Overview
The article emphasizes the creation of a successful stakeholder management course outline, highlighting the critical role of effective stakeholder engagement in enhancing project outcomes and organizational resilience. It details the essential components of the course, including:
- Stakeholder identification
- Engagement strategies
Furthermore, evidence indicates that organizations with robust stakeholder involvement achieve significantly higher success rates and profitability. This underscores the necessity for a structured approach to stakeholder management, ultimately driving better results for organizations.
Introduction
Crafting an effective stakeholder management course outline is essential for organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of stakeholder engagement. Understanding the nuances of stakeholder dynamics enables businesses to significantly enhance their project success rates and resilience in challenging times. However, the challenge lies in identifying the key components and teaching methods that resonate with participants, ensuring they are equipped to foster collaboration and trust among diverse interest groups.
What best practices can be employed to develop a course that not only educates but also empowers individuals to implement stakeholder management strategies effectively?
Define Stakeholder Management and Its Importance
A stakeholder management course outline is crucial for identifying, analyzing, and engaging individuals or groups with a vested interest in an organization or project. This includes both internal parties, such as employees and management, and external parties, including customers, suppliers, and investors. Effective engagement of these stakeholders is essential, especially during challenging periods like financial downturns or restructuring initiatives, as it significantly influences an organization’s trajectory.
In times of difficulty, understanding the needs and concerns of stakeholders enables businesses to tailor their strategies, thereby mitigating risks and fostering collaboration. For instance, firms that prioritize interaction with stakeholders can experience a 20% increase in profits, according to industry experts. Furthermore, organizations that actively involve participants in decision-making processes are 78% more likely to achieve project success compared to those with limited engagement.
Successful examples of stakeholder management during turnaround situations demonstrate the effectiveness of clear communication with constituents to align expectations and build trust. For example, during a financial crisis, a retail company implemented regular updates and feedback sessions with employees and customers, resulting in a 30% boost in customer satisfaction and loyalty. This proactive approach not only preserved cash flow but also enhanced operational efficiency through real-time analytics, facilitating ongoing monitoring of stakeholder engagement and business performance.
