Overview
The article "Mastering Stakeholder Mapping in Change Management: A Step-by-Step Guide" serves as a pivotal resource, presenting a comprehensive framework for the effective identification and engagement of stakeholders within the realm of change management. It underscores the necessity of systematic stakeholder mapping as a fundamental strategy for minimizing resistance and bolstering project success. By continuously analyzing stakeholder dynamics and customizing engagement strategies to address their distinct needs, organizations can achieve more favorable outcomes.
Introduction
In the intricate landscape of change management, stakeholder mapping stands out as a crucial strategy for organizations striving to navigate the complexities of diverse interests and influences. This strategic process entails the identification and analysis of individuals or groups who possess a vested interest in a project, ultimately influencing its success.
As organizations increasingly acknowledge the significance of proactive stakeholder engagement, grasping the dynamics of these relationships becomes essential. By prioritizing and effectively managing stakeholder interactions, businesses can reduce resistance and cultivate a collaborative environment that not only supports change initiatives but also propels sustainable growth.
As the landscape continues to evolve, the necessity for ongoing evaluation and adaptation in stakeholder mapping will be vital for organizations aiming to flourish in an ever-changing world.
Understanding Stakeholder Mapping: Definition and Importance
The process of stakeholder mapping change management involves the strategic identification and analysis of individuals or groups with a vested interest in or impacted by a project. This practice is essential in stakeholder mapping change management, as it enables organizations to grasp the intricacies of participant relationships and their potential impact on transformation initiatives. By effectively identifying key parties, organizations can prioritize their engagement efforts, ensuring that essential contributors are actively involved and their concerns are adequately addressed.
The significance of stakeholder mapping change management is paramount; it serves as a proactive measure to minimize resistance and cultivate a supportive environment for change. Recent trends reveal that organizations increasingly recognize the value of continuous evaluation and adaptation in mapping relationships to address shifting influences and priorities. For instance, a software company recently achieved a remarkable Net Promoter Score of +70, reflecting high satisfaction among participants and underscoring the effectiveness of robust engagement strategies.
Moreover, the concept of Engagement ROI highlights the tangible benefits of participant involvement. A case study titled "Engagement ROI: Quantifying the Value of Participant Involvement" illustrates how measuring Engagement ROI allows organizations to refine their strategies, manage risks more effectively, and enhance relationships, ultimately leading to more successful project outcomes. This aligns with our approach at Transform Your Small/ Medium Business, where we identify underlying business issues and collaboratively create plans to mitigate weaknesses, allowing for reinvestment in key strengths.
In 2025, specialists emphasize that stakeholder mapping change management is not merely a one-time task but a continuous process that adapts to the shifting environment of organizational development. This dynamic method of stakeholder mapping change management ensures that organizations remain adaptable to the needs of interested parties, fostering a culture of collaboration and support that is essential for effective management of transitions. Additionally, with 39% of social media users desiring quick responses, it is crucial for organizations to implement timely engagement strategies.
Our pragmatic approach to data testing and measurement ensures maximum return on invested capital, further highlighting the importance of the services offered by Transform Your Small/ Medium Business to help businesses navigate challenges and achieve sustainable growth.
