Overview
The article emphasizes the critical importance of stakeholder analysis methods in natural resource management. It clearly identifies who the stakeholders are and articulates why their involvement is essential. Effective stakeholder analysis not only enhances collaboration but also resolves conflicts, ultimately leading to more sustainable management practices. This is achieved by ensuring that diverse perspectives are included in decision-making processes. Case studies provide compelling evidence of improved outcomes resulting from inclusive engagement strategies. Therefore, integrating stakeholder analysis is not merely beneficial; it is imperative for achieving sustainable resource management.
Introduction
Stakeholder analysis is essential in the complex realm of natural resource management, serving as a guiding compass for decision-makers navigating the diverse interests and influences of various parties. This article explores the intricate dynamics of stakeholder involvement, revealing methods and frameworks that can transform engagement into a potent instrument for sustainability.
However, significant challenges remain: how can stakeholders with conflicting priorities communicate effectively and collaborate to achieve equitable outcomes? This inquiry underscores the importance of inclusive practices and raises critical questions about the future of resource governance.
Understanding Stakeholder Analysis in Natural Resource Management
Stakeholder analysis, which can be understood as who's in and why? A typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management, serves as a structured framework for recognizing and assessing the interests, influence, and connections of parties involved in natural asset governance. This process is essential for understanding the complexities of and recognizing how their interests shape allocation choices, particularly in the framework of who's in and why? A typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management. As Debra Perrone aptly notes, "Incorporating varied perspectives and requirements during sustainability planning and management can yield improved results among participants, particularly those who are most at risk from the effects of natural resource depletion." By ensuring that diverse voices are included in the decision-making process, participant analysis cultivates more sustainable and equitable outcomes.
