Overview
The instrumental argument posits that stakeholder management is essential for achieving effective participant relationships that lead to improved financial performance and sustainable growth. The article supports this by illustrating how successful companies, through prioritizing stakeholder needs and ethical considerations, enhance their reputation, drive loyalty, and navigate crises, as exemplified by the recovery of Malden Mills after a disaster.
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of corporate governance, the significance of stakeholder management has never been more pronounced. Organizations are increasingly recognizing that the relationships they cultivate with stakeholders—ranging from customers and employees to suppliers and the wider community—are pivotal to their financial success.
This article delves into the instrumental argument that effective stakeholder management directly influences profitability and innovation, offering compelling case studies and insights into best practices.
By prioritizing stakeholder interests and integrating ethical considerations into decision-making, businesses can navigate challenges and foster a reputation that drives sustainable growth.
As the corporate world shifts towards a more interconnected approach, understanding these dynamics becomes essential for leaders looking to enhance their strategic framework and achieve lasting success.
Understanding the Instrumental Argument in Stakeholder Management
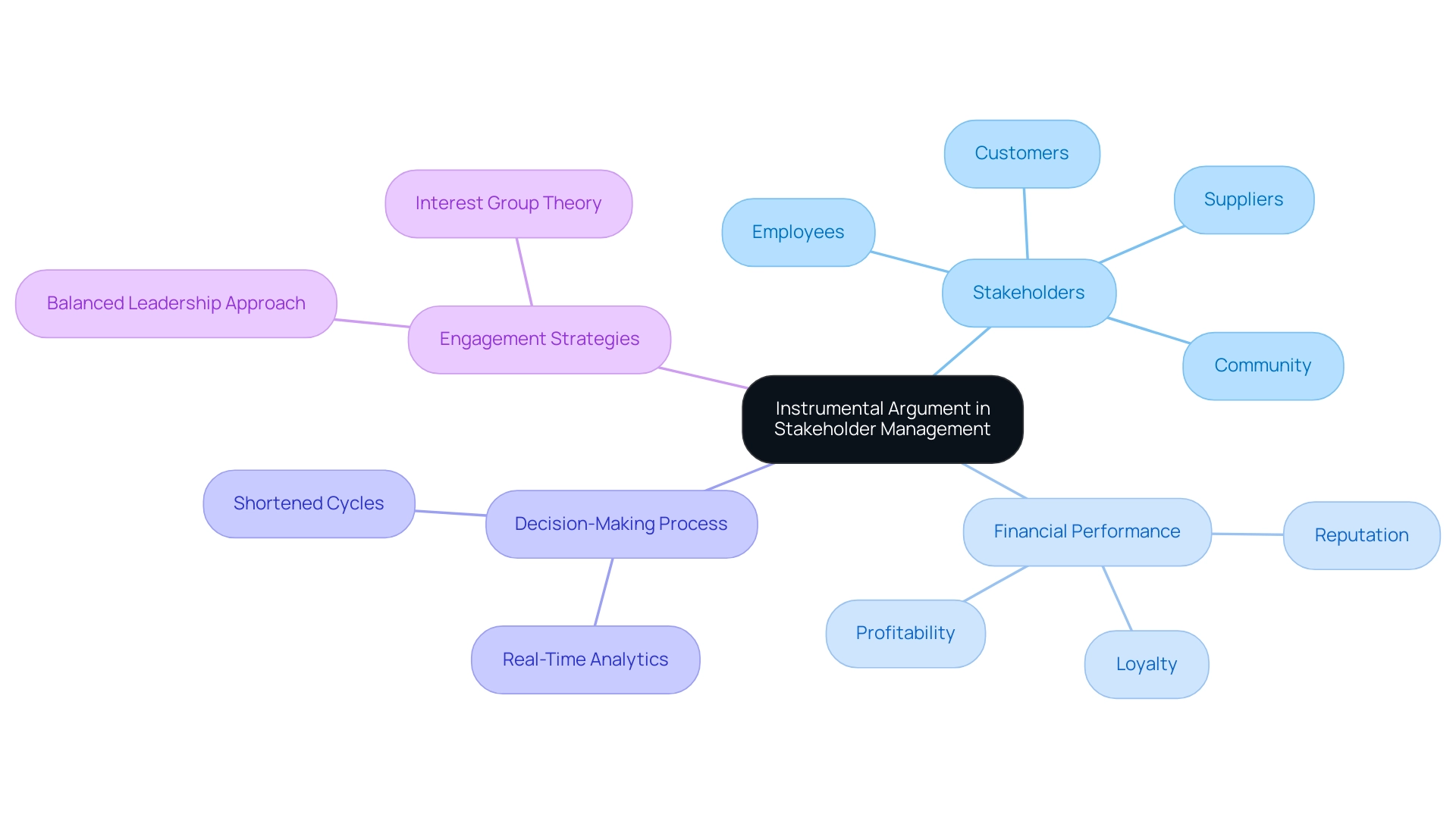
The instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is crucial for effective handling of participant relationships, which directly correlates with improved financial performance. Successful companies recognize that stakeholders—including customers, employees, suppliers, and the broader community—are integral to their success. By prioritizing their needs and interests, organizations can significantly enhance their reputation, foster loyalty, and drive profitability.
This approach transcends traditional profit-centric models, as the instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is emphasizing the interconnectedness of all participants in the economic ecosystem. A compelling illustration of this principle is the case of Malden Mills, which managed to recover from a severe financial crisis within a year following a catastrophic industrial accident in 1995. This swift recovery was largely due to the company's commitment to its stakeholders, illustrating that the instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is essential for demonstrating the potential of effective stakeholder engagement.
In addition, our team's commitment to a shortened decision-making cycle throughout the turnaround process enables decisive actions that preserve organizational health. We continually monitor the success of our plans through real-time analytics via our client dashboard, which provides critical insights for continuous business performance monitoring and relationship-building. Moreover, the implications of corporate control transactions, as examined in recent studies, demonstrate how involvement from interested parties plays a crucial role in navigating such changes.