Identifying Different Types of Stakeholders in Change Management
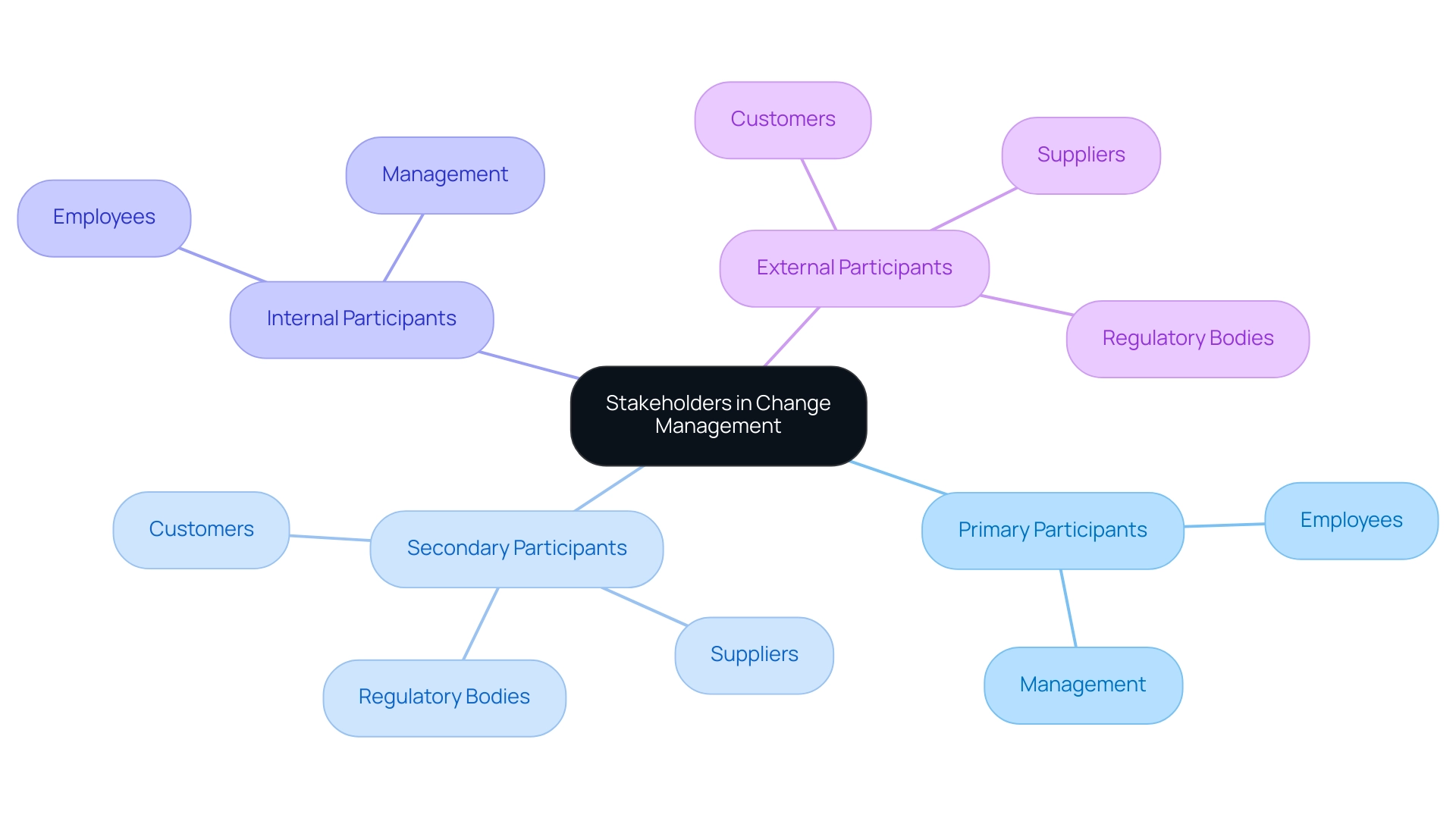
Participants in transformation management are categorized into distinct groups crucial for effective stakeholder mapping and change management, which are vital for the success of any initiative. Primary participants, such as employees and management, are those directly impacted by project outcomes, while secondary participants, including customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies, are indirectly affected. Internal participants consist of employees and management, essential for implementing change, whereas external participants encompass those outside the organization who may influence or be influenced by the project.
In 2025, understanding the dynamics between these groups is essential. Alarmingly, only 43% of employees feel their organizations effectively manage change, a significant drop from nearly 60% in 2019. This statistic underscores the urgent need for organizations to proactively involve interested parties. For instance, a technology company undergoing digital transformation utilized stakeholder mapping to conduct a thorough analysis of interested parties, identifying key groups such as employees, management, customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies.
By addressing the diverse interests of these parties throughout the process, the company navigated the transformation more effectively and achieved positive outcomes. The distinction between primary and secondary groups is critical; primary participants often have a more immediate impact on success, while secondary ones can influence perceptions and support. Organizations should aim for a balanced engagement strategy, recognizing that investing in employee training can reduce costs by 15%, thereby enhancing overall project outcomes and fostering greater buy-in from involved parties.
Expert insights reveal that with top-down strategies, only 20% of the workforce comprehends the changes they face, highlighting the importance of effective communication and engagement strategies in managing relationships. A notable case study, 'The Leadership Lighthouse,' illustrates this point well. In a healthcare organization overhauling a major patient care system, strong leadership from the CEO, who actively sought input from various parties, led to a successful rollout that improved patient care metrics and boosted staff morale.
This case exemplifies how engaging both primary and secondary parties can lead to transformative results. By implementing stakeholder mapping and effectively categorizing involved individuals while understanding their unique interests, organizations can foster a collaborative environment that addresses immediate concerns and paves the way for sustainable growth and transformation.
Step 1: Identifying Key Stakeholders for Your Project
Identifying key participants is a critical first step in stakeholder mapping change management. Begin by brainstorming a comprehensive list of individuals and groups involved in or impacted by the project. Tools such as participant registers and organizational charts can effectively visualize these relationships, facilitating a deeper understanding of the dynamics at play.
Interacting with team members is essential; their insights can reveal important parties that may not be immediately apparent. This collaborative approach not only broadens the stakeholder mapping process but also fosters a sense of ownership among team members.
In 2025, leveraging management software can further enhance this process by tracking the influence and engagement levels of various participants throughout the project lifecycle. Influence management software can assist in assessing the potential impact an interested party may have on an initiative, which is crucial for informed decision-making. Understanding the risk tolerances of involved parties is vital for quantifying risks and enabling more informed decisions.
Furthermore, stakeholder mapping change management is indispensable for effective project management, as it entails maintaining a register of interested parties that serves as a living document outlining roles, interests, and communication needs.
