Overview
Conducting an information security risk assessment for financial institutions is not merely beneficial; it is essential. This process identifies vulnerabilities and threats that could compromise sensitive data, ensures compliance with regulations, and enhances overall operational resilience. A comprehensive assessment process—encompassing asset identification, threat analysis, and continuous monitoring—is crucial for mitigating risks. Furthermore, it protects customer trust in an evolving cybersecurity landscape. As institutions navigate these complexities, the imperative for robust security measures becomes increasingly clear.
Introduction
In the intricate world of finance, where trust and security are paramount, understanding the landscape of information security risk assessments is crucial. Financial institutions face constant threats from a myriad of vulnerabilities, including cyberattacks and regulatory compliance issues. As the stakes rise, so does the necessity for a comprehensive approach to risk management that not only identifies potential threats but also implements robust mitigation strategies.
This article delves into the essential components of effective risk assessments, explores common pitfalls to avoid, and highlights the role of technology and continuous monitoring in safeguarding sensitive information. By examining best practices and frameworks, financial institutions can enhance their resilience and maintain the trust of their clients in an ever-evolving risk environment.
Understanding Information Security Risk Assessments in Financial Institutions
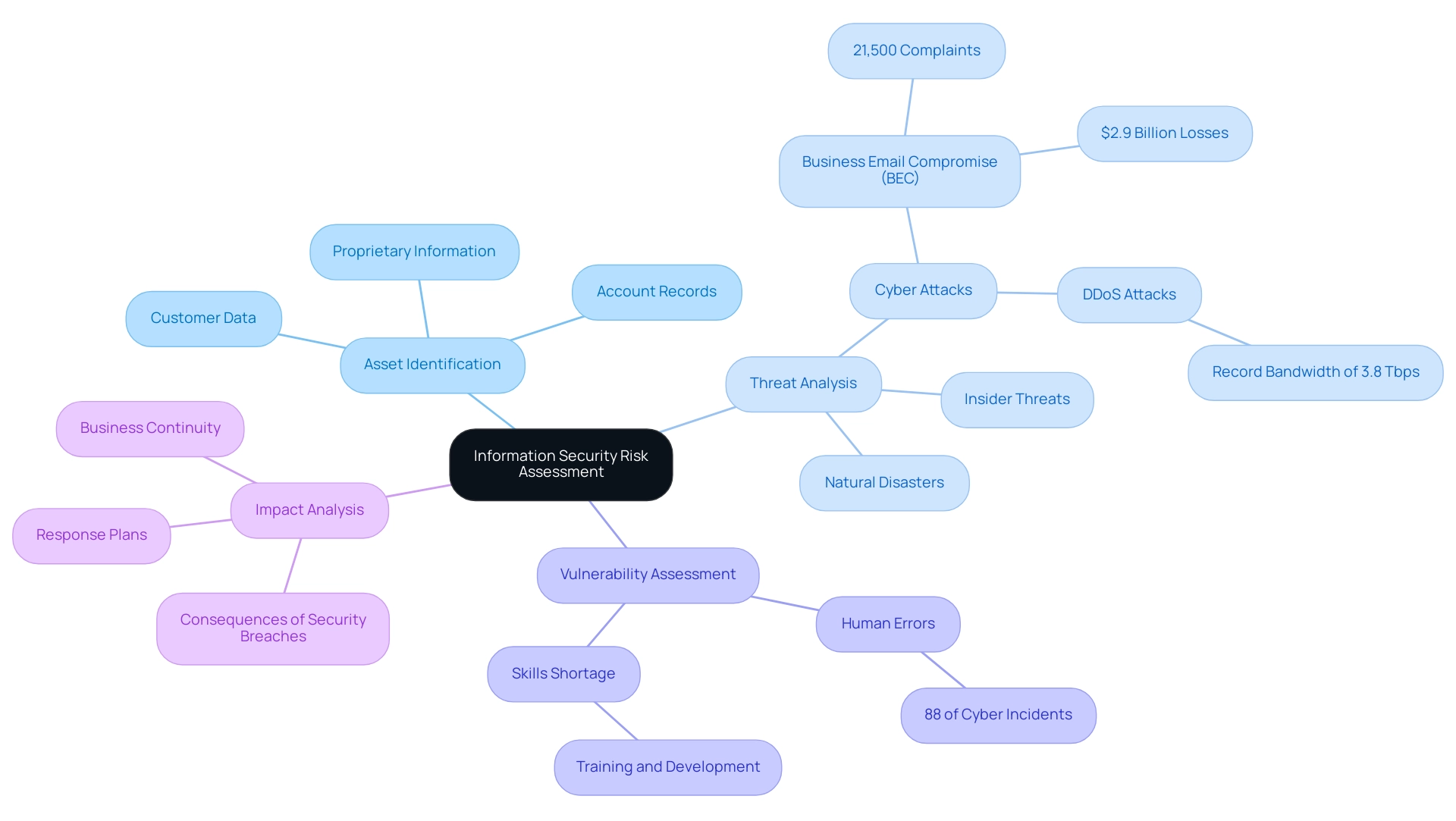
Information security vulnerability evaluations are pivotal components of the information security risk assessment for financial institutions. They meticulously analyze potential threats that could jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data within banking entities. These evaluations systematically identify vulnerabilities, assess threats, and evaluate the potential impact of security breaches. By comprehensively understanding the risk landscape, organizations can conduct an information security risk assessment for financial institutions and implement effective controls to mitigate these threats.
Key components of a robust risk assessment include:
- Asset Identification: Recognizing critical assets that require protection—such as customer data, account records, and proprietary information—is essential. Effective asset identification lays the groundwork for prioritizing security measures and resource allocation, particularly for organizations managing sensitive client information.
