Overview
The responsibility for stakeholder management in an organization typically falls to designated individuals or teams tasked with identifying, engaging, and communicating with both internal and external stakeholders. Moreover, the article emphasizes that clearly defining roles using frameworks like the RACI matrix is essential for effective engagement. This approach enhances accountability and ensures that all stakeholders are appropriately involved in decision-making processes. Consequently, this ultimately leads to better project outcomes.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of stakeholder management can be the decisive factor between project success and failure. This essential process not only involves identifying and engaging those with a vested interest in an organization’s initiatives but also hinges on clearly defined roles and responsibilities. However, with numerous stakeholders—from employees to investors—who truly holds the reins of stakeholder management? This article delves into the critical aspects of stakeholder management, exploring:
- Who is responsible for it
- The importance of effective engagement
- How organizations can navigate this complex landscape to enhance decision-making and foster collaboration
Define Stakeholder Management and Its Importance
The systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and engaging individuals or groups with an interest in or influence over an initiative or organization is critical for those who are responsible for stakeholder management. This process is crucial, as it ensures that all participants understand who is responsible for stakeholder management along with their roles and responsibilities, significantly impacting outcomes. Efficient engagement of stakeholders, who is responsible for stakeholder management, fosters strong relationships, enhances communication, and mitigates risks, ultimately leading to improved decision-making and project success. By recognizing the importance of stakeholder coordination, organizations can align their strategies with the expectations of involved parties, thereby enhancing overall performance and accountability for those who are responsible for stakeholder management.
In the realm of crisis management, understanding the dynamics of stakeholders becomes even more vital. Stakeholders can encompass employees, customers, suppliers, investors, and the community, each possessing unique interests and influences. By adeptly managing these relationships and leveraging real-time analytics through tools such as the client dashboard, organizations can navigate challenges more effectively and emerge resilient from crises. The client dashboard provides real-time business analytics that facilitate monitoring of engagement and business health, ensuring that stakeholder needs are consistently met. Furthermore, a commitment to implementing insights gained during turnaround processes can help establish robust, lasting connections with stakeholders.
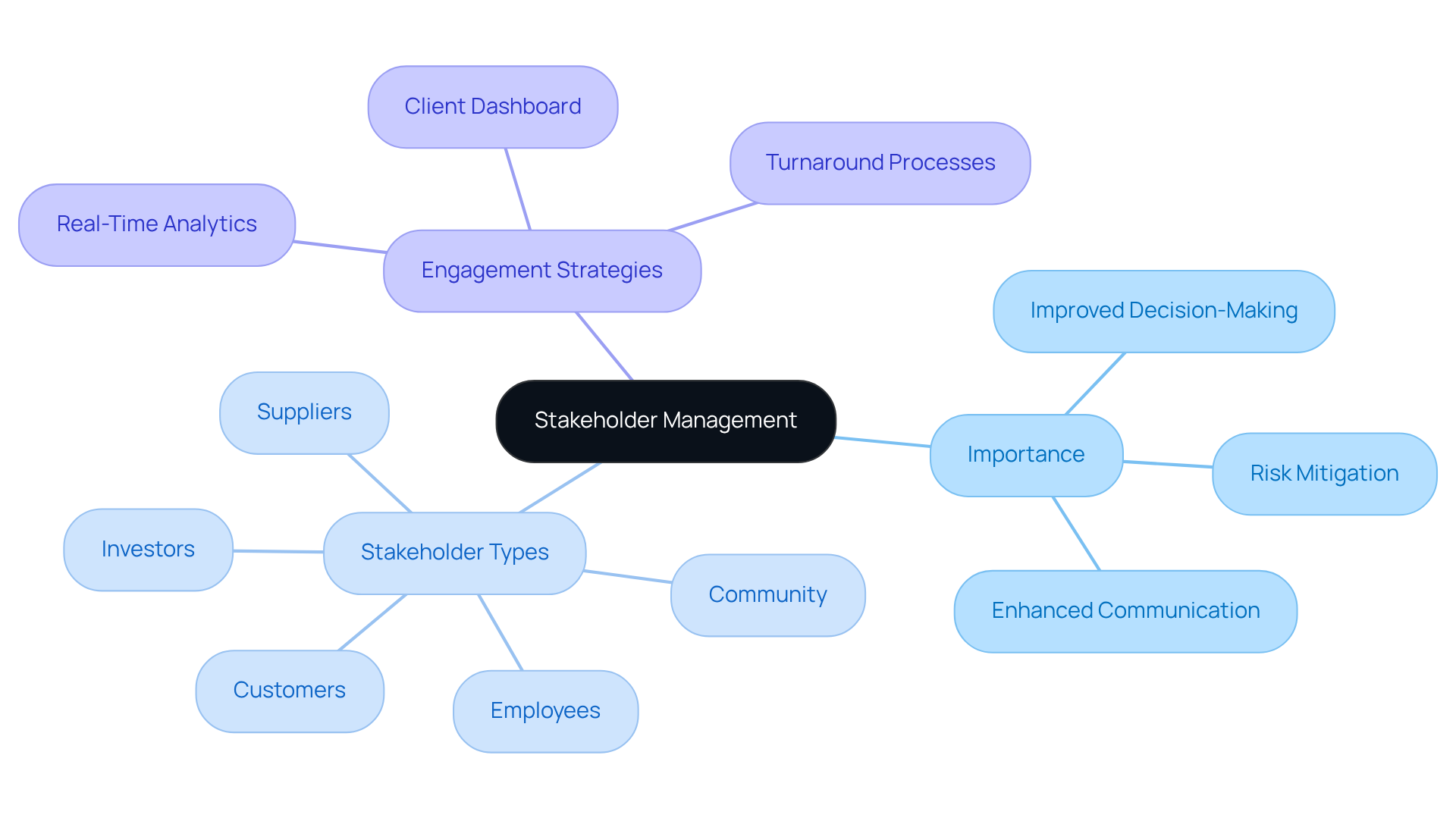
Identify Different Types of Stakeholders
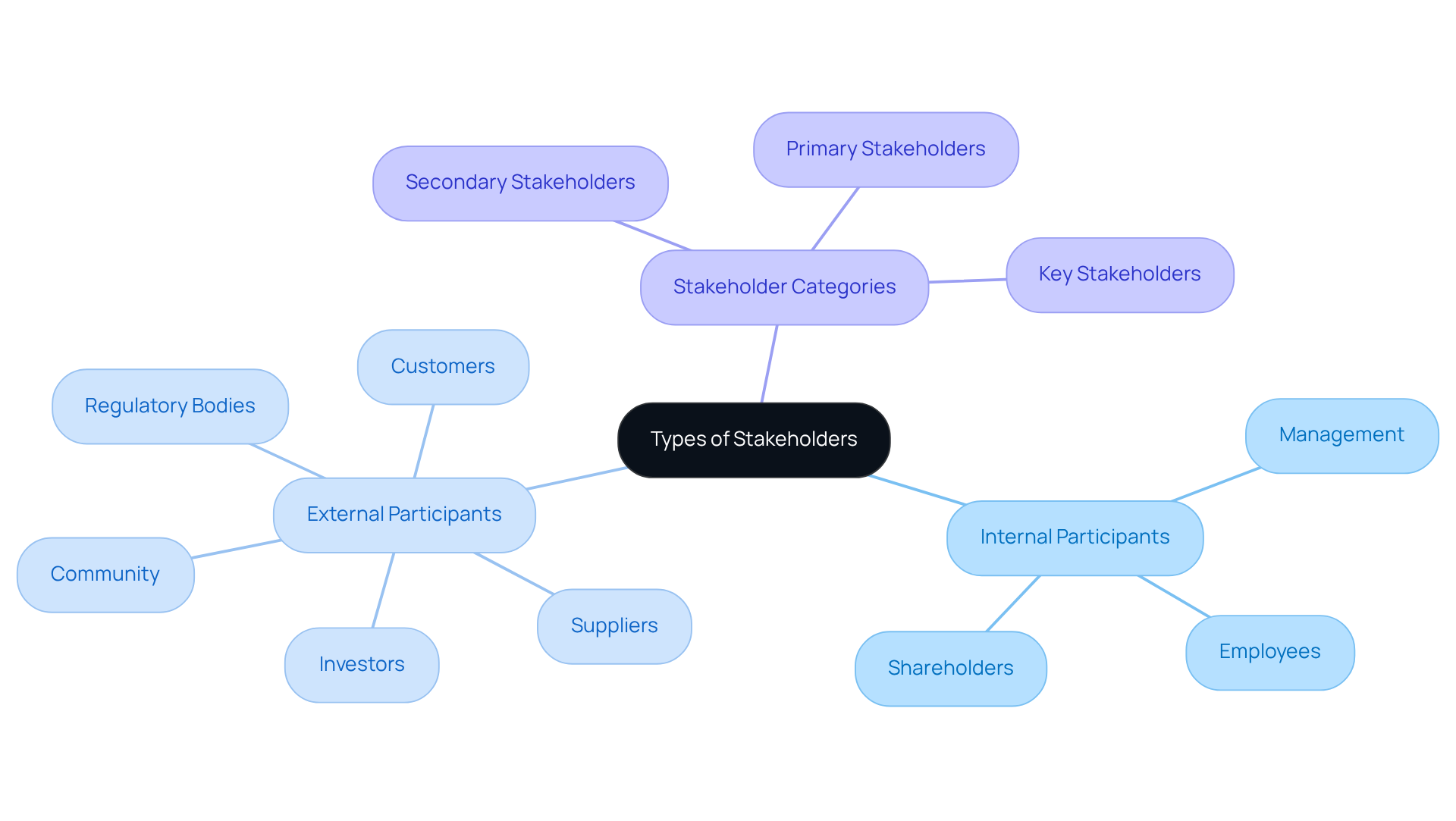