The importance of involving stakeholders in crisis management is emphasized in outline. Companies that engage effectively with their partners are better equipped to confront challenges, as illustrated by that reduced project delivery times by 25% through strong relationships. Such results underscore the necessity of incorporating a stakeholder management course outline into crisis response plans, ensuring organizations are prepared to adapt and thrive in adversity. Additionally, as Scott Keller emphasizes, establishing trust with stakeholders before a crisis is vital for effective management during tough times. By applying insights from past experiences, organizations can strengthen their relationships with stakeholders and enhance overall resilience.
Identify Core Components of the Course Outline
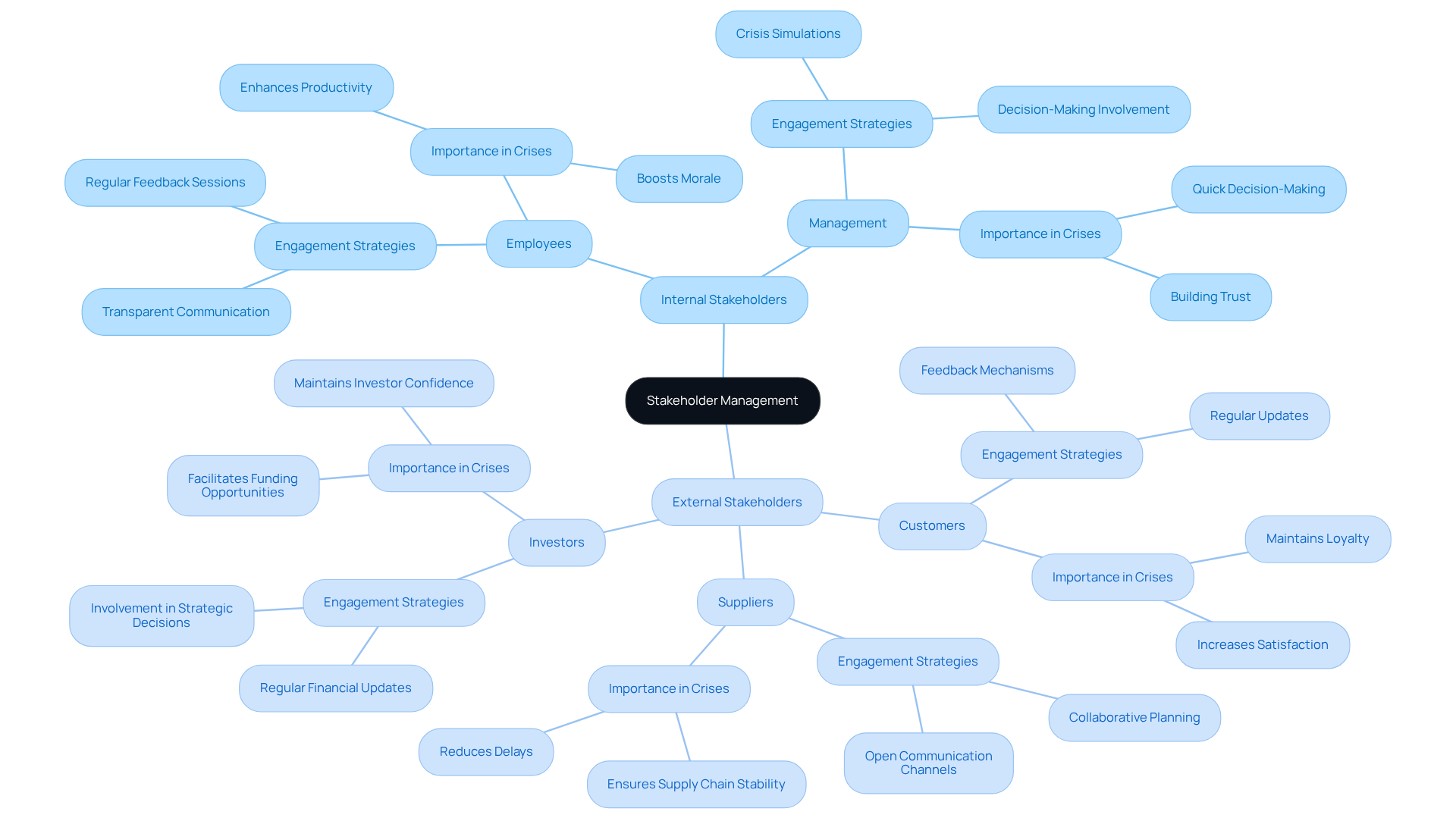
To create a comprehensive stakeholder management course outline for participant management training, it is essential to define the core components that will shape the learning experience. These components typically encompass:
- Introduction to Interested Party Management: This section offers a summary of essential ideas and emphasizes the importance of interested party management in attaining success in endeavors. Effective engagement with involved parties is crucial, as studies indicate that initiatives with strong involvement strategies succeed 83% of the time compared to only 32% for those lacking them.
- Participant Identification: Attendees will acquire techniques for recognizing interested parties, including approaches to comprehend their interests and impact on outcomes. Optimal methods in participant identification will be addressed, highlighting the necessity for comprehensive analysis prior to the start of the endeavor.
- Stakeholder Assessment: This element emphasizes instruments and methods for evaluating participant influence and impact, allowing individuals to analyze the dynamics of relationships effectively. Insights from case studies will demonstrate the significance of interest group analysis in reducing risks and aligning objectives.
- Engagement Strategies: This section discusses various methods for involving interested parties, emphasizing the importance of customized approaches to meet diverse needs and expectations. Participants will explore successful engagement strategies that have been proven to enhance satisfaction and project outcomes.
- Communication Plans: Participants will create communication strategies tailored for various interest groups, ensuring timely and relevant information dissemination. The importance of in building trust among parties involved will be emphasized.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: This final element entails evaluating the success of participant involvement initiatives, applying metrics and feedback to improve strategies and enrich future interactions. Participants will learn how to assess involvement success and adjust their methods accordingly.
Each component of the stakeholder management course outline should be clearly defined with specific objectives and expected outcomes, ensuring that participants gain practical skills and insights applicable to real-world scenarios. For example, objectives might involve creating an engagement strategy that aligns with project aims and improves overall project success.
