Overview
Stakeholder management is an essential, structured approach to identifying, analyzing, and engaging individuals or groups with a vested interest in a project. This process is crucial for fostering positive relationships and enhancing communication. Effective stakeholder management not only aligns interests but also facilitates smoother project execution. Moreover, it significantly increases the likelihood of success, particularly in crisis situations where informed engagement can determine recovery outcomes. Therefore, prioritizing stakeholder management is not just beneficial; it is imperative for achieving project goals.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of modern business, the capability to adeptly manage stakeholders stands as a fundamental pillar of successful project execution and organizational resilience. Stakeholder management transcends mere reactive measures; it embodies a strategic framework that encompasses the identification, analysis, and engagement of individuals with a vested interest in a project. This thorough process is vital for nurturing positive relationships and aligning diverse interests with overarching project objectives.
As organizations confront unprecedented challenges and crises, grasping the evolution of stakeholder management and its essential components becomes imperative. By delving into the advantages of effective stakeholder engagement, businesses can enhance communication, refine decision-making, and ultimately propel sustainable growth.
Define Stakeholder Management and Its Significance
represents a structured approach to identifying, analyzing, and engaging individuals or groups with a vested interest in or influence over an initiative. This process encompasses a thorough understanding of their needs, expectations, and potential impact on success.
The description emphasizes that effectively managing these parties is crucial; it cultivates positive relationships, enhances communication, and aligns their interests with project objectives. This alignment ultimately facilitates smoother project execution and significantly increases the likelihood of success.
In organizational contexts facing crises, an description can distinguish between recovery and failure, ensuring that all stakeholders remain informed and engaged throughout the process.