Parties involved can be broadly classified into two primary categories: internal and external participants. Internal participants comprise individuals or groups within the entity, such as employees, management, and shareholders, all of whom have a direct interest in the entity's operations and outcomes. Conversely, external parties are those outside the organization, including customers, suppliers, investors, regulatory bodies, and the community.
To effectively manage stakeholders, it is crucial to identify who is responsible for stakeholder management and their specific roles and interests. For instance:
- Primary Stakeholders: Those who are directly affected by the project, such as customers and employees.
- Secondary Stakeholders: Individuals or groups indirectly affected, like suppliers and community members.
- Key Stakeholders: Those with significant influence over the initiative, such as executives and investors.
By understanding these categories, organizations can prioritize their engagement efforts and ensure that all relevant voices are heard in the decision-making process.
Assign Responsibilities for Stakeholder Management
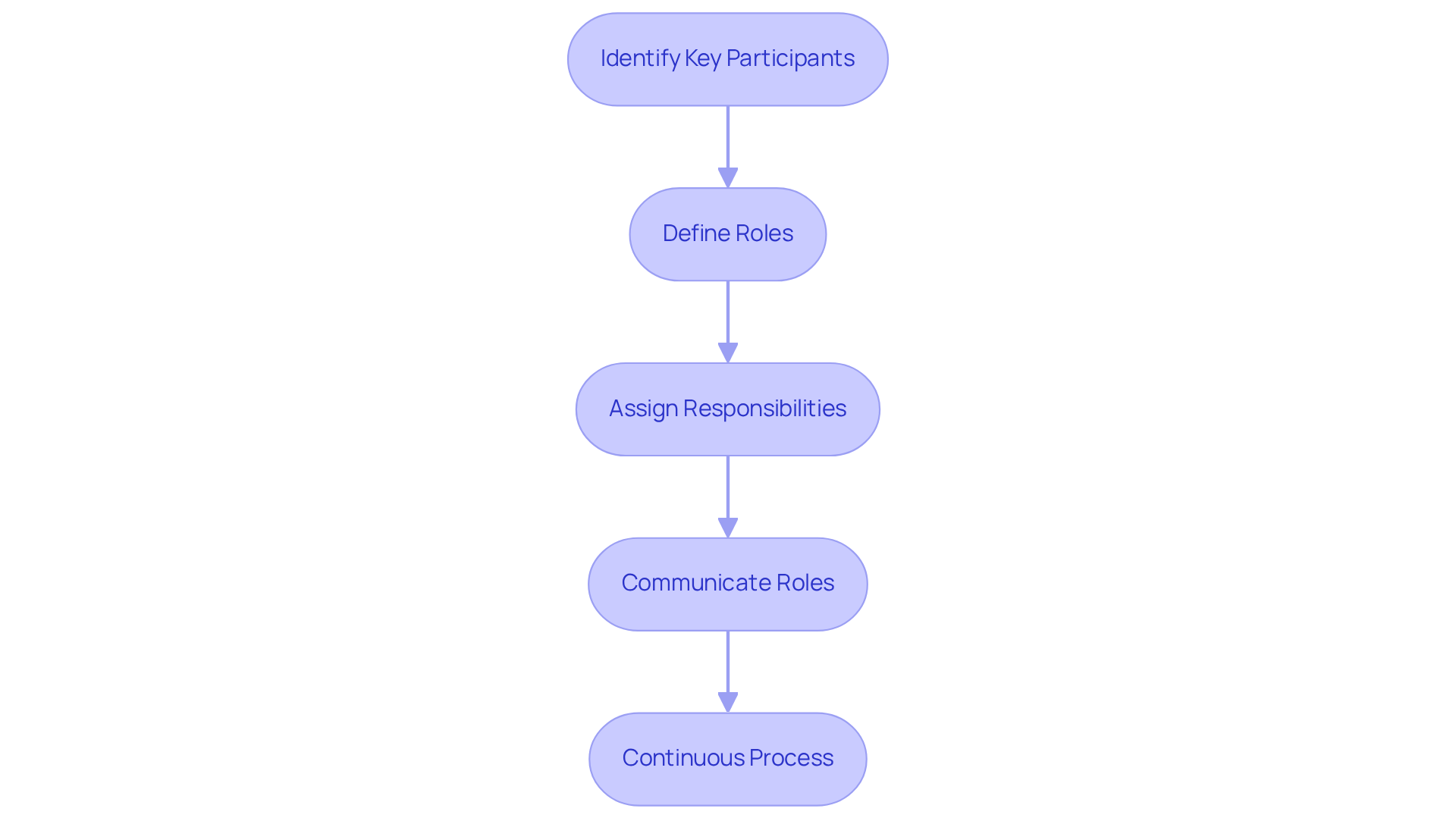
Successful engagement of interested parties hinges on clearly defining who is responsible for stakeholder management within task groups. Utilizing the RACI matrix—an acronym for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed—provides a structured approach to delineate roles and expectations. As Pabel Khan observes, "A management plan for involved parties is your guide for navigating the individuals who can influence the success or failure of your endeavor." Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing this framework:
- Identify Key Participants: Compile a comprehensive list of all individuals involved in the endeavor, including those who may not be directly engaged but can influence outcomes.
- Define Roles: Evaluate each participant's level of involvement and influence, categorizing them based on their impact on the project.
- Assign Responsibilities: Employ the RACI matrix to classify each stakeholder's role:
- Responsible: Identify who will execute the task.
- Accountable: Determine who holds ultimate accountability for the task's success.
- Consulted: Specify who should be consulted for their input and expertise.
- Informed: Clarify who needs to be kept updated on progress and developments.
- Communicate Roles: Ensure that all team members are aware of their responsibilities and comprehend the essential nature of engaging with interested parties.
Statistics indicate that companies do not achieve the changes they plan about 70% of the time (APQC, 2014), highlighting the significance of efficient management of interested parties. By clearly defining and communicating these roles, including who is responsible for stakeholder management, organizations can foster accountability and streamline interactions with interested parties. This organized method not only enhances clarity but also reduces the risk of miscommunication, ultimately resulting in better outcomes. Involving interested parties effectively is a continuous process that demands ongoing adjustment and responsiveness to their needs. As demonstrated in the case study "Real-World Application of Interest Holder Coordination," a strong interest holder strategy can convert project disorder into clarity, ensuring that each participant feels appreciated and aligned with the project's objectives.