Develop a Step-by-Step Course Structure
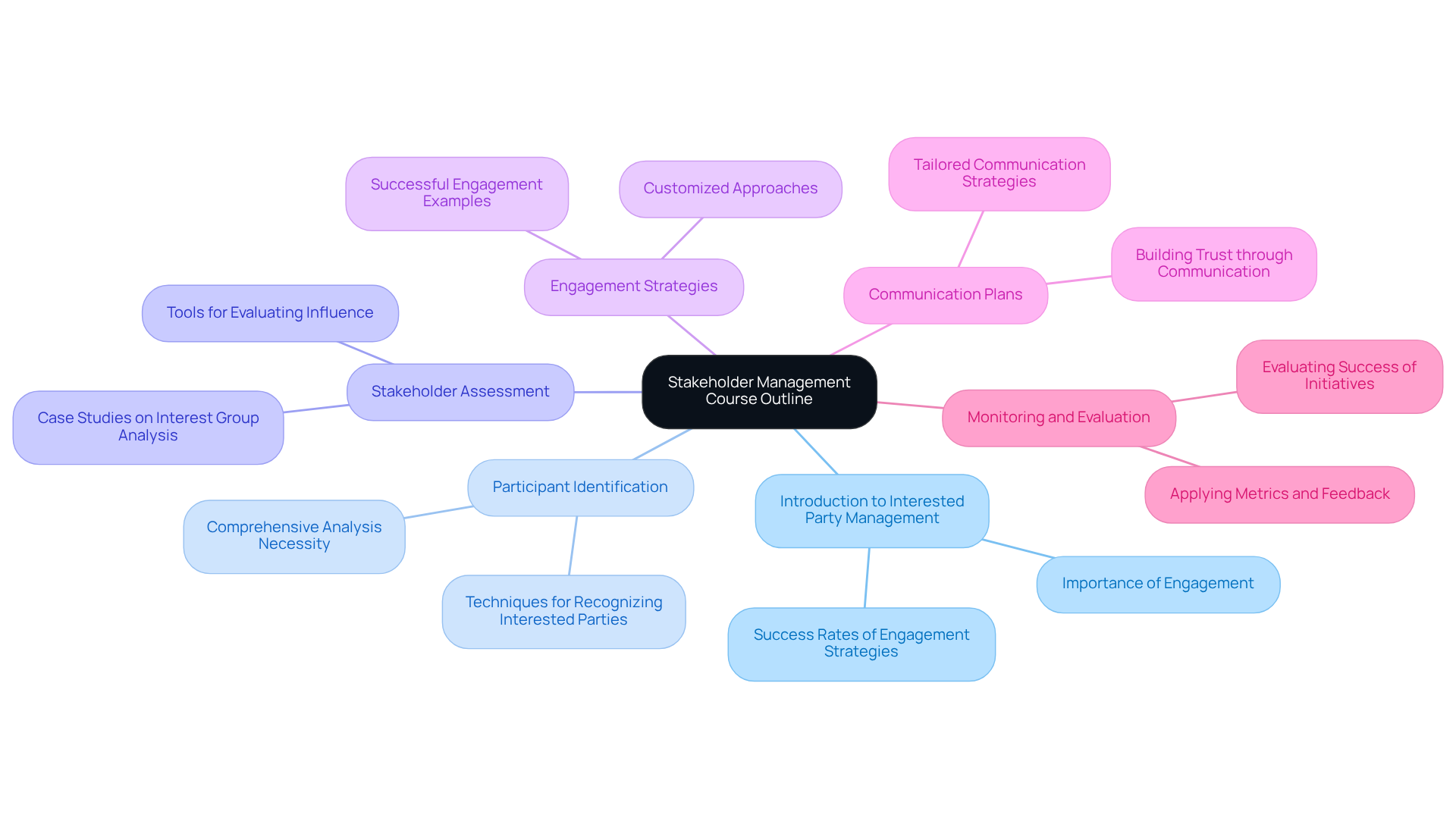
Creating a detailed stakeholder management course outline involves breaking down essential components into digestible lessons. Below is a proposed outline:
-
Week 1: Introduction to Stakeholder Management
- Lesson 1: Defining Stakeholder Management
- Lesson 2: Significance in Crisis Scenarios
-
Week 2: Stakeholder Identification
- Lesson 3: Techniques for Identifying Stakeholders
- Lesson 4: Mapping Stakeholder Interests and Influence
-
Week 3: Stakeholder Analysis
- Lesson 5: Evaluating Stakeholder Influence
- Lesson 6: Prioritizing Stakeholders Based on Impact
-
Week 4: Engagement Strategies
- Lesson 7: Crafting Effective Engagement Plans
- Lesson 8: Executing Engagement Strategies in Practice
-
Week 5: Communication Plans
- Lesson 9: Developing Compelling Messages
- Lesson 10: Customizing Communication for Diverse Stakeholders
-
Week 6: Monitoring and Evaluation
- Lesson 11: Measuring Engagement Success
- Lesson 12: Adapting Strategies Based on Stakeholder Feedback
Additional Considerations:
- Incorporate interactive elements such as case studies and group discussions to foster deeper understanding and application of concepts.