Expert guidance underscores the importance of routinely updating these registers and integrating them with organizational charts to ensure clarity in relationships with involved parties. Patrick Gregoire emphasizes that "the aim of analyzing interests is to identify and interpret these motivations so they can be adequately addressed," highlighting the importance of understanding participant involvement. This proactive strategy can significantly reduce communication costs and enhance overall success, particularly in light of the demand for innovative solutions in engaging interested parties, as evidenced by the challenges faced during the global pandemic.
![]()
Step 2: Analyzing Stakeholder Characteristics and Influence
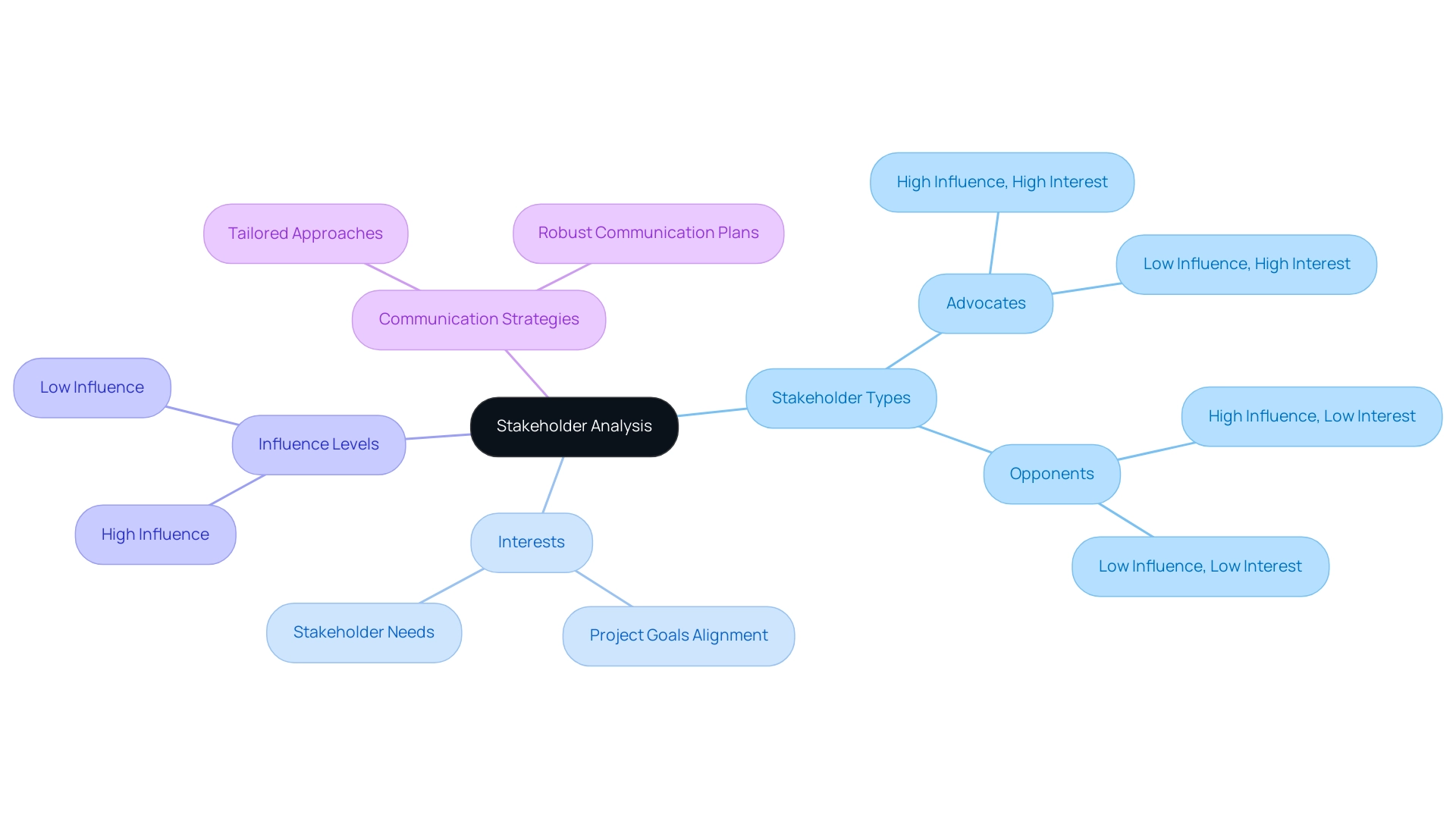
Recognizing essential participants is merely the beginning; the subsequent critical step in stakeholder mapping change management is to analyze their traits, which include their interests, influence, and potential impact on the initiative. Utilizing tools such as the power-interest grid is crucial for effective stakeholder mapping change management, as it allows for a systematic classification of participants based on their level of influence and interest in the initiative. This grid not only aids in visualizing participant dynamics but also provides a strategic framework for stakeholder mapping change management and prioritizing engagement efforts.
For instance, a case study on an international technical initiative highlighted the significance of clearly defined roles and responsibilities among participants. The manager recognized that establishing these roles at the outset was vital. By implementing a robust communications strategy, the team ensured participant involvement throughout the lifecycle.