- Threat Analysis: Organizations must assess potential threats, ranging from cyber attacks and insider threats to natural disasters. Recent statistics reveal that nearly 21,500 complaints regarding business email compromise (BEC) attacks were reported in a single year, resulting in losses exceeding $2.9 billion. This underscores the urgency of understanding and preparing for diverse threat vectors. Moreover, one of the largest and most sophisticated DDoS attacks in 2024, reported by Cloudflare, peaked at a record bandwidth of 3.8 Tbps, emphasizing the evolving nature of cyber threats that for financial institutions must address.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identifying weaknesses in systems and processes is crucial, as these vulnerabilities can be exploited by various threats. With 88% of all cyber incidents linked to human errors, organizations must prioritize employee training and awareness to effectively reduce these threats. The cybersecurity workforce challenges highlighted in recent discussions emphasize the skills shortage in the industry, suggesting that organizations should invest in training and development to enhance their ability to conduct an information security risk assessment for financial institutions and build a more capable cybersecurity workforce.
- Impact Analysis: Assessing the potential consequences of a security breach is essential for understanding the broader implications for the organization and its stakeholders. This examination aids in formulating a response plan that reduces harm and ensures business continuity.
As the cybersecurity environment evolves—especially with the emergence of generative AI threats—banking institutions must remain proactive regarding the information security risk assessment for financial institutions. Investing in next-generation security awareness programs and enhancing recruitment processes to address the skills shortage in cybersecurity will be vital for building a resilient workforce capable of tackling emerging challenges. Practical instances from banks and monetary services demonstrate the efficacy of thorough evaluations in protecting assets and preserving trust with clients.
The Importance of Risk Assessments in the Financial Sector
In the monetary sector, conducting an information security risk assessment for financial institutions is crucial. Threat evaluations extend beyond mere regulatory adherence; they are essential for safeguarding the safety and stability of operations. A comprehensive monetary evaluation can identify opportunities to conserve cash and reduce obligations, which is vital for monetary entities facing unique challenges that demand , including:
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to laws such as the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) and the Dodd-Frank Act is obligatory, necessitating regular assessments to ensure conformity and minimize potential penalties. Notably, Standard Chartered has allocated US$1.5 billion over the next three years for its 'Fit for Growth' program, underscoring the financial commitment organizations are making towards threat management and operational efficiency.
- Cybersecurity Threats: The landscape of cyber threats is continually evolving, with monetary organizations encountering an increasing number of attacks. By 2025, the average cost of a data breach in the monetary sector is anticipated to reach $5.85 million, highlighting the necessity for organizations to identify and mitigate threats effectively to protect sensitive customer information.