- Include statistics such as '78% of projects succeed with involved parties, compared to only 40% with less engagement' to emphasize the importance of engagement from interested groups.
- Utilize quotes like "Companies that truly engage with interested parties are 50% more likely to reach their significant goals" to add credibility.
- Consider incorporating a lesson on metrics for evaluating participant involvement, as emphasized in external sources.
- Reference effective involvement strategies, such as including key employees to increase transformation success rates.
Select Effective Teaching Methods and Assessment Strategies
Selecting effective teaching methods and assessment strategies is crucial for delivering outline. Consider the following approaches:
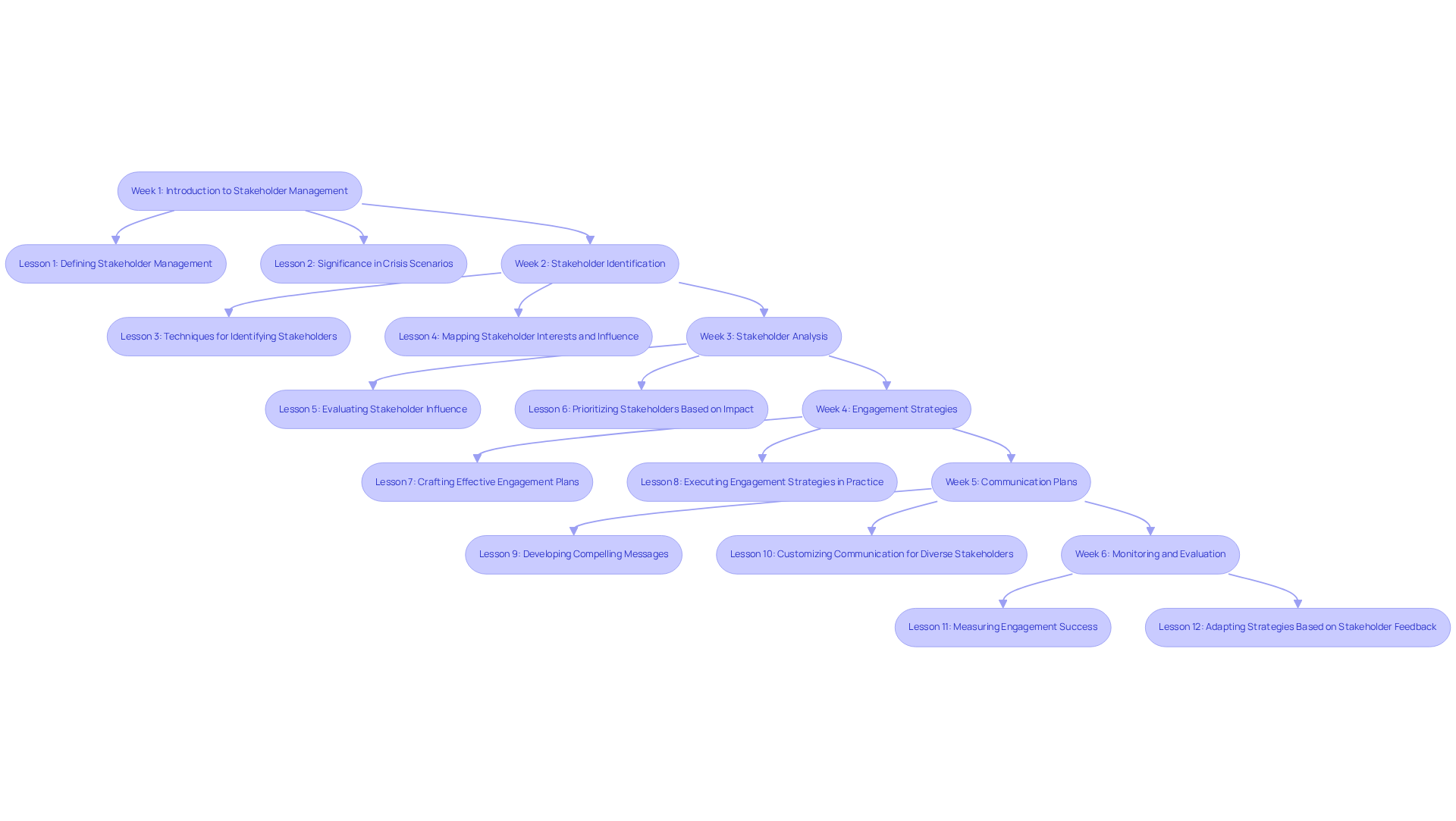
Teaching Methods:
- Interactive Workshops: Facilitate hands-on learning through group activities and discussions, achieving two times higher normalized learning gains compared to traditional methods. Active learning settings produce 13 times more learner discussion time than passive settings, significantly improving involvement levels.