Develop a Stakeholder Management Plan
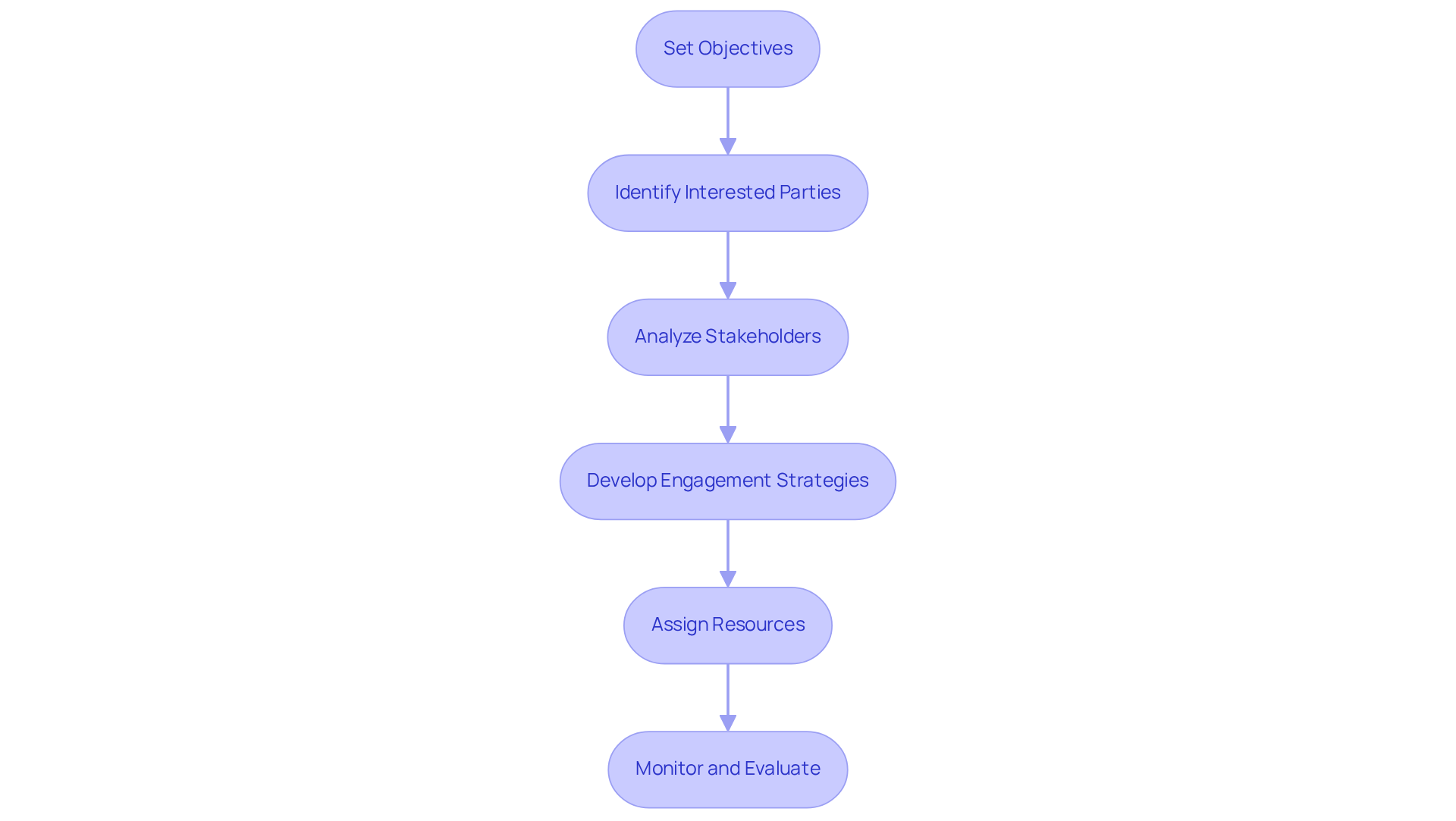
A well-organized management plan serves as a crucial guide for effectively engaging individuals who are responsible for stakeholder management. To develop such a plan, follow these essential steps:
- Set Objectives: Clearly define what you aim to achieve through the involvement of interested parties, whether it be enhancing communication or increasing support.