For instance, a case study of a community-managed forest demonstrated how interest analysis unveiled conflicting priorities between local communities and logging companies. This insight led to a collaborative approach to asset management that effectively balanced economic needs with environmental conservation. Moreover, data reveals that 91% of Sustainability Plans fail to adequately address participant integration elements, underscoring the critical need for effective stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management, specifically exploring who's in and why?
The benefits of such analysis extend beyond mere conflict resolution; they enhance participant engagement, bolster policy legitimacy, and ultimately contribute to superior resource management practices. Methods for identifying participants, such as interest mapping and snowball sampling, are vital in this process, ensuring that all relevant concerns are acknowledged.
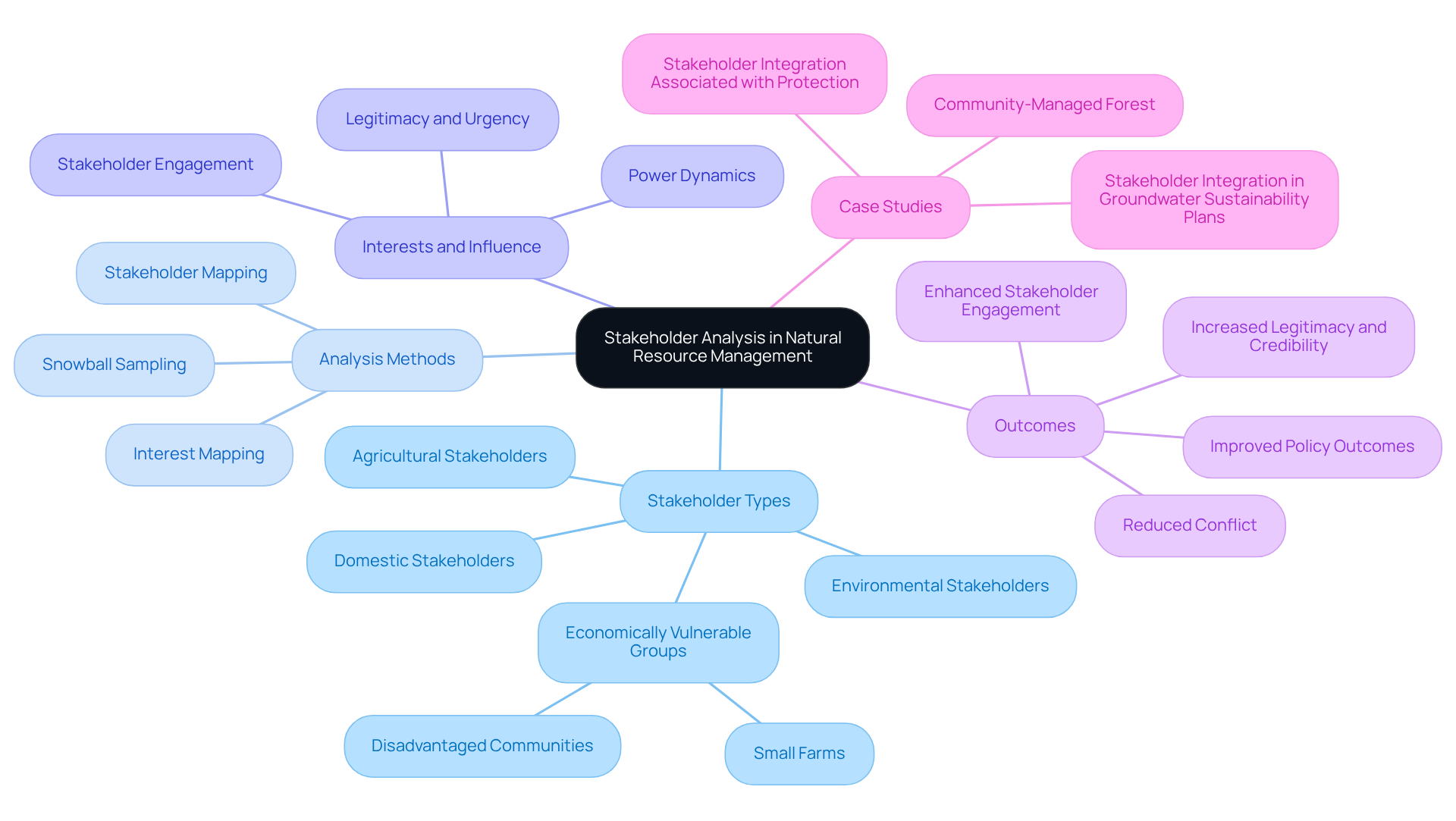
Identifying Challenges in Stakeholder Engagement
The challenges faced in stakeholder engagement, highlighted in 'who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management,' often impede effective collaboration. Communication barriers frequently arise, where involved parties may lack a clear understanding of processes or objectives, fostering mistrust and disengagement. Confidence is crucial for the efficient administration of natural assets, making it essential to address these obstacles.
Power imbalances can exacerbate these issues, as more influential participants may dominate discussions, marginalizing less powerful voices. For instance, in a water resource management initiative, agricultural participants might prioritize irrigation needs, while environmental advocates push for conservation efforts. This scenario necessitates a careful negotiation method to reconcile these differing interests and ensure that all perspectives are considered.
Moreover, conflicting interests among involved parties can lead to disputes that hinder progress, which underscores the need for effective communication methods and inclusive engagement practices, as discussed in 'who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management'. Involving interested parties can extend one to three months at each stage of the evaluation, highlighting the real-world implications of these challenges.
As Ziyan Han observes, 'Thus, involving participants in a systemic manner and engaging them through inclusive, reflective, and adaptive methods is essential for managing.' Furthermore, the case study titled '' illustrates practical difficulties faced, such as time constraints and resource allocation, which can complicate the engagement process.