This proactive approach empowered the team to identify and address design and implementation challenges before they escalated into critical issues, demonstrating the effectiveness of participant analysis in managing risks.
Furthermore, comprehending the motivations of involved parties through thorough stakeholder mapping change management analysis can greatly enhance the efficacy of communication and engagement activities. Research indicates that managers who meticulously design their communication strategies using stakeholder mapping change management based on stakeholder characteristics are more likely to achieve success. As David I. Cleland noted, "The difference between success and failure can be simply in stakeholder mapping change management, which involves knowing advocates and opponents, understanding their respective needs and levels of influence, and aligning the initiative accordingly."
This underscores the necessity of stakeholder mapping change management to identify project advocates and opponents, essential for aligning project goals and ensuring overall success. By tailoring communication approaches to meet the unique needs of each stakeholder, organizations can foster stronger relationships and drive transformational progress.
Step 3: Prioritizing Stakeholders Using Mapping Techniques
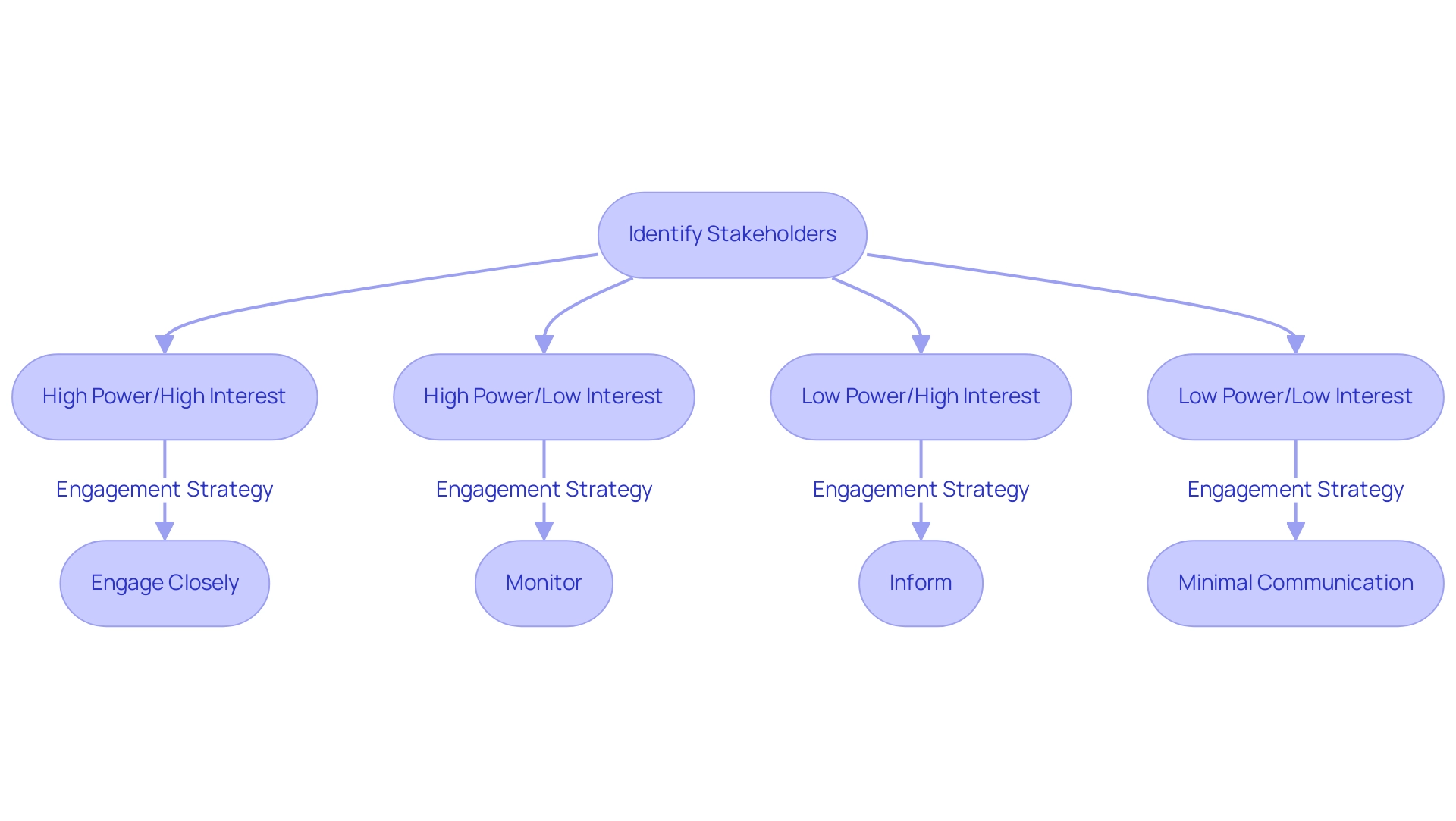
To effectively prioritize involved parties in stakeholder mapping change management, organizations can employ mapping techniques such as the power-interest grid and the salience model. These frameworks enable the strategic mapping of participants based on their influence and interest levels concerning the initiative. For instance, parties categorized as high-power and high-interest should be engaged closely and regularly, as their support is crucial for the success of the initiative.