- Identify Interested Parties: Compile a comprehensive list of all parties identified previously, utilizing tools such as the power/interest grid to categorize them based on their influence and interest.
- Analyze Stakeholders: Conduct a thorough assessment of their interests, influence, and potential impact on the endeavor. This analysis is vital, as approximately 50% of project failures are linked to insufficient participant involvement and oversight, highlighting the importance of someone who is responsible for stakeholder management.
- Develop Engagement Strategies: Tailor approaches for each interested party based on their unique needs and interests. This may include regular updates, meetings, or feedback sessions designed to foster collaboration and trust.
- Assign Resources: Identify the necessary resources (time, personnel, budget) required to implement the engagement strategies effectively.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Establish metrics to assess the effectiveness of your participant engagement efforts. Be prepared to acknowledge challenges such as resistance to change and conflicting interests, making adjustments as necessary.
By adhering to these steps, organizations can formulate a comprehensive relationship strategy that nurtures positive connections and enhances success in initiatives, focusing on who is responsible for stakeholder management. The strategic involvement of interested parties, particularly those who are responsible for stakeholder management, can yield a remarkable 78% success rate in initiatives, in stark contrast to just 40% for those with minimal involvement, underscoring the critical importance of efficient management of involved parties. As Dale Malcolm aptly states, "By actively involving stakeholders, project leaders can gain valuable insights, build consensus, mitigate risks, optimize resource allocation, and improve communication.
Conclusion
Effective stakeholder management is crucial for any organization striving to meet its objectives while fostering robust relationships with involved parties. By clearly defining roles and responsibilities, organizations can ensure that stakeholder engagement is systematic and impactful. The necessity of recognizing who is responsible for stakeholder management cannot be overstated, as it establishes the foundation for effective communication and collaboration among all stakeholders.
Throughout this article, we have shared key insights regarding:
- The classification of stakeholders into internal and external categories
- The significance of the RACI matrix in assigning responsibilities
- The steps to develop a comprehensive stakeholder management plan
Each of these components contributes to a structured approach that enhances organizational performance and mitigates risks associated with miscommunication and disengagement.
In a landscape where project success often hinges on stakeholder involvement, organizations are urged to prioritize the development and execution of robust stakeholder management strategies. By actively engaging stakeholders and continuously refining management plans, organizations can not only improve project outcomes but also cultivate a culture of collaboration and transparency. Embracing these practices will ultimately lead to a more resilient and successful organization, adept at navigating the complexities of stakeholder dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stakeholder management?
Stakeholder management is the systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and engaging individuals or groups who have an interest in or influence over an initiative or organization.
Why is stakeholder management important?
It is important because it ensures that all participants understand their roles and responsibilities, which significantly impacts outcomes. Effective engagement fosters strong relationships, enhances communication, mitigates risks, and leads to improved decision-making and project success.
Who are considered stakeholders in an organization?
Stakeholders can include employees, customers, suppliers, investors, and the community, each with unique interests and influences.
How does stakeholder management impact crisis management?
In crisis management, understanding stakeholder dynamics is vital as it helps organizations manage relationships effectively and navigate challenges, ultimately leading to resilience.
What tools can assist in stakeholder management?
Tools such as the client dashboard provide real-time business analytics that facilitate the monitoring of engagement and business health, ensuring that stakeholder needs are consistently met.
How can organizations improve their stakeholder relationships?
Organizations can improve stakeholder relationships by implementing insights gained during turnaround processes, which helps establish robust and lasting connections.