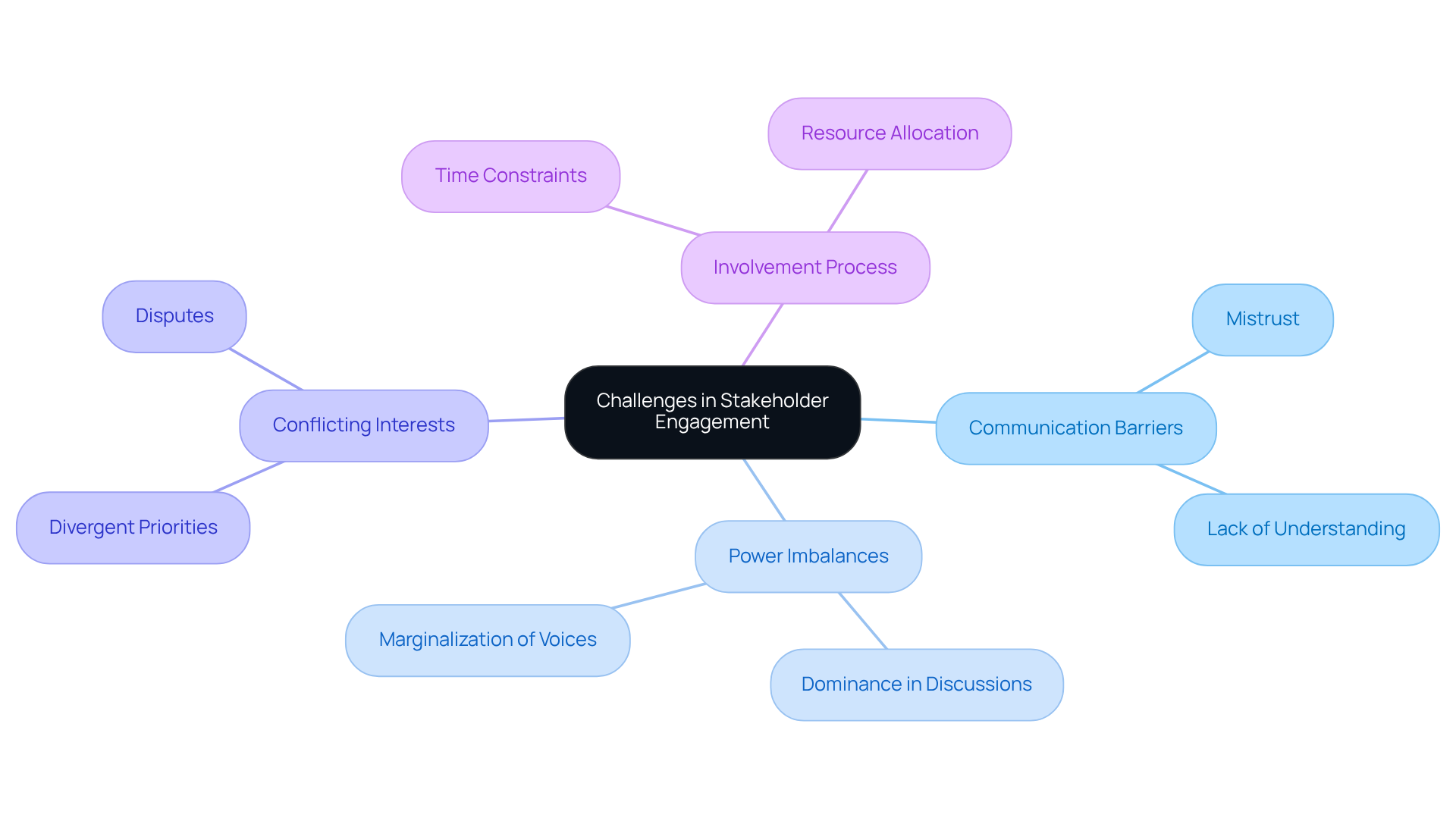
Applying Stakeholder Analysis Methods: A Case Study Approach
A striking illustration of participant analysis in practice, particularly in the context of who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management, is observed in the oversight of a coastal ecosystem, where a varied group of participants—including local fishermen, tourism operators, and conservationists—was recognized. efficiently classified individuals according to their levels of influence and interest by employing participant mapping and influence-interest grids, illustrating the concept of who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management. This organized approach allowed the prioritization of engagement efforts, ensuring that key participants were actively involved in the decision-making process, which is critical in understanding who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management.
