navigate these complexities, managers must prioritize involvement from the outset, ensuring that every voice is acknowledged and valued.
This strategy not only promotes inclusivity but also lays the groundwork for trust among all parties involved.
Regular check-ins and updates are crucial for mitigating misunderstandings and fostering open lines of communication. By keeping stakeholders informed and engaged, managers can cultivate a collaborative environment that encourages feedback and adaptability. Furthermore, employing conflict resolution techniques—such as negotiation and compromise—can adeptly align the diverse interests of stakeholders.
For instance, organizations that have successfully managed relationships with stakeholders have reported enhanced outcomes, underscoring the value of thoughtful engagement.
Recent case studies highlight the necessity of directly addressing challenges posed by stakeholders. A notable example involved an initiative that faced substantial opposition due to conflicting priorities among stakeholders. By implementing a structured communication plan and facilitating open discussions, the team managed to realign interests and reach a satisfactory resolution.
This not only salvaged the initiative but also strengthened relationships with stakeholders for future projects. This aligns with the findings from the case study titled 'Combatting Stakeholder Challenges,' which emphasizes the criticality of diligent participant oversight and the formulation of effective communication strategies.
In conclusion, adept management of stakeholders transforms initiatives from simple tasks into impactful endeavors. As articulated by iQuasar, "every team member is committed to productive interaction and strives to elevate tasks into significant endeavors by fostering open dialogue, listening attentively, and adapting strategies as needed." By prioritizing involvement, ensuring clear communication, and utilizing conflict resolution strategies, managers can adeptly navigate the complexities inherent in stakeholder management and drive success.
Moreover, statistics reveal that beneficiaries have experienced the social and economic benefits of effective participant oversight, achieving a satisfaction score of 4.90 or 97.95%, which highlights the tangible advantages of successful engagement strategies.
Integrating Stakeholder Management into Project Management Practices
Incorporating participant engagement into program practices is vital for guaranteeing that their needs are prioritized throughout the initiative lifecycle. This integration entails incorporating participant considerations into every stage of planning, execution, and assessment. A well-organized participant oversight plan acts as a foundational tool, outlining engagement strategies, communication protocols, and feedback mechanisms customized to the distinct dynamics of each initiative.
To effectively develop a stakeholder management plan, organizations should focus on several key elements:
- Identification and Analysis: Recognizing all relevant stakeholders and understanding their interests, influence, and potential impact on the project.
- Engagement Strategies: Developing customized methods for involving interested parties, ensuring their voices are heard and their concerns addressed. This emphasis on engagement is vital for moving initiatives from installation to implementation.
- Communication Protocols: Establishing clear lines of communication that facilitate ongoing dialogue and information sharing among involved parties.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing systems to collect input from interested parties, enabling modifications and enhancements during the initiative.
By incorporating participant coordination as a fundamental element of initiative practices, organizations can promote teamwork, improve outcomes, and greatly boost the chances of success. Recent studies suggest that effective engagement of interested parties can result in enhanced project performance, with data demonstrating that projects with strong involvement plans are more likely to achieve their goals and provide value. Significantly, approximately 20% of instances of influence lacked a documented, visible effect, highlighting the significance of efficient participant oversight.
Moreover, expert insights highlight that "effective sponsorship is regarded as absolutely essential for change success," reinforcing the need for robust relationships with involved parties. As the terrain of initiative oversight changes, agility and flexibility in participant engagement practices are becoming ever more essential for sustainable growth. By embracing current best practices and learning from case studies, organizations can enhance their engagement strategies, ensuring they stay responsive to the evolving nature of relationships and demands.
The Impact of Technology on Stakeholder Management
Technology is essential for enhancing participant oversight, significantly improving communication, data gathering, and analysis. Sophisticated task oversight software and specialized participant interaction platforms empower coordinators to reach a wider audience and gather immediate responses—crucial for informed decision-making. Transform Your Small/ Medium Business accelerates the decision-making cycle throughout the turnaround process, enabling your team to take decisive action to preserve your business.
Recent innovations in program oversight technology have introduced features that simplify interactions with participants, making it easier to monitor involvement and feedback. Data analytics tools further enhance participant oversight by providing insights into participant behavior and preferences. This enables managers to create more focused engagement strategies, ensuring that communication is not only efficient but also relevant to the needs of those involved. We continually monitor the success of our plans and teams through our client dashboard, which provides real-time business analytics to diagnose your business health continuously.