Conversely, those identified as low-power and low-interest may require less frequent communication, allowing resources to be allocated more efficiently.
Regularly reviewing party priorities is essential, as project dynamics can shift over time. Mature organizations often demonstrate a more comprehensive prioritization system compared to startups, reflecting their experience in navigating complex interest group landscapes. This adaptability is essential, especially when considering the unique opportunities and threats presented at various stages of an organization’s life cycle, as highlighted in case studies examining management strategies.
For instance, companies like Bentley and Rolls-Royce have shown success through customized interaction strategies that resonate with their constituents, particularly their emphasis on personalized service. By identifying key participants effectively, organizations can ensure that important voices are heard and that their contributions are maximized, ultimately supporting the initiative's objectives.
In 2025, utilizing advanced mapping techniques for participant prioritization will be crucial. These methods not only improve involvement but also cultivate a cooperative atmosphere where participants feel appreciated and committed to the transformation process. As Juha Uotila observes, comprehending the dynamics of interested parties is essential for effective management of transformation.
By prioritizing interested parties through stakeholder mapping change management strategies, organizations can navigate change more effectively and achieve sustainable growth.
Step 4: Creating Your Stakeholder Map
Developing a participant map necessitates synthesizing previously collected information into a clear visual representation. This can be accomplished through specialized software tools or straightforward diagrams. Essential elements to incorporate include participant names, their interests, levels of influence, and tailored interaction strategies.
A well-structured stakeholder mapping change management approach not only provides a comprehensive overview of relationships but also highlights potential areas for conflict or collaboration.
For instance, the Community Engagement team at RMI has effectively implemented inclusive community engagement strategies within heavy industry sectors, including ammonia and clean hydrogen. Their initiatives have resulted in securing multi-million dollar federal and state grant awards, notably significant funding from the US Department of Energy for projects like the Advanced Industrial Demonstrations program, which boasts a budget of $6.2 billion allocated for clean energy projects. This case study illustrates the practical application of stakeholder mapping change management in achieving successful funding outcomes.
Moreover, employing visual tools for mapping can significantly enhance understanding and communication among team members. Tools featuring mapping capabilities for involved parties, such as those developed by Borealis, have gained traction in the Social Performance marketplace, underscoring the increasing recognition of the importance of community and social risk in project execution. As Patrick Grégoire, founder of Borealis, remarked, "The tool is free to use, but we do request that you reference the citation below when including S.A.M.’s outputs or interface in any publications, presentations, proposals, etc."
In 2025, experts emphasize that effective participant maps should not only visualize relationships but also facilitate strategic decision-making. By employing visual participant mapping methods, organizations can enhance their stakeholder mapping change management, enabling them to navigate the complexities of transition while ensuring that all perspectives are acknowledged and considered throughout the process.
Step 5: Developing Effective Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
To effectively engage stakeholders during change management, it is crucial to develop tailored engagement strategies for each group, grounded in a comprehensive participant map. This process entails a detailed analysis of their interests, influence, and preferred communication methods. For example, providing regular updates can keep stakeholders informed, while one-on-one meetings may nurture deeper connections and address specific concerns.
Collaborative workshops can also prove advantageous, enabling participants to actively contribute to the change process.
Moreover, integrating real-time analytics into your engagement strategy can significantly enhance decision-making. By consistently monitoring the effectiveness of your initiatives through the client dashboard offered by Transform Your Small/Medium Business, you can furnish stakeholders with current insights into business performance, thereby fostering transparency and trust. Research reveals that:
- 36% of IT and data leaders frequently collaborate with data science and analytics teams.
- 33% most often engage with executive leadership when formulating data and analytics initiatives.
This underscores the importance of grasping the unique needs and challenges of these groups to frame projects in terms of their benefits.
A case study titled "Involvement of Key Participants in Data and Analytics Initiatives" exemplifies how an organization sought to improve interaction with key contributors involved in data and analytics initiatives. Participants ranked various interest groups based on their influence over initiative approval, highlighting the necessity of understanding their needs and challenges. Effective involvement strategies encompassed:
- Framing projects in terms of advantages for participants.
- Narrating compelling stories about the impact of data and analytics.
- Cultivating trustworthy relationships.
Collaboration with data science teams and executive leadership was pivotal, as they represent some of the most frequently engaged groups.
Effective involvement strategies should weave captivating narratives about the influence of data and analytics, which can resonate with stakeholders and enhance stakeholder mapping change management to bolster their support. Establishing reliable connections is vital; as emphasized by iQuasar, every team member must commit to effective communication with involved parties by maintaining open dialogues, listening attentively, and adapting strategies as necessary. By applying lessons learned from previous initiatives, you can further fortify these relationships and ensure a more effective interaction process.
Incorporating elements of stakeholder mapping change management into your engagement plan will not only keep participants informed and engaged but also nurture their support throughout the change process, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes.