Recent surveys involving over 20,000 individuals—including emerging leaders and CEOs—highlight the increasing demand for a balanced leadership approach that includes engagement with all parties across various dimensions. This highlights the necessity for leaders to incorporate interest group theory into their business practices for sustained success. As Jeff Oxman notes, 'I document an increase in the number of options awarded to CEOs following LBO activity in an industry, and a decrease in annual bonuses and restricted stock grants as LBO activity slows down.'
This observation highlights the changing dynamics of interest group engagement and its significant effect on financial results. Ultimately, understanding these relationships is essential for companies aiming to navigate crises and achieve what the instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is: sustainable growth.
The Effectiveness of Stakeholder Management as a Corporate Strategy
The instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is a pivotal corporate strategy that drives long-term success across various industries. The instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is essential for companies that prioritize engagement with their interested parties, leading to significant benefits such as heightened innovation, improved risk management, and superior overall performance. For example, Unilever illustrates how incorporating input from interested parties into product development can result in remarkable outcomes.
The instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is essential for aligning corporate goals with interest groups, as this not only cultivates a competitive advantage but also promotes sustainable growth amidst evolving market conditions. Harsha Vardhan Mudumba Venkata, an Engineering Manager, emphasizes that identifying these involved parties, understanding their roles, tailoring communication strategies, managing expectations, and building trust are critical skills every tech leader must master. Furthermore, the adoption of real-time analytics enables continuous business performance monitoring, allowing organizations to operationalize lessons learned from past turnarounds.
Recent metrics indicate that effective communication quality, task completion rates, and participant satisfaction are vital for assessing the ROI of engagement efforts. Significantly, 87% of senior project managers fully comprehend the importance of PM practices, highlighting the necessity of strong participant oversight. The complexities of changing expectations from customers and interested parties during project completion can complicate achieving project goals.