- Operational Threats: Assessing dangers linked with internal processes, systems, and external factors is essential. For instance, many banks are hindered by legacy systems that obstruct growth and modernization efforts. Incremental modernization strategies, as demonstrated by Zions Bancorporation, reveal that gradual upgrades to core systems can enhance operational capabilities and resilience. Citigroup is also undertaking significant measures to streamline its organizational structure and exit noncore markets, partly to control costs, emphasizing how major banking entities are responding to the demand for improved oversight.
By executing detailed evaluations and extensive reviews of their finances, banking institutions can bolster their resilience, protect their assets, and maintain customer confidence. Furthermore, having a dedicated incident response team can save businesses an average of $14 for each record lost or stolen, emphasizing the financial advantages of proactive management. As competition intensifies and regulatory oversight increases, the importance of a thorough information security risk assessment for financial institutions cannot be overstated.
Moreover, the exploration of generative AI for modernizing banking systems illustrates innovative solutions that organizations are considering to enhance their operational capabilities.
Step-by-Step Process for Conducting a Risk Assessment
Conducting a risk assessment in financial institutions is a critical process that involves several essential steps:
- Define the Scope: Clearly outline the boundaries of the assessment. This includes specifying which systems, processes, and data will be evaluated to ensure a focused and effective analysis.
- Identify Assets: Compile a comprehensive list of all assets requiring protection. This includes hardware, software, and sensitive data, which are essential for the organization's operations and reputation.
- Identify Threats and Vulnerabilities: Conduct a thorough analysis of potential threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise the identified assets. This step is crucial as it aids in comprehending the environment of challenges that the institution encounters.
- Assess Hazards: Evaluate the likelihood and potential impact of each identified hazard. Prioritize these concerns based on their severity, directing resources to the most critical areas. Recent statistics indicate that the average annual cost of insider threats has surged to $16.2 million, underscoring the importance of this assessment phase. This statistic emphasizes the necessity for an information security risk assessment for financial institutions, particularly in identifying vulnerabilities that could lead to significant financial losses.
- Develop Mitigation Strategies: Formulate a robust plan to address the identified threats. This includes implementing appropriate controls and monitoring mechanisms to mitigate potential impacts effectively. As Michael Meis, Associate CISO, mentions, "The initial steps focused on identifying pain points in existing practices and tailoring the FAIR approach to address specific challenges," highlighting the significance of a customized strategy in management.
- Document Findings: Meticulously record the evaluation process, findings, and mitigation strategies. This documentation is essential for future reference and compliance purposes, ensuring that the institution can demonstrate due diligence in its management practices.
Incorporating methodologies such as the COSO ERM Framework can enhance the effectiveness of for financial institutions. This framework offers a thorough method for handling enterprise challenges, incorporating management into the overall business strategy, and thus enhancing resilience against various threats. By explicitly applying the COSO ERM Framework, organizations can ensure that management of uncertainties is not just a standalone process but a fundamental part of their operational strategy.
By measuring uncertainties, financial organizations can enhance decision-making, operational efficiency, and compliance precision, ultimately resulting in improved management outcomes.
Identifying Key Risks: Cybersecurity, Compliance, and Beyond
Financial organizations face a myriad of challenges that can significantly impact their operations and reputation. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. The key types of threats include:
- Cybersecurity Threats: Financial organizations are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals employing tactics such as hacking, malware, and phishing attacks. According to the Forrester State of Data Security report, 2025 is projected to see a rise in cyber threats, with 60% of organizations reporting an increase in cyber incidents over the past year. This underscores the necessity for robust cybersecurity protocols and proactive evaluations of potential threats.
- Compliance Challenges: Adhering to regulatory obligations is vital for financial entities. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and long-lasting reputational damage. As regulations evolve, particularly with , organizations must remain informed and agile to avoid compliance pitfalls. The upcoming live webinar on January 14, 2024, will explore emerging trends and forecasts that will shape the future of enterprise IT and security, providing valuable insights for compliance strategies.
- Operational Challenges: These challenges stem from internal processes, system failures, or external events that can disrupt normal operations. Financial organizations must conduct an information security risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities in their operational frameworks that could lead to significant disruptions. Engaging in routine evaluations can help alleviate these operational difficulties.