- Case Studies: Utilize real-world examples to illustrate concepts and foster critical thinking, evidenced by improved retention rates and participation metrics in active learning environments. For instance, students in active learning environments achieve 54% higher test scores and are 1.5 times less likely to fail.
- Guest Speakers: Invite industry experts to share insights and experiences related to stakeholder management, enhancing the learning experience through practical knowledge.
- Online Modules: Incorporate technology to provide flexible learning options, allowing participants to engage with content at their own pace, leading to a 40% reduction in training time.
Assessment Strategies:
- Quizzes and Tests: Implement regular assessments to gauge understanding of key concepts, ensuring participants retain 93.5% of information compared to 79% in passive learning settings.
- Group Projects: Encourage collaboration and the application of learned strategies in practical scenarios, significantly enhancing team involvement and problem-solving skills.
- Feedback Sessions: Provide opportunities for participants to receive constructive feedback on their engagement strategies, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Final Evaluation:
Consider a capstone project where participants develop a comprehensive stakeholder management plan for a hypothetical crisis scenario. This project will demonstrate their understanding of the course material and their ability to apply it in real-world contexts, reflecting the success rates observed in stakeholder management course outline. Incorporating quotes such as Confucius's "I hear and I forget. I see and I remember. I do and I understand" can further emphasize the importance of experiential learning.
Conclusion
Crafting a comprehensive stakeholder management course outline is essential for equipping individuals with the skills needed to effectively engage various parties involved in an organization or project. By focusing on the nuances of stakeholder identification, assessment, and engagement strategies, organizations can foster collaboration and mitigate risks, ultimately enhancing project success and resilience during challenging times.
Throughout the article, key components of a successful course outline were discussed, including:
- The importance of clear communication
- Tailored engagement strategies
- The incorporation of interactive teaching methods
Insights from real-world examples highlighted the tangible benefits of effective stakeholder management, such as increased profits and improved project delivery times. Moreover, the emphasis on continuous evaluation and adaptation of strategies underscores the dynamic nature of stakeholder relationships.
In conclusion, the significance of stakeholder management cannot be overstated. Organizations that prioritize stakeholder engagement not only navigate crises more effectively but also build lasting relationships that contribute to long-term success. As industries continue to evolve, investing in stakeholder management education will be crucial for fostering a culture of collaboration and trust. Embracing these best practices will empower organizations to thrive in an increasingly complex landscape, ensuring they remain responsive to the needs of all stakeholders involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stakeholder management?
Stakeholder management involves identifying, analyzing, and engaging individuals or groups with a vested interest in an organization or project, including both internal parties (like employees and management) and external parties (such as customers, suppliers, and investors).
Why is stakeholder management important?
Effective stakeholder management is crucial, especially during challenging times, as it influences an organization’s trajectory. Understanding stakeholder needs and concerns allows businesses to tailor strategies, mitigate risks, and foster collaboration.
How does stakeholder engagement impact business performance?
Companies that prioritize stakeholder engagement can experience significant benefits, such as a 20% increase in profits and a 78% higher likelihood of achieving project success when compared to those with limited engagement.
Can you provide an example of successful stakeholder management?
During a financial crisis, a retail company that implemented regular updates and feedback sessions with employees and customers saw a 30% boost in customer satisfaction and loyalty, which helped preserve cash flow and enhance operational efficiency.
How does stakeholder management relate to crisis management?
Engaging stakeholders effectively during crises helps organizations confront challenges more successfully. For example, a construction firm reduced project delivery times by 25% through strong stakeholder relationships.
What role does trust play in stakeholder management?
Establishing trust with stakeholders before a crisis is essential for effective management during tough times. This trust allows organizations to better navigate challenges and strengthens relationships, enhancing overall resilience.