Identifying underlying business issues is crucial in this context, as the instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is necessary for developing targeted management strategies for the involved parties. The integration of strategic planning and digital tools has transformed these engagement practices, emphasizing the collaborative nature of planning solutions with involved parties. This is highlighted in the case study titled 'Utilizing Digital Tools for Engagement.'
This case illustrates how ongoing evaluations and feedback systems are essential for maintaining alignment with the expectations of interested parties, facilitating streamlined decision-making, and driving innovation through collaborative partnerships.
Ethical Considerations in Stakeholder Management
Ethical considerations are crucial in handling those involved, as companies have a moral duty to their constituents. This responsibility encompasses not only transparency in communication but also fairness in dealings and accountability for decisions made. Research indicates that 60% of European companies have implemented internal mechanisms for employees to report unethical behavior, highlighting a growing commitment to ethical practices.
Companies prioritizing transparency, especially regarding supply chain practices, are finding that this openness fosters stronger consumer relationships, particularly among those increasingly concerned with ethical sourcing. Moreover, communication with interested parties regarding model maintenance and modifications is essential to ensure that all parties are aligned and informed. The significance of ethical project oversight is further emphasized by the long-term societal and environmental effects of corporate actions.
As articulated in the Irish Protected Disclosures Act of 2014, "the Act provides legal protection for whistleblowers reporting workplace wrongdoing," emphasizing the need for organizations to protect those who report unethical behavior. The case study titled 'The Importance of Applying Business Ethics' illustrates that the instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is incorporating ethical considerations into the management of involved parties, which emphasizes prioritizing ethical considerations over short-term gains, allowing companies to enhance their corporate reputation and mitigate risks associated with unethical practices, including the potential for scandals or legal repercussions. A holistic approach to decision-making that prioritizes ethics not only builds trust but also contributes to long-term sustainability, ensuring that businesses thrive in a socially responsible manner.
Challenges and Critiques of Stakeholder Theory
While the theory of interest groups offers significant advantages, it is not without its challenges and critiques. A primary concern is the inherent difficulty in reconciling the often conflicting interests of various parties. For example, initiatives aimed at maximizing shareholder returns can clash with the needs of employees or the community, leading to potential ethical dilemmas.
Moreover, skepticism continues about whether effective engagement of interested parties results in enhanced financial performance or if it stays a theoretical ideal. Flore Bridoux emphasizes this perspective, stating,
If advertisers care at least to some extent about the fair treatment of users, they may refrain from imposing their demands on the company and create the latitude for managers to treat users better.
This emphasizes the delicate balance needed in managing involved parties.
The infamous Volkswagen emissions scandal serves as a stark reminder of the consequences of neglecting this balance; the company's focus on shareholder interests through deceptive practices resulted in substantial financial losses, reputational harm, and adverse environmental consequences. Notably, this article has garnered 9,357 views, underscoring the relevance of these discussions within the business community. To navigate these complexities and realize the full benefits of engagement, the instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is essential for organizations to develop strategies that align with corporate goals while prioritizing ethical conduct and corporate social responsibility.
Such an approach fosters stronger relationships with interested parties and enhances corporate reputation, ultimately contributing to sustainable success. Additionally, when advertisers prioritize fair treatment of users, it can lead to better results for all parties involved, reinforcing the notion that balancing interests is not only ethical but also advantageous for financial performance.