Overcoming Challenges in Stakeholder Mapping
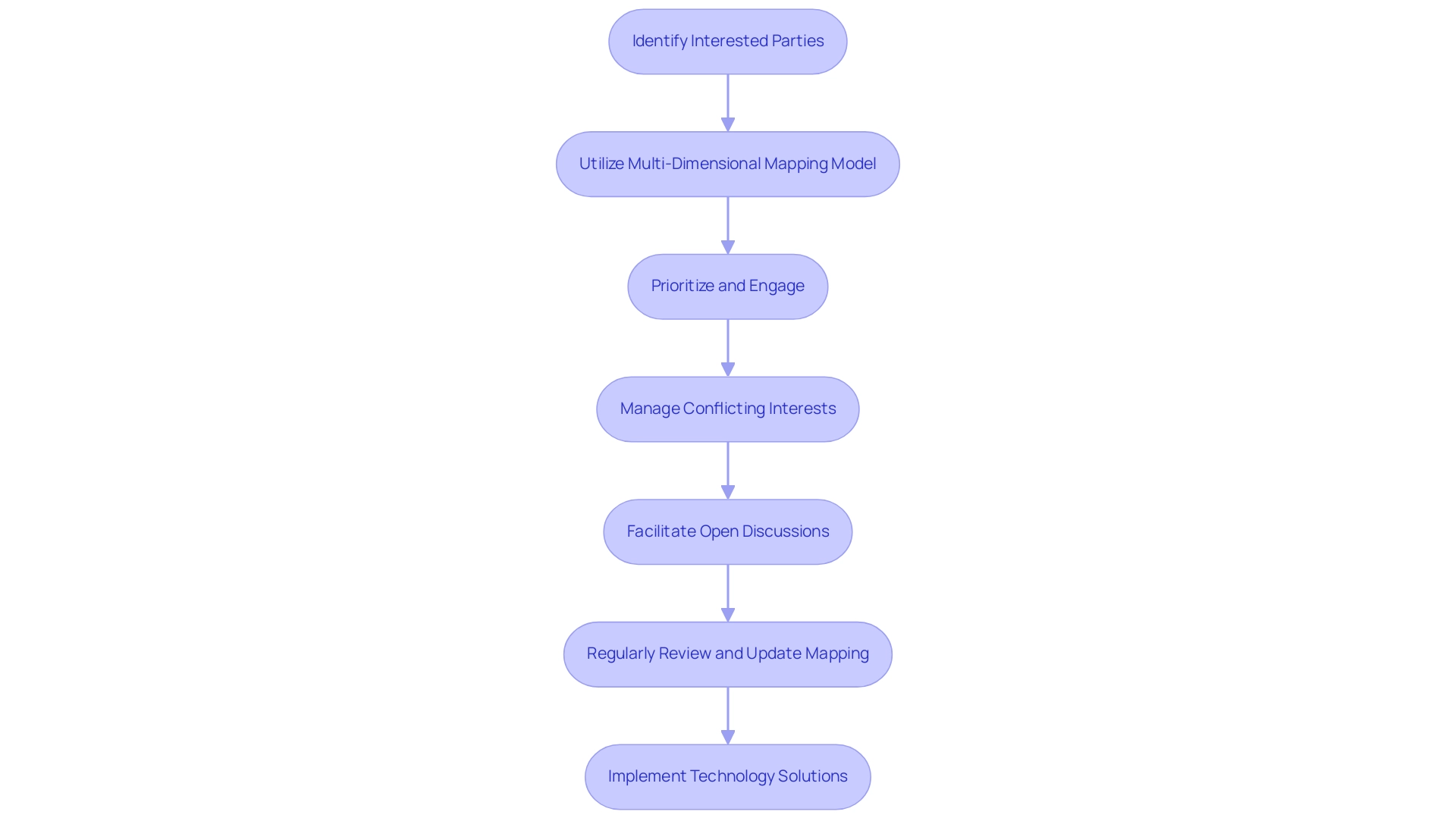
Mapping presents several challenges, particularly in identifying all relevant parties, managing conflicting interests, and maintaining an up-to-date participant map. As we approach 2025, organizations encounter growing complexities in participant dynamics, necessitating a robust approach to mapping. A significant hurdle is the difficulty in identifying interested parties, with statistics indicating that many organizations struggle to accurately pinpoint all parties involved in change initiatives.
To address this, it is essential to implement a structured process for stakeholder mapping change management. This includes identifying interested parties and utilizing tools such as a multi-dimensional mapping model developed by Simply Stakeholders. This model segments participants based on six attributes: influence, interest, impact, criticality, position, and effort, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of their roles and concerns. The outcome of using this model enables better prioritization and engagement with parties most affected by projects, emphasizing stakeholder mapping change management to generate visual charts for consultation reports and making engagement maps a dynamic tool throughout project development.
Moreover, managing conflicting interests is another critical aspect of engaging with involved parties. For example, during transformation initiatives, involved parties may have differing priorities that can complicate decision-making. Involving interested parties in open discussions can help clarify their concerns and expectations, fostering a collaborative environment. This approach not only assists in conflict resolution but also boosts participant buy-in, which is essential for the success of stakeholder mapping change management initiatives.