By endorsing a shortened decision-making cycle and leveraging real-time analytics, organizations can consistently monitor performance and apply lessons learned from the turnaround process. This commitment to ongoing relationship development and performance evaluation is essential for sustaining participant engagement and ensuring long-term success.
Trace the Evolution of Stakeholder Management
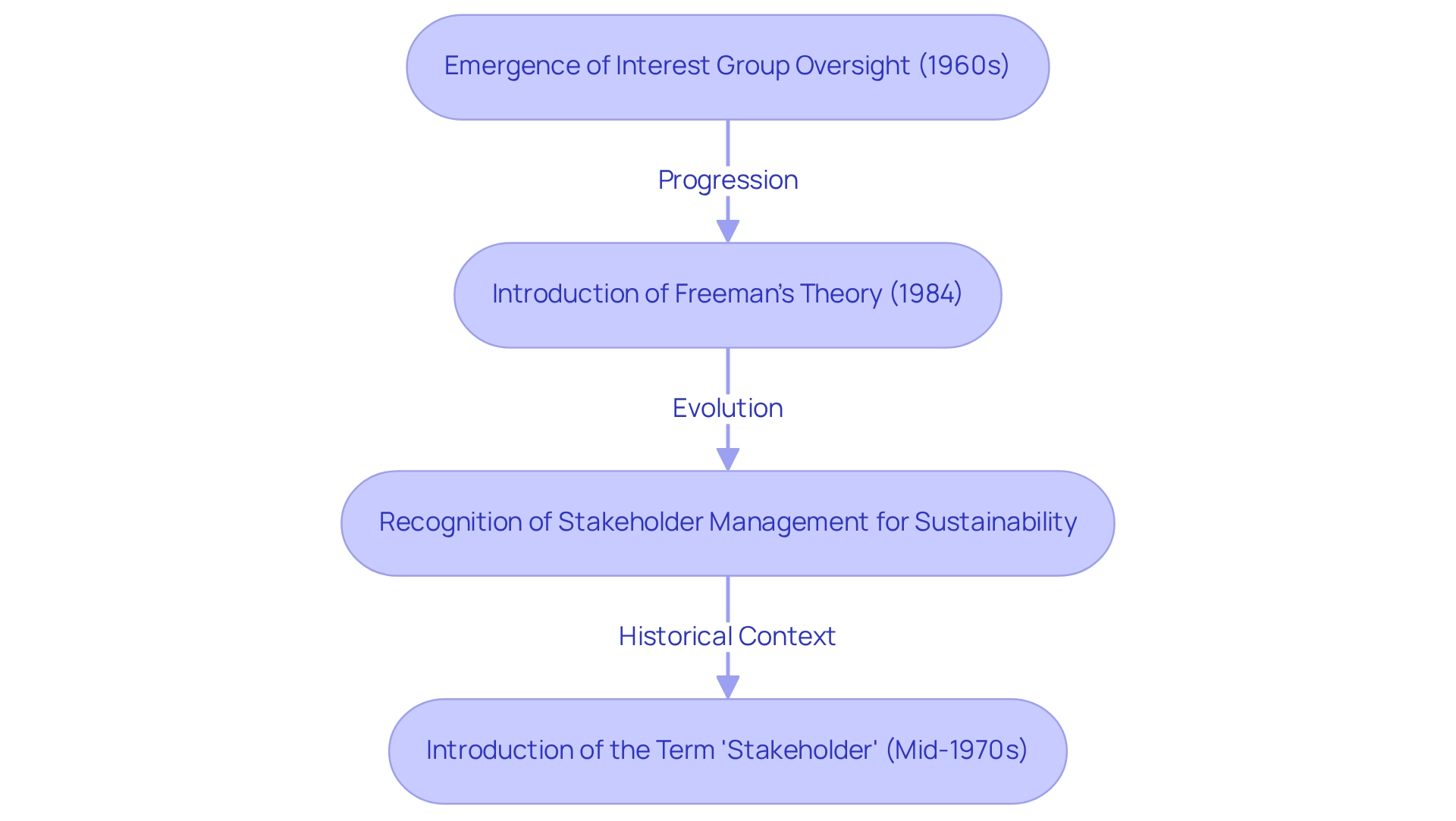
The concept of interest group oversight emerged in the 1960s, driven by escalating discussions surrounding corporate accountability and the necessity for companies to consider the concerns of all stakeholders, not just shareholders. Initially perceived as a reactive measure, participant management primarily addressed conflicts and issues as they surfaced. Over the decades, however, it has evolved into a proactive strategy that emphasizes engagement and collaboration among all parties involved.
A critical moment in this evolution occurred in 1984, with the introduction of a theory by advocating for a more . Freeman's reflections on his contributions highlight the collaborative essence of developing interest holder theory and underscore the ongoing need for its evolution:
- 'But the task is not yet finished.'
- We must urgently accelerate the transition to a more inclusive form of capitalism.
This shift has led to the recognition of as an essential component of , particularly in sectors experiencing rapid change and disruption. Historical case studies, including Freeman's insights, illustrate the successful application of interest group theory, showcasing its impact on fostering responsible corporate practices and the importance of .
As companies navigate complex environments, the [stakeholder management description](https://news.darden.virginia.edu/2024/05/16/stakeholder-how-ed-freemans-vision-for-responsible-business-moved-from-theory-to-reality) that integrates interest holder coordination into strategic planning is crucial for achieving long-term success. Notably, the term 'stakeholder' was introduced into discussions about business impacts by researchers in the mid-1970s, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of oversight concerning these parties.