Future Directions for Stakeholder Management
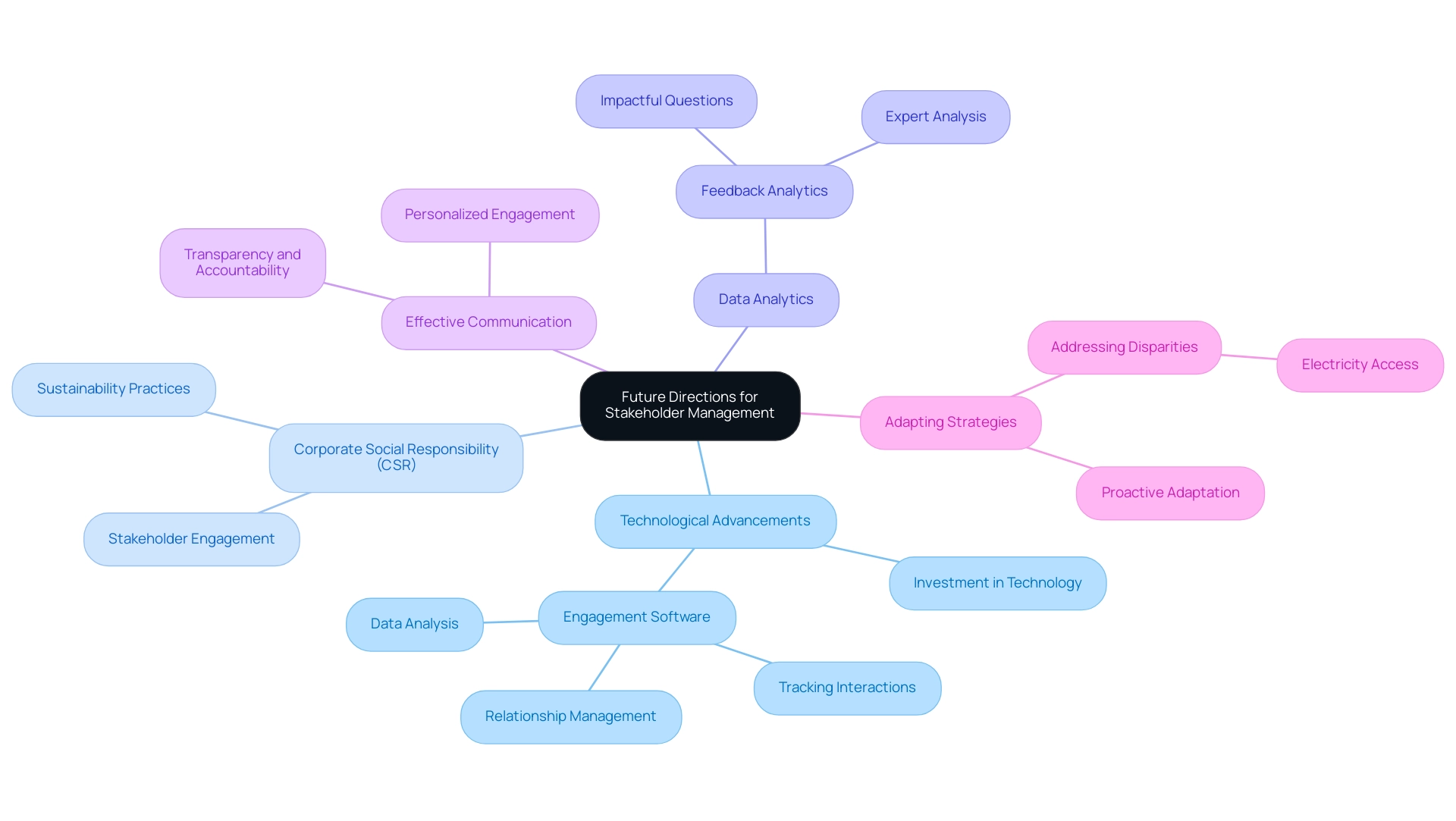
Anticipating the future of participant management reveals a landscape profoundly influenced by technological advancements and shifting societal expectations. Currently, in sub-Saharan Africa, only 44% of the population has access to electricity, highlighting the urgent need for businesses in the region to innovate their interaction strategies to address these disparities. As organizations increasingly utilize data analytics and digital platforms, involvement from interested parties will shift towards more personalized and effective communication methods.
SoPact emphasizes the significance of creating impactful questions and performing expert analysis in feedback analytics, which are essential for effective participation. This evolution aligns with the growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility (CSR) and sustainability, compelling companies to reassess their approaches to interested parties. Experts emphasize that 61% of executives feel unprepared for strategic challenges upon entering senior roles, underscoring the importance of proactive adaptation.