- Reputational Threats: Negative publicity or customer dissatisfaction can severely damage an organization's reputation. In an age where information spreads rapidly, maintaining a positive public image is essential for sustaining customer trust and loyalty. The case study presented in the live webinar will illustrate how organizations can adapt to evolving cybersecurity regulations and trends, highlighting the importance of reputation management.
By systematically identifying and categorizing these challenges, entities can formulate targeted strategies, including information security risk assessments, to address them effectively. Regular evaluations not only assist in compliance but also enhance overall operational resilience, ensuring that organizations are well-prepared to navigate the complexities of the economic landscape in 2025.
Choosing the Right Framework for Risk Assessment
When conducting a risk assessment, financial institutions must evaluate several established frameworks tailored to their unique operational and regulatory environments:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: This framework provides a robust set of guidelines designed to help organizations manage and mitigate cybersecurity risks effectively. Its adoption is becoming increasingly essential, particularly as the cybersecurity market is projected to reach $212 billion by the conclusion of 2025. This underscores the growing emphasis on safeguarding sensitive financial information.
- ISO 31000: Recognized globally, this international standard offers principles and guidelines for effective management practices. It promotes a systematic approach to identifying, evaluating, and addressing challenges, making it particularly relevant for financial entities navigating complex regulatory landscapes.
- COSO ERM Framework: This framework integrates the management of uncertainties into the governance structure of an organization, fostering a comprehensive view of threats at all levels. It is especially beneficial for organizations seeking to align their management strategies with overarching business objectives.
Choosing the appropriate framework for in financial institutions hinges on the organization’s specific needs, regulatory obligations, and the current risk landscape. For instance, as cybercrime costs are expected to soar to nearly $14 trillion by 2028, institutions must prioritize frameworks that enhance their cybersecurity posture. The case study on the global financial impact of cybercrime highlights the urgency of this necessity, revealing that the average cost of a data breach is escalating to approximately $4.88 million.
Notably, while 74% of organizations have dedicated cybercrime coverage, a significant gap in readiness remains, emphasizing the need for comprehensive evaluations that incorporate these frameworks. As Fortra underscores, "Together, we can continue to force attackers to change their moves as we learn about them, analyze them, and fight them in the year ahead." By leveraging expert insights and case studies on the implementation of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO 31000, organizations can better position themselves to confront emerging threats and ensure sustainable growth, aligning with the overarching goal of overcoming challenges and achieving success.