Regularly reviewing and updating the stakeholder mapping change management is vital to reflect current dynamics and ensure that all relevant voices are heard. This practice enables organizations to adjust to changing participant landscapes and maintain effective communication channels. Additionally, utilizing technology-enabled consulting services can simplify this process, making it easier to monitor participant movements and adjust strategies accordingly.
Ethical considerations in data collection and use are paramount, requiring respect for participants' rights and adherence to ethical guidelines. Case studies illustrate the effectiveness of these strategies. For instance, entities that embraced a systematic method to mapping interested parties reported enhanced prioritization and interaction with key participants, ultimately resulting in more successful project outcomes.
By adopting these practices, businesses can navigate the complexities of stakeholder mapping change management and promote transformational progress efficiently.
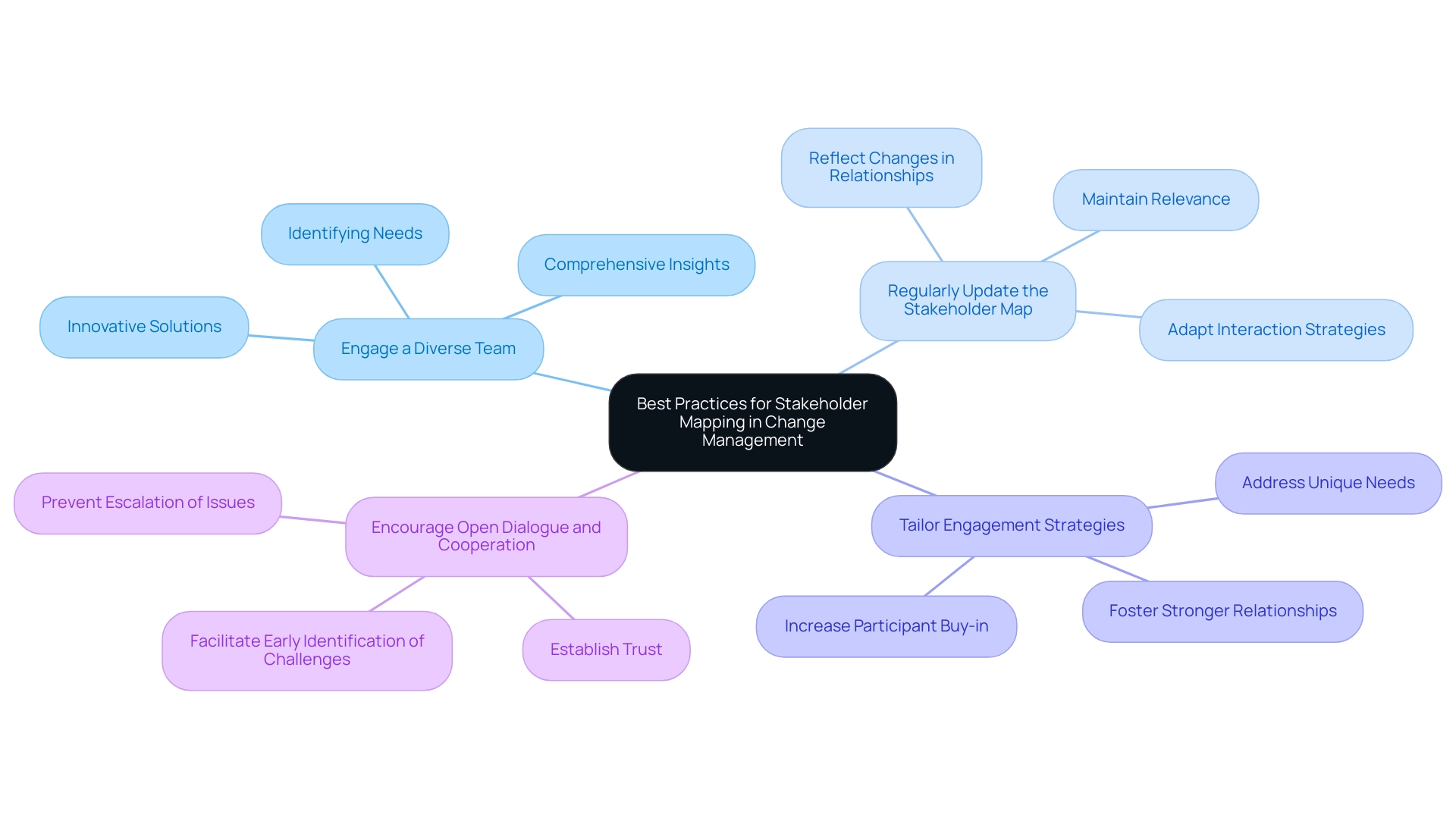
Best Practices for Successful Stakeholder Mapping in Change Management
To achieve effective participant mapping in change management, organizations must implement the following best practices:
- Engage a Diverse Team: Involving a diverse team in the mapping process is crucial. This approach ensures a wide range of perspectives, leading to comprehensive insights and innovative solutions. Diverse teams are better equipped to identify various party needs and expectations, ultimately enhancing the mapping process.