To prosper among these changes, CFOs must invest in technologies that improve participant involvement, such as specialized software that monitors interactions, oversees relationships, and analyzes data for better outreach effectiveness, as demonstrated in the case study on engagement software. Unmesh Sheth aptly states,
Let's make 2024 a year of meaningful change together!
This call to action serves as a reminder that fostering a culture of transparency and accountability is essential for organizations, as the instrumental argument states that stakeholder management is crucial for enhancing their practices.
By embracing these strategies, companies can secure long-term success in an ever-evolving business environment.
Conclusion
Effective stakeholder management is not merely a strategic advantage; it is a fundamental necessity for organizations aiming to thrive in today's complex business landscape. By prioritizing stakeholder interests, companies can:
- Enhance their financial performance
- Foster innovation
- Build a resilient corporate reputation
The case studies discussed, such as Malden Mills and Unilever, illustrate how aligning corporate objectives with stakeholder needs leads to significant competitive advantages and sustainable growth.
Moreover, the ethical dimensions of stakeholder management cannot be overlooked. Companies that embrace transparency and accountability ultimately cultivate stronger relationships with their stakeholders, mitigating risks associated with unethical practices. As the challenges and critiques of stakeholder theory reveal, balancing diverse interests is essential for navigating potential conflicts and ensuring that all parties feel valued and heard.
Looking ahead, the future of stakeholder management will be shaped by technological advancements and evolving societal expectations. Organizations must adapt by integrating data analytics and digital tools into their engagement strategies, ensuring that they not only meet current demands but also proactively address future challenges. By committing to ethical practices and fostering a culture of transparency, businesses can secure their place as leaders in stakeholder management, driving long-term success in an interconnected world. Now is the time for organizations to take decisive action, embrace these principles, and position themselves for sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the instrumental argument regarding stakeholder management?
The instrumental argument posits that stakeholder management is crucial for effectively handling participant relationships, which directly correlates with improved financial performance. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of all stakeholders, including customers, employees, suppliers, and the broader community, in driving organizational success.
How does stakeholder management impact a company's reputation and profitability?
By prioritizing the needs and interests of stakeholders, companies can enhance their reputation, foster loyalty, and ultimately drive profitability, moving beyond traditional profit-centric models.
Can you provide an example of a company that successfully implemented stakeholder management?
Malden Mills is a notable example; after a catastrophic industrial accident in 1995, the company recovered within a year largely due to its commitment to stakeholder management, showcasing the effectiveness of engaging with all parties involved.
What role does real-time analytics play in stakeholder management?
Real-time analytics facilitate continuous business performance monitoring and relationship-building, allowing organizations to make informed decisions and adapt strategies based on current insights.
What recent trends highlight the importance of stakeholder engagement in leadership?
Surveys involving over 20,000 individuals, including emerging leaders and CEOs, indicate a growing demand for a balanced leadership approach that incorporates engagement with all parties, underscoring the relevance of interest group theory in business practices for sustained success.
What are the benefits of effective stakeholder management?
Effective stakeholder management leads to heightened innovation, improved risk management, and superior overall performance, as seen in examples like Unilever, which integrates stakeholder input into product development.
What skills are essential for tech leaders in stakeholder management?
Tech leaders must master skills such as identifying involved parties, understanding their roles, tailoring communication strategies, managing expectations, and building trust to effectively engage stakeholders.
How can organizations measure the ROI of their stakeholder engagement efforts?
Metrics such as effective communication quality, task completion rates, and participant satisfaction are vital for assessing the ROI of engagement efforts, with a significant percentage of senior project managers acknowledging the importance of strong participant oversight.
What is the significance of identifying underlying business issues in stakeholder management?
Identifying underlying business issues is crucial for developing targeted management strategies for involved parties, ensuring that stakeholder management aligns with organizational goals.
How has technology influenced stakeholder engagement practices?
The integration of strategic planning and digital tools has transformed stakeholder engagement practices, emphasizing collaboration and ongoing evaluations to maintain alignment with stakeholder expectations and drive innovation.