Leveraging Technology for Effective Risk Assessments
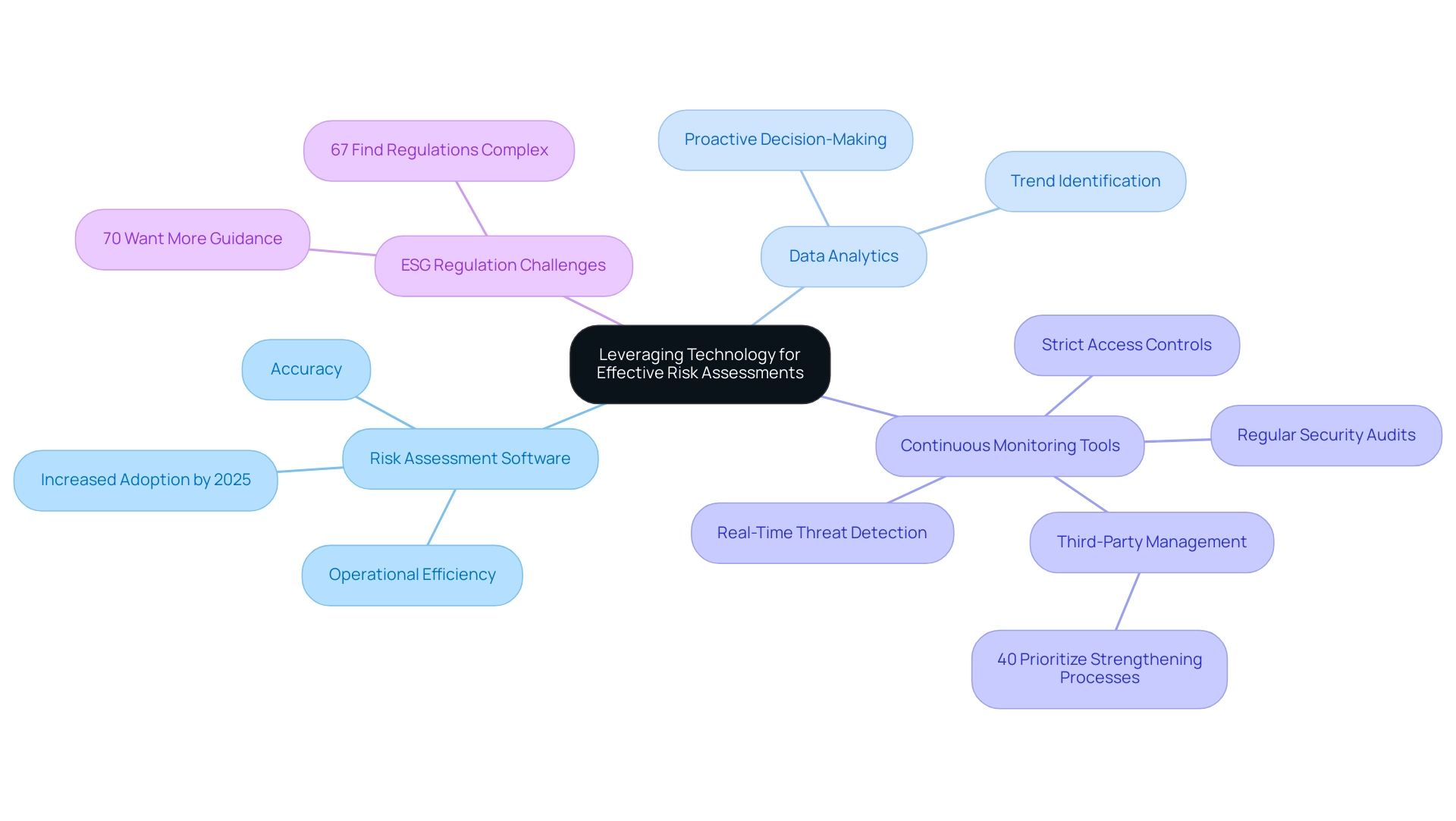
In today's swiftly changing financial environment, technology is essential for conducting effective evaluations. Financial institutions can harness a variety of advanced tools and technologies to bolster their risk management strategies, including:
- : These automated tools streamline the risk assessment process, enabling institutions to efficiently identify and evaluate potential risks. By 2025, the adoption of such software is expected to significantly increase, with many organizations recognizing its value in enhancing operational efficiency and accuracy.
- Data Analytics: Utilizing data analytics enables financial organizations to reveal trends and patterns that may indicate developing challenges. This proactive approach not only assists in threat identification but also supports informed decision-making, ensuring that institutions remain ahead of potential challenges.
- Continuous Monitoring Tools: Implementing technologies that facilitate real-time monitoring of systems and networks is crucial for detecting vulnerabilities and threats as they arise. Regular security audits and strict access controls are essential components of this strategy, particularly in light of the growing reliance on third-party vendors. In fact, 40% of legal and compliance leaders prioritize enhancing third-party management processes, highlighting the urgency of this issue.
The heightened dependence on vendors necessitates stricter management policies to protect against external breaches, as demonstrated by the case study titled 'Strengthening Third-Party Management,' which emphasizes the importance of regular security audits and strict access controls.
Moreover, 67% of worldwide executives believe that ESG regulation is overly complicated, creating additional difficulties for organizations in managing compliance. By incorporating these technologies into their evaluation processes, organizations can significantly enhance their information security risk assessment for financial institutions and improve their overall management frameworks. This technological integration not only safeguards against potential breaches but also aligns with the increasing demand for robust compliance measures in a complex regulatory environment.
The Role of Continuous Monitoring in Risk Management
Ongoing monitoring stands as a cornerstone of effective information security risk assessment for financial institutions striving to manage uncertainties. This proactive approach encompasses several key elements:
- Regular Reviews: Periodic evaluations of assessments are essential to ensure they reflect the current landscape and remain relevant to emerging threats. This practice not only aids in identifying new challenges but also in reassessing existing ones, thereby maintaining a robust management framework.