- Regularly Update the Stakeholder Map: Effective stakeholder mapping in change management is necessary because stakeholder dynamics can shift throughout a project’s lifecycle. It is essential to revisit and revise the participant map periodically to reflect these changes in relationships and influence. This practice helps maintain relevance and effectiveness in interaction strategies.
- Tailor Engagement Strategies: Each group involved has unique needs and priorities. Customizing engagement strategies to address these specific requirements fosters stronger relationships and increases the likelihood of successful outcomes. This tailored approach can significantly enhance participant buy-in and support.
- Encourage Open Dialogue and Cooperation: Establishing trust among participants is essential for successful transformation efforts. Encouraging open lines of communication and collaboration not only strengthens relationships but also facilitates the identification of potential challenges early on. This proactive involvement can prevent issues from escalating and guarantee smoother execution of tasks.
By adhering to these best practices of stakeholder mapping in change management, organizations can greatly enhance their interactions with interested parties, driving successful change initiatives. For instance, in a recent international technical initiative, the manager highlighted the importance of clearly defined roles and responsibilities, as well as the involvement of customers and vendors throughout all phases. This method resulted in successful communication tactics that assisted the team in tackling design and implementation obstacles before they became crucial, underscoring the effect of strategic involvement in attaining success.
As emphasized by the Project Management Institute (PMI), the project management team must manage and influence the expectations of interested parties to ensure a successful project. Furthermore, leveraging technology-enabled consulting services can further enhance the understanding of client needs, making stakeholder engagement more effective.
Conclusion
Effective stakeholder mapping is paramount for organizations aiming to successfully manage change in a complex environment. By identifying and analyzing stakeholders—those who are either directly or indirectly impacted by a project—organizations can prioritize engagement and address concerns proactively. This strategic approach not only minimizes resistance but also fosters a collaborative atmosphere conducive to sustainable growth.
Understanding the distinct categories of stakeholders, including primary and secondary groups, allows organizations to tailor their engagement strategies effectively. By employing tools such as the power-interest grid, organizations can prioritize their efforts and ensure that high-power, high-interest stakeholders receive the attention they need to support change initiatives. Furthermore, creating a well-structured stakeholder map provides a visual representation that enhances communication and decision-making processes.
Challenges in stakeholder mapping, such as identifying all relevant parties and managing conflicting interests, can be addressed through structured processes and ongoing updates to stakeholder maps. Best practices, including engaging diverse teams and promoting open communication, further strengthen stakeholder relationships and increase the likelihood of project success.
In conclusion, as organizations navigate the ever-evolving landscape of change management, investing in robust stakeholder mapping and engagement strategies is not just beneficial—it is essential. By prioritizing and adapting these strategies, organizations can enhance stakeholder relationships, mitigate risks, and ultimately drive transformational change that aligns with their long-term goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stakeholder mapping change management?
Stakeholder mapping change management involves the strategic identification and analysis of individuals or groups who have a vested interest in or are impacted by a project. This practice helps organizations understand participant relationships and their potential impact on transformation initiatives.
Why is stakeholder mapping important?
Stakeholder mapping is essential as it minimizes resistance to change and fosters a supportive environment. It allows organizations to prioritize engagement efforts with key parties, ensuring their concerns are addressed and enhancing the likelihood of successful project outcomes.
How do organizations adapt their stakeholder mapping strategies?
Organizations increasingly recognize the need for continuous evaluation and adaptation in stakeholder mapping to address shifting influences and priorities. This dynamic approach helps maintain engagement and support throughout the project lifecycle.
What is Engagement ROI, and why is it significant?
Engagement ROI quantifies the value of participant involvement, allowing organizations to refine their strategies, manage risks effectively, and improve relationships. This ultimately leads to more successful project outcomes.
How are participants in transformation management categorized?
Participants are categorized into primary participants (e.g., employees and management) who are directly impacted, and secondary participants (e.g., customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies) who are indirectly affected. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective stakeholder mapping.
What is the current state of employee perceptions regarding change management?
As of 2025, only 43% of employees feel their organizations effectively manage change, a decline from nearly 60% in 2019, highlighting the urgent need for organizations to proactively involve interested parties.
What strategies can improve stakeholder engagement?
Organizations should implement balanced engagement strategies that involve both primary and secondary participants. Investing in employee training can reduce costs and enhance project outcomes, while effective communication is critical for managing relationships.
What tools can assist in stakeholder mapping?
Tools such as participant registers, organizational charts, and influence management software can help visualize relationships and track engagement levels of various participants throughout the project lifecycle.
How should stakeholder registers be maintained?
Stakeholder registers should be kept as living documents that outline roles, interests, and communication needs, and should be routinely updated and integrated with organizational charts to ensure clarity in relationships with involved parties.
What is the overall goal of stakeholder mapping change management?
The goal is to identify and interpret the motivations of participants to adequately address their interests, thereby reducing communication costs and enhancing overall success in project management.