Identify Key Components of Stakeholder Management
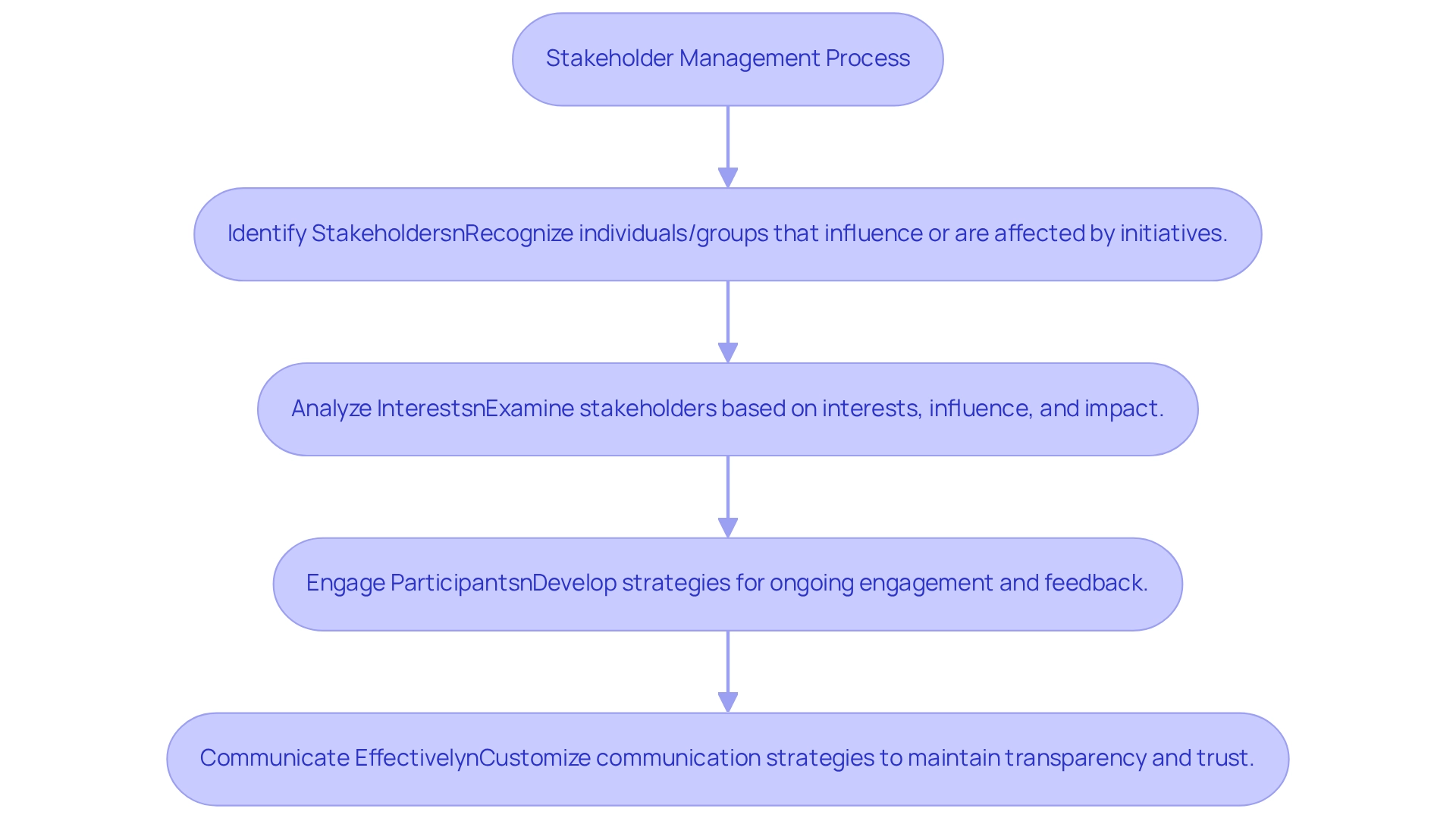
Key elements of encompass identifying, analyzing, engaging, and communicating with involved parties.
: This process entails recognizing all individuals or groups that may influence or be affected by an initiative, including employees, customers, suppliers, investors, and regulatory bodies. Efficient recognition is crucial; research indicates that organizations with a strong stakeholder management description can significantly enhance results.
: Following identification, interested parties are examined based on their interests, influence, and potential impact on the initiative. Utilizing tools such as the power-interest grid facilitates effective categorization, enabling teams to prioritize engagement efforts. Organizations employing structured analysis methods report a 30% increase in satisfaction among interested parties, as outlined in .
Participant Involvement: This element emphasizes the development of strategies to engage participants throughout the lifecycle of the initiative. Regular updates, feedback mechanisms, and opportunities for involvement in decision-making processes are essential. A case study on the finalization of a town plan proposal illustrates how ongoing engagement led to successful project approval, demonstrating the effectiveness of collaborative approaches in managing interested parties. The practices of internal participants facilitated the framing of the megaproject's identity and governance structure, further underscoring the importance of continuous engagement.
is vital for maintaining transparency and trust, as described in the stakeholder management description among interested parties. Customizing communication strategies to meet the diverse needs of various parties ensures that their concerns are acknowledged and expectations managed. Organizations that prioritize clear communication as part of their stakeholder management description often experience improved relationships with involved parties and higher project success rates. As noted by a senior manager of real estate investment, the established theses are critical as they provide a shared direction for development, fostering positive progress in relationships with involved parties.