As Sarah Lee observed, 'analyzing involved parties, specifically who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management, is crucial in coastal area oversight because it aids in recognizing and prioritizing those involved.' Consequently, a cooperative strategy developed, addressing the diverse needs of all parties involved. This method not only boosted the sustainability of assets but also greatly enhanced the satisfaction of interested parties, showcasing the effectiveness of mapping techniques in asset management.
Moreover, it is essential to acknowledge that challenges like restricted access to information, varied interests, conflicting priorities, and scarce resources can complicate the identification of involved parties, as explored in who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management. Involving interested parties consistently during the process is essential, as understanding who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management should impact the whole engagement process and not merely be a singular event.
Organizations that interact with interested parties are 50% more likely to achieve their major objectives, highlighting the importance of efficient engagement with those involved.
![]()
Evaluating Outcomes and Insights from Stakeholder Analysis
Assessing the results of interest group analysis is essential for comprehending its efficiency in natural resource management, particularly through the lens of who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management. Metrics such as participant satisfaction, engagement levels, and the success of implemented strategies provide valuable insights.
For instance, a recent project focused on restoring a degraded wetland revealed that participant input indicated a high level of satisfaction with the collaborative approach taken. The analysis demonstrated that engaging interested parties early in the process resulted in heightened support and dedication to the restoration efforts.
Moreover, projects with actively involved participants are up to 70% more likely to achieve their initial objectives, underscoring the significance of . Furthermore, organizations that emphasize the involvement of interested parties are 30% more likely to succeed in their initiatives, and companies interacting with these groups are also 30% more likely to succeed with new products.
Insights gained from this evaluation highlighted the importance of ongoing communication and flexibility in engagement strategies, ensuring that all voices are acknowledged throughout the project lifecycle. As Sarah Lee notes, stakeholder engagement can be measured through metrics such as the number of stakeholders engaged and feedback received, which reinforces the critical role of effective stakeholder management in achieving sustainable outcomes, particularly when exploring who's in and why? a typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management.
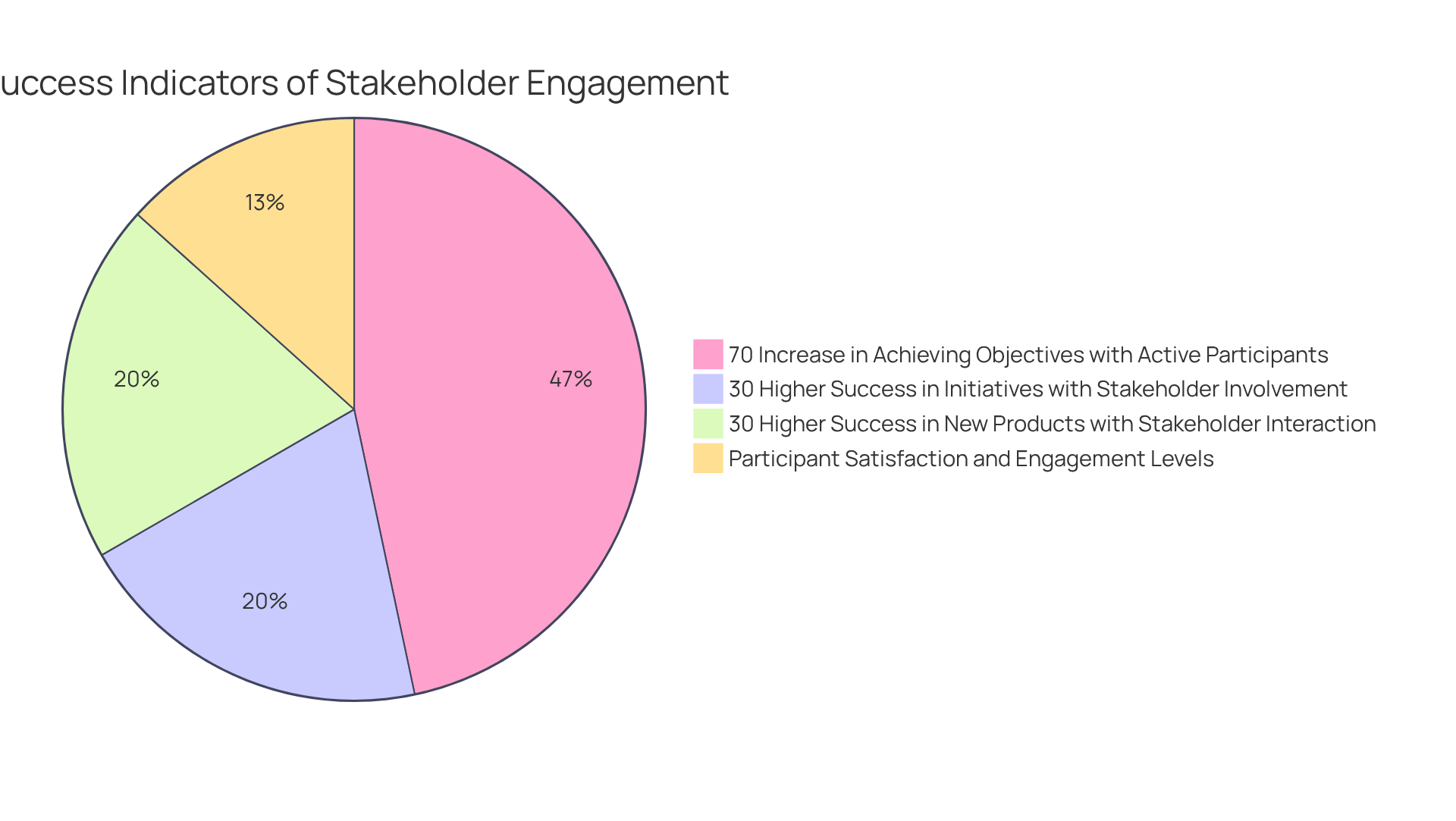
Conclusion