- Real-Time Alerts: Implementing systems that deliver immediate notifications regarding fluctuations in threat levels or the emergence of new dangers is crucial. In 2025, statistics indicate that organizations utilizing real-time alerts significantly improved their response times to potential threats, enhancing their overall operational resilience. This capability enables institutions to act swiftly, mitigating potential impacts before they escalate. Transform Your Small/Medium Business supports a shortened decision-making cycle throughout the turnaround process, enabling decisive actions that preserve business integrity.
- Feedback Loops: Establishing mechanisms for feedback is vital for continuous improvement. Learning from previous incidents allows organizations to enhance their assessments and strategies, fostering a culture of adaptability and resilience. We continually monitor the success of our plans through our client dashboard, which provides real-time business analytics to effectively diagnose your business health.
The importance of continuous monitoring cannot be overstated. A recent case study on operational resilience highlights how utilizing data for real-time insights into an organization's vulnerability profile results in early identification of threats and adaptive strategies. This dynamic approach not only strengthens decision-making but also fortifies an organization's ability to withstand disruptions. The case study reveals that organizations implementing continuous monitoring experienced early detection of threats, adaptive strategies, and enhanced decision-making, ultimately bolstering their resilience against disruptions.
In 2025, expert insights emphasize that is integral to enhancing compliance and security postures, with 97% of organizations reporting strengthened defenses through such practices. Additionally, 27% of security and IT professionals cite mitigating internal audit fatigue as a top compliance challenge, underscoring the need for effective monitoring systems. By adopting a continuous monitoring framework, financial organizations can proactively tackle challenges associated with information security risk assessment, ensuring they are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of today's financial landscape.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Risk Assessments
Financial institutions often encounter critical challenges during evaluations that can significantly undermine their effectiveness.
- Inadequate Scope Definition: A poorly defined scope can lead to incomplete evaluations, leaving substantial threats unaddressed. In 2025, the repercussions of insufficient scope definition are anticipated to be considerable, with data indicating that organizations failing to establish clear evaluation boundaries may overlook up to 30% of potential threats.
- Disregarding Stakeholder Input: Excluding key stakeholders from the evaluation process can result in the oversight of critical dangers. Engaging stakeholders is essential for a comprehensive understanding of the operational landscape, enhancing the identification of vulnerabilities. A UserEvidence survey conducted in February 2024 revealed that organizations actively involving stakeholders in their evaluations report a 25% improvement in danger detection precision.
- Failure to Update Evaluations: Evaluations must be perceived as dynamic documents evolving with the shifting threat landscape. Regular updates are crucial to reflect new threats, regulatory changes, and shifts in business operations. Statistics show that organizations performing regular updates to their threat evaluations are 40% more likely to effectively manage emerging challenges. Furthermore, routine evaluations of lending practices and policies are vital for promptly identifying and rectifying issues, ensuring that monetary institutions remain vigilant.
By recognizing and addressing these common pitfalls, financial institutions can significantly enhance the quality and reliability of their information security risk assessments, ultimately leading to more resilient management strategies. Additionally, as noted by VPNRanks, by 2025, the average cost of cybersecurity incidents is projected to rise to $5.00 million, driven by increasing complexity in cybersecurity challenges and stricter data protection regulations. This underscores the economic implications of inadequate evaluations. Moreover, the case study titled 'AI in Compliance' indicates that 70% of believe AI will have a transformative or major impact on their functions within the next one to five years, suggesting a pivotal shift towards leveraging AI technologies to enhance compliance processes and improve overall management strategies.