Examine the Benefits of Effective Stakeholder Management
The highlights that efficient management of interested parties provides various advantages, particularly for organizations facing crises during the thorough review process. These benefits include:
- Improved Communication: Establishing clear lines of communication fosters transparency and trust, reducing misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Improved Decision-Making: Involving participants in the decision-making process results in more informed choices that consider various viewpoints and expertise. This is especially vital during , where aligning key participants helps uncover underlying issues and strengths. Our team will utilize various analytical tools and contributor feedback to pinpoint these issues effectively.
- Risk Management: By recognizing and addressing concerns of interested parties early, organizations can mitigate potential risks that could disrupt initiatives. This proactive approach is essential for operationalizing lessons learned from the turnaround process.
- : When involved parties feel heard and valued, they are more likely to support the project, resulting in smoother execution and greater success. This commitment to engagement reinforces the importance of collaboration as outlined in the [stakeholder management description](https://blog.smbdistress.com/stakeholder-management-plan-vs-stakeholder-engagement-plan-a-comparative-analysis) in strategic planning.
- Long-Term Relationships: Establishing robust connections with interested parties can lead to continuous collaboration and assistance, which is crucial during periods of crisis. This aligns with the goal of reinforcing strengths and addressing weaknesses in the organization.
- Sustainable Growth: Ultimately, an description contributes to the long-term sustainability of the organization by aligning stakeholder interests with business objectives, ensuring that the organization can reinvest in its key strengths.
Conclusion
Effective stakeholder management is not merely a vital component of project success; it stands as an essential strategy for cultivating resilience in today’s complex business landscape. By systematically identifying, analyzing, and engaging stakeholders, organizations can foster positive relationships that enhance communication and align interests with project objectives. This proactive approach has evolved significantly since its inception, transitioning from a reactive measure to a cornerstone of sustainable business practices.
Understanding the key components of stakeholder management—identification, analysis, engagement, and communication—is crucial for organizations aiming to thrive. Each element plays a pivotal role in ensuring that stakeholders are informed, involved, and supportive throughout the project lifecycle. By employing structured methods and maintaining transparent communication, businesses can significantly improve stakeholder satisfaction and project outcomes.
The benefits of effective stakeholder management extend beyond immediate project success. Improved communication, enhanced decision-making, and risk mitigation contribute to stronger relationships and increased buy-in from stakeholders. Ultimately, these practices pave the way for sustainable growth and long-term resilience, reinforcing the idea that stakeholder engagement is not merely an option but a necessity in navigating the challenges of modern business. Organizations that prioritize this strategic framework are better positioned to adapt, thrive, and succeed in an ever-evolving landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stakeholder management?
Stakeholder management is a structured approach to identifying, analyzing, and engaging individuals or groups who have a vested interest in or influence over an initiative. It involves understanding their needs, expectations, and potential impact on the project's success.
Why is effective stakeholder management important?
Effective stakeholder management is crucial because it cultivates positive relationships, enhances communication, and aligns stakeholders' interests with project objectives. This alignment facilitates smoother project execution and significantly increases the likelihood of success.
How does stakeholder management impact organizations facing crises?
In organizational contexts facing crises, effective stakeholder management can distinguish between recovery and failure by ensuring that all stakeholders remain informed and engaged throughout the recovery process.
What role do decision-making cycles and analytics play in stakeholder management?
By endorsing a shortened decision-making cycle and leveraging real-time analytics, organizations can consistently monitor performance and apply lessons learned from the turnaround process, enhancing stakeholder engagement.
What is essential for sustaining participant engagement in stakeholder management?
A commitment to ongoing relationship development and performance evaluation is essential for sustaining participant engagement and ensuring long-term success in stakeholder management.