Stakeholder analysis is a pivotal mechanism in natural resource management, facilitating a thorough understanding of the varied interests and influences that shape decision-making processes. By systematically identifying and engaging diverse stakeholders, this analysis cultivates a collaborative environment that not only addresses conflicts but also enhances the sustainability and equity of resource management outcomes.
Key points highlighted throughout this article include:
- The necessity of inclusive participation
- The challenges arising from power imbalances and communication barriers
- The practical application of stakeholder analysis methods
Case studies exemplify how effective stakeholder engagement can lead to more balanced decision-making, ultimately resulting in heightened satisfaction among participants and greater success in achieving resource management objectives.
In essence, the insights derived from stakeholder analysis emphasize its importance as a foundational element for effective environmental governance. By prioritizing the inclusion of diverse voices and addressing the challenges inherent in stakeholder engagement, organizations can enhance their decision-making processes and contribute to more sustainable outcomes. Emphasizing the significance of ongoing collaboration and open communication ensures that all stakeholders are acknowledged and valued, paving the way for a more equitable and resilient approach to natural resource management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stakeholder analysis in natural resource management?
Stakeholder analysis is a structured framework for recognizing and assessing the interests, influence, and connections of parties involved in the governance of natural resources. It helps understand participant interactions and how their interests shape allocation choices.
Why is stakeholder analysis important?
It is essential for incorporating diverse perspectives during sustainability planning and management, which can lead to improved results, particularly for those most affected by natural resource depletion.
Can you provide an example of stakeholder analysis in action?
A case study of a community-managed forest revealed conflicting priorities between local communities and logging companies. This insight allowed for a collaborative approach to asset management that balanced economic needs with environmental conservation.
What percentage of Sustainability Plans fail to address participant integration elements?
Data indicates that 91% of Sustainability Plans fail to adequately address participant integration elements, highlighting the need for effective stakeholder analysis methods.
What are the benefits of conducting stakeholder analysis?
The benefits include enhanced participant engagement, increased policy legitimacy, and improved resource management practices.
What methods are used to identify participants in stakeholder analysis?
Methods such as interest mapping and snowball sampling are vital for identifying participants and ensuring that all relevant concerns are acknowledged.