Effective Communication and Reporting in Risk Assessments
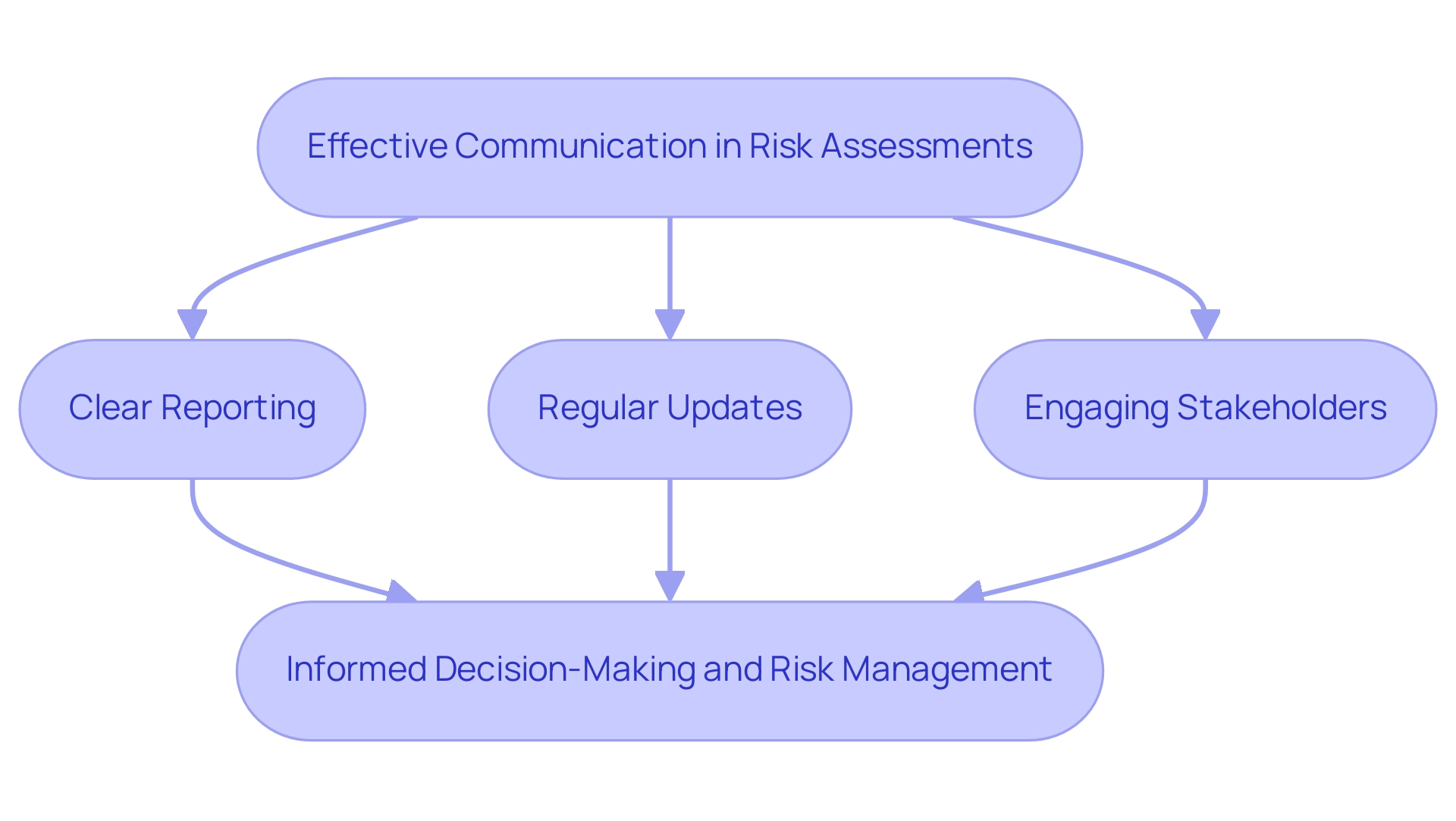
Effective communication and reporting are crucial components of the information security risk assessment for financial institutions during the evaluation process. Key practices that enhance this process include:
- Clear Reporting: Findings should be presented in a straightforward and concise manner, ensuring accessibility for all stakeholders. This clarity is essential, as it enables decision-makers to quickly understand the implications of the assessment results.
- Regular Updates: Stakeholders must be kept informed about any changes in threat levels and the effectiveness of mitigation strategies. Consistent communication promotes clarity and confidence, allowing prompt modifications to management strategies.
- Engaging Stakeholders: Actively involving stakeholders in discussions regarding uncertainties and mitigation efforts cultivates a culture of awareness. This engagement not only enhances understanding but also encourages collaborative problem-solving.
The significance of clear reporting cannot be overstated. As emphasized by industry specialists, organizations that prioritize effective communication in their evaluations often experience significant advantages. Chris Matlock, vice president and analyst team manager for the corporate strategy practice at Gartner, notes, "It is difficult to do, but the payoff for organizations that do it is extremely high."