The impact of technology on managing stakeholders is evident in project management, where organizations utilizing these tools report enhanced collaboration and satisfaction among involved individuals. However, the complexities of contractual agreements often hinder collaborative projects, as highlighted in the case study "Governance Challenges in Collaborative Initiatives." This underscores the need for clear governance structures to facilitate smoother collaboration. Furthermore, the rise of purpose-driven organizations utilizing online marketplaces exemplifies how technology can facilitate real-time collaboration and access to educational and career opportunities.
As Susanna Gallani notes, a major aspect of her work focuses on innovations in incentive models, which can significantly improve engagement strategies with involved parties. Additionally, Isaac Castro emphasizes the need for more empathetic technology, particularly in light of social tensions exacerbated by economic challenges. This shift highlights the importance of nurturing human connections through technology, resulting in more meaningful relationships with stakeholders.
Moreover, effectively utilizing technology can yield environmental benefits; for instance, freight pooling technology can reduce carbon emissions by 40%. In summary, embracing technology in stakeholder project management not only enhances operational efficiency but also cultivates stronger, more resilient relationships between project teams and their stakeholders, ultimately driving project success.
Conclusion
Effective stakeholder management is crucial for project success, laying the groundwork for collaboration, communication, and alignment of interests. The article explores the diverse roles and classifications of stakeholders, emphasizing the importance of identifying and understanding both internal and external stakeholders. Techniques such as stakeholder mapping and the Power/Interest Grid equip project managers with the tools to engage stakeholders effectively, ensuring their needs are addressed and expectations managed.
The significance of stakeholder analysis cannot be overstated; it allows project managers to prioritize engagement strategies, fostering a collaborative environment that mitigates risks and enhances project outcomes. By employing tailored communication strategies and establishing robust feedback mechanisms, organizations cultivate trust and satisfaction among stakeholders, thus improving the likelihood of project success.
Moreover, integrating technology into stakeholder management practices has proven to be a game changer. It streamlines communication and enables real-time feedback, enhancing operational efficiency and fostering stronger relationships between project teams and stakeholders, contributing to sustainable project outcomes.
In conclusion, prioritizing stakeholder engagement is imperative in today's dynamic project landscape. By understanding stakeholder dynamics, implementing effective management strategies, and leveraging technology, organizations can navigate the complexities of project management and drive successful, sustainable outcomes. Embracing these principles is not just beneficial; it is essential for realizing the full potential of any project.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who are considered stakeholders in project management?
Stakeholders in project management include a diverse range of individuals and groups such as team members, customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies—essentially anyone who can influence or be influenced by the initiative.
Why is understanding stakeholders important in project management?
Recognizing and understanding stakeholders is crucial because their support and active engagement can significantly impact the success of the initiative.
How can effective stakeholder management benefit a project?
Efficient management of stakeholders addresses their needs and expectations, fosters collaboration, and minimizes resistance throughout the project lifecycle, ultimately leading to better project outcomes.
What are the two main categories of stakeholders?
Stakeholders can be categorized into internal participants (such as team members and project leaders) and external parties (such as clients, suppliers, and regulatory bodies).
How are stakeholders classified based on their influence and interest?
Stakeholders can be classified as primary, secondary, or key participants. Key participants are directly affected by the initiative, while secondary participants may experience a non-direct impact.
What is the significance of aligning stakeholder interests?
Strong alignment among stakeholders mitigates risks, enhances communication, and builds trust, leading to smoother execution and improved project results.
What role does customer feedback play in stakeholder management?
Customers, as external participants, can profoundly affect a company's success through their collective purchasing behavior and feedback, making it essential to focus on their interests for business growth.
How can the integration of AI technologies improve stakeholder involvement?
AI technologies can automate tasks and enhance workflows, facilitating better communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
What is a practical example of stakeholder management discussed in the article?
The client involvement process at Transform Your Small/Medium Business, which includes a comprehensive business review to identify issues and develop strategic plans, exemplifies effective stakeholder management.
What is the overall conclusion regarding stakeholder management in project management?
A comprehensive understanding of both internal and external stakeholders, along with their classifications, is critical for navigating the complexities of managing initiatives and ensuring successful outcomes.