This underscores the value of investing in robust communication strategies.
Moreover, adherence to is essential for financial institutions, as it emphasizes the importance of conducting an information security risk assessment for financial institutions that manage sensitive financial information, highlighting the necessity for frequent evaluations. Statistics indicate that these evaluations, specifically the information security risk assessment for financial institutions, should be conducted at least annually, or whenever new systems or vendors are introduced, or following a security incident. A case study on the consequences of non-compliance with the GLBA Safeguards Rule illustrates that failing to communicate hazards effectively can lead to severe repercussions, including hefty fines and reputational damage.
This proactive approach, coupled with effective communication, ensures that risk assessment findings translate into informed decision-making and proactive risk management strategies.
Conclusion
In the realm of financial institutions, the significance of information security risk assessments cannot be overstated. Systematic evaluations that encompass asset identification, threat analysis, and vulnerability assessment enable organizations to recognize potential risks and implement effective mitigation strategies. This comprehensive approach not only safeguards sensitive information but also enhances operational resilience against the backdrop of evolving cyber threats and regulatory demands.
Moreover, continuous monitoring and the adoption of established frameworks, such as NIST and ISO 31000, are crucial in navigating the complexities of risk management. By leveraging advanced technologies and maintaining open lines of communication, financial institutions can foster a culture of awareness and adaptability. This proactive stance aids in compliance and builds client trust, reinforcing the institution's reputation in a highly competitive landscape.
Ultimately, the journey towards robust risk management is one of ongoing commitment and diligence. As financial institutions face an increasingly intricate risk environment, prioritizing effective risk assessments is essential for preserving operational integrity and ensuring long-term success. By learning from common pitfalls and continuously refining their strategies, these organizations can protect their assets and thrive amid the challenges of the modern financial landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are information security vulnerability evaluations important for financial institutions?
Information security vulnerability evaluations are essential for financial institutions as they analyze potential threats to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data. They help identify vulnerabilities, assess threats, and evaluate the impact of security breaches, enabling organizations to implement effective controls to mitigate these risks.
What are the key components of a robust risk assessment in financial institutions?
The key components include: Asset Identification: Recognizing critical assets that need protection; Threat Analysis: Assessing potential threats like cyber attacks and natural disasters; Vulnerability Assessment: Identifying weaknesses in systems and processes; Impact Analysis: Evaluating the consequences of a security breach for the organization and stakeholders.
What types of threats must financial institutions prepare for?
Financial institutions must prepare for various threats, including cyber attacks, insider threats, and natural disasters. Statistics show significant losses from business email compromise attacks and highlight the evolving nature of cyber threats, such as sophisticated DDoS attacks.
How do human errors contribute to cybersecurity incidents in financial institutions?
Human errors are linked to 88% of all cyber incidents, emphasizing the need for organizations to prioritize employee training and awareness to reduce these threats effectively.
What is the importance of conducting an impact analysis during a risk assessment?
An impact analysis is crucial for understanding the potential consequences of a security breach. It helps formulate a response plan that minimizes harm and ensures business continuity.
What regulatory compliance requirements do financial institutions face?
Financial institutions must comply with laws such as the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) and the Dodd-Frank Act, necessitating regular assessments to ensure conformity and avoid penalties.
What are some operational challenges faced by financial institutions?
Financial institutions often face operational challenges linked to internal processes and legacy systems that hinder growth and modernization, requiring effective strategies for improvement.
What steps are involved in conducting a risk assessment for financial institutions?
The steps include: 1. Define the scope of the assessment; 2. Identify assets that require protection; 3. Identify threats and vulnerabilities; 4. Assess hazards based on likelihood and impact; 5. Develop mitigation strategies; 6. Document findings for future reference and compliance.
How can the COSO ERM Framework enhance risk assessments in financial institutions?
The COSO ERM Framework provides a structured approach to managing enterprise challenges and integrating risk management into the overall business strategy, enhancing resilience against various threats and improving decision-making and operational efficiency.
What financial advantages can a dedicated incident response team provide?
Having a dedicated incident response team can save businesses an average of $14 for each record lost or stolen, highlighting the financial benefits of proactive management in cybersecurity.




